A Slice of the World: Analyzing International Inhabitants Distribution By Continental Pie Charts
Associated Articles: A Slice of the World: Analyzing International Inhabitants Distribution By Continental Pie Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to A Slice of the World: Analyzing International Inhabitants Distribution By Continental Pie Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Slice of the World: Analyzing International Inhabitants Distribution By Continental Pie Charts
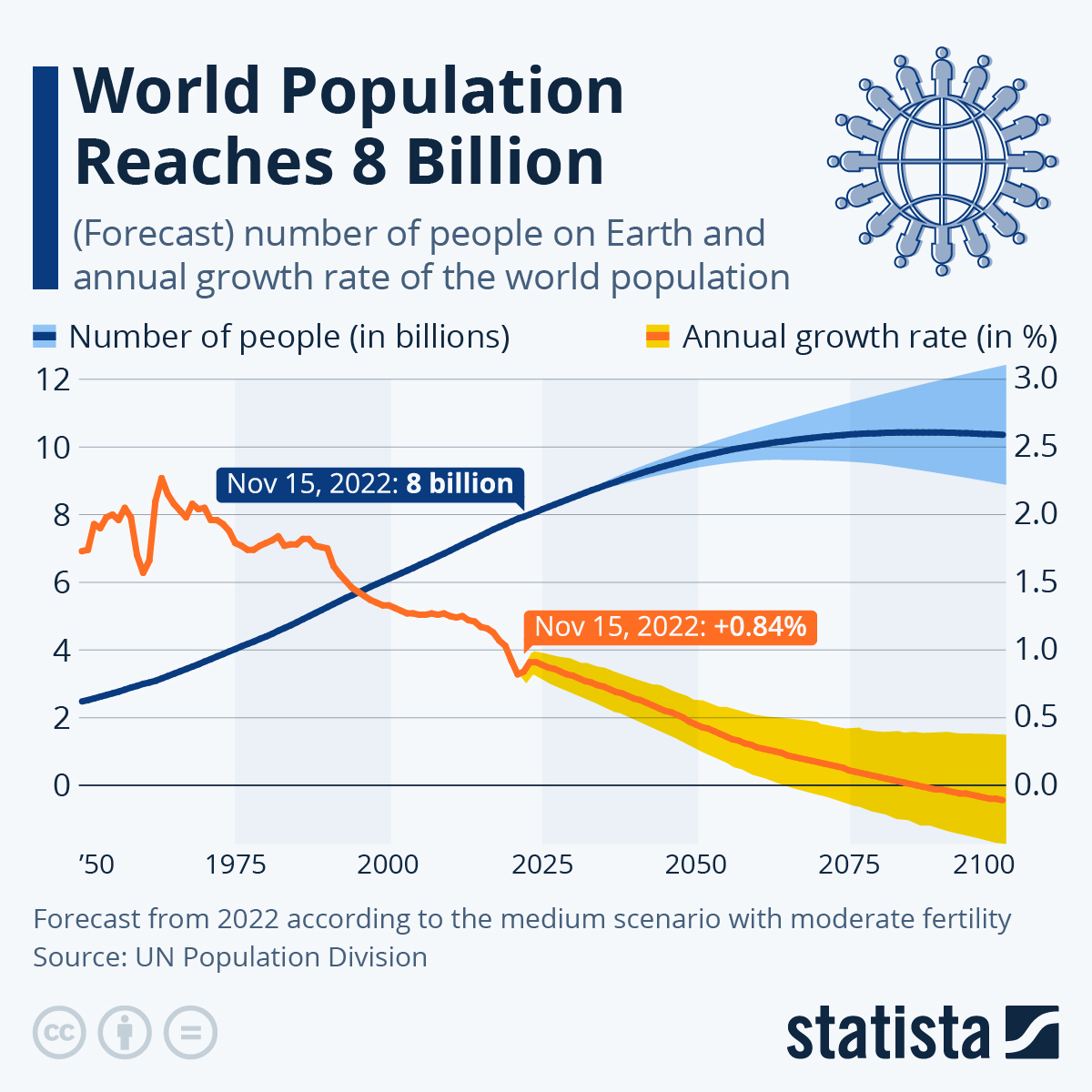
The world’s inhabitants, a staggering 8 billion and counting, is just not evenly distributed throughout the globe. Understanding this uneven distribution is essential for addressing numerous world challenges, from useful resource administration and infrastructure growth to healthcare entry and financial planning. A compelling solution to visualize this disparity is thru a continental pie chart, which supplies a transparent and quick understanding of the relative inhabitants sizes of various continents. This text will delve into the intricacies of such a chart, analyzing the info, exploring the historic traits, and discussing the implications of those inhabitants distributions for the longer term.
Establishing the Pie Chart: Knowledge and Methodology
Creating an correct and informative pie chart requires dependable and up-to-date knowledge. We’ll make the most of inhabitants estimates from respected sources just like the United Nations Inhabitants Division (UNPD) or the World Financial institution, making certain consistency and accuracy. These organizations commonly acquire and analyze demographic knowledge, offering probably the most dependable figures out there. The chart will symbolize the world’s inhabitants by continent, utilizing the usual continental groupings: Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, South America, Australia/Oceania, and Antarctica (which may have a negligible slice attributable to its uninhabitable nature).
The method includes calculating the share of the worldwide inhabitants residing in every continent. For instance, if the worldwide inhabitants is estimated at 8 billion and Asia accounts for 60% of that complete, Asia’s slice within the pie chart will symbolize 60% of the circle’s space. This proportion is then translated into the corresponding angle within the pie chart (60% of 360 levels equals 216 levels). The identical calculation is repeated for every continent, leading to a visually compelling illustration of the worldwide inhabitants distribution.
Decoding the Continental Pie Chart: A Visible Overview
A typical pie chart constructed utilizing latest knowledge would reveal a hanging dominance of Asia. Asia’s slice can be considerably bigger than every other continent, reflecting its immense inhabitants density and huge landmass. Africa would doubtless symbolize the second largest slice, showcasing its quickly rising inhabitants. Europe, North America, and South America would observe, every with significantly smaller slices in comparison with Asia and Africa. Australia/Oceania and Antarctica would have comparatively tiny slices, reflecting their comparatively low inhabitants densities.
The visible affect of such a chart is highly effective. It immediately communicates the disproportionate distribution of the worldwide inhabitants, highlighting the areas that require extra consideration relating to useful resource allocation, infrastructure growth, and social packages. The chart’s simplicity permits for straightforward understanding, even for these and not using a robust background in demographics or statistics.
Historic Traits and Future Projections: A Dynamic Panorama
The continental inhabitants distribution is just not static; it has advanced considerably over time and is projected to proceed altering within the coming many years. A historic evaluation, evaluating pie charts from completely different many years, would reveal attention-grabbing traits. As an illustration, whereas Asia has all the time been a populous continent, its share of the worldwide inhabitants has fluctuated over time. Equally, the expansion charges of various continents have assorted, with Africa experiencing notably fast inhabitants development in latest many years.
Future projections, primarily based on present demographic traits and fertility charges, recommend that Asia’s dominance would possibly steadily lower, albeit slowly, whereas Africa’s share of the worldwide inhabitants is anticipated to extend considerably. This shift may have profound implications for world useful resource administration, financial growth, and political dynamics. The pie chart, when offered alongside these projections, gives a priceless device for understanding the longer term trajectory of world inhabitants distribution.
Implications and Challenges: A International Perspective
The unequal distribution of the world’s inhabitants presents quite a few challenges and alternatives. Areas with excessive inhabitants densities typically face important stress on sources like water, meals, and vitality. Overpopulation can exacerbate points like poverty, unemployment, and environmental degradation. Conversely, areas with decrease inhabitants densities could face challenges associated to financial growth and infrastructure upkeep.
Understanding these disparities is essential for efficient policymaking. Governments and worldwide organizations must tailor their methods to the precise wants of various areas. This includes addressing points like entry to healthcare, schooling, and sustainable growth in a context-specific method. The pie chart supplies a visible start line for these discussions, highlighting the necessity for a nuanced and geographically knowledgeable method to world challenges.
Past the Pie Chart: A Deeper Dive into Regional Variations
Whereas the continental pie chart supplies a priceless overview, it masks important regional variations inside continents. For instance, inhabitants density inside Asia varies dramatically, with extremely populated areas like India and China contrasting with much less densely populated areas. Equally, Africa’s inhabitants distribution is uneven, with some international locations experiencing fast inhabitants development whereas others have comparatively secure and even declining populations.
To achieve a extra full understanding, we have to transfer past the continental degree and analyze inhabitants distribution at finer geographical scales, utilizing maps, regional breakdowns, and different visible instruments. This enables for a extra granular evaluation of the challenges and alternatives offered by inhabitants distribution.
Conclusion: A Visible Instrument for Understanding a Advanced World
The continental pie chart, whereas a simplified illustration, gives a robust visible device for understanding the worldwide distribution of the world’s inhabitants. Its simplicity permits for straightforward comprehension of the relative inhabitants sizes of various continents, highlighting the numerous disparities that exist. By combining the pie chart with historic knowledge and future projections, we will acquire a deeper understanding of the dynamic nature of inhabitants distribution and its implications for the longer term. This data is crucial for addressing the quite a few world challenges associated to useful resource administration, financial growth, and environmental sustainability. Finally, the pie chart serves as a place to begin for a extra complete evaluation, encouraging a deeper exploration of the advanced and ever-evolving panorama of world demographics.

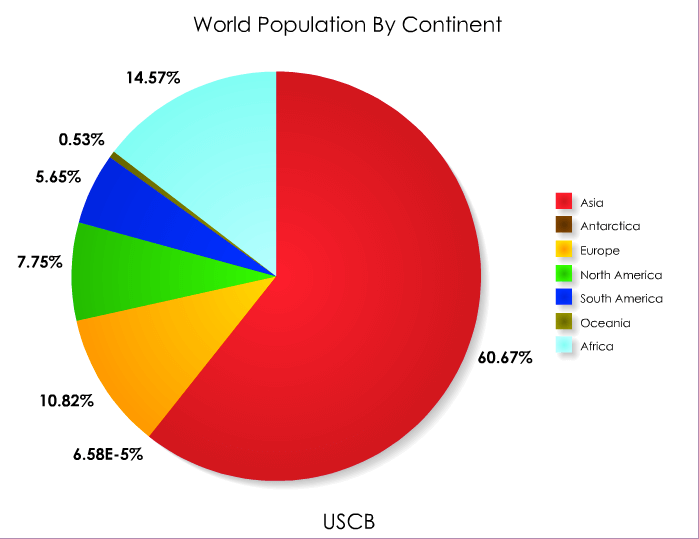

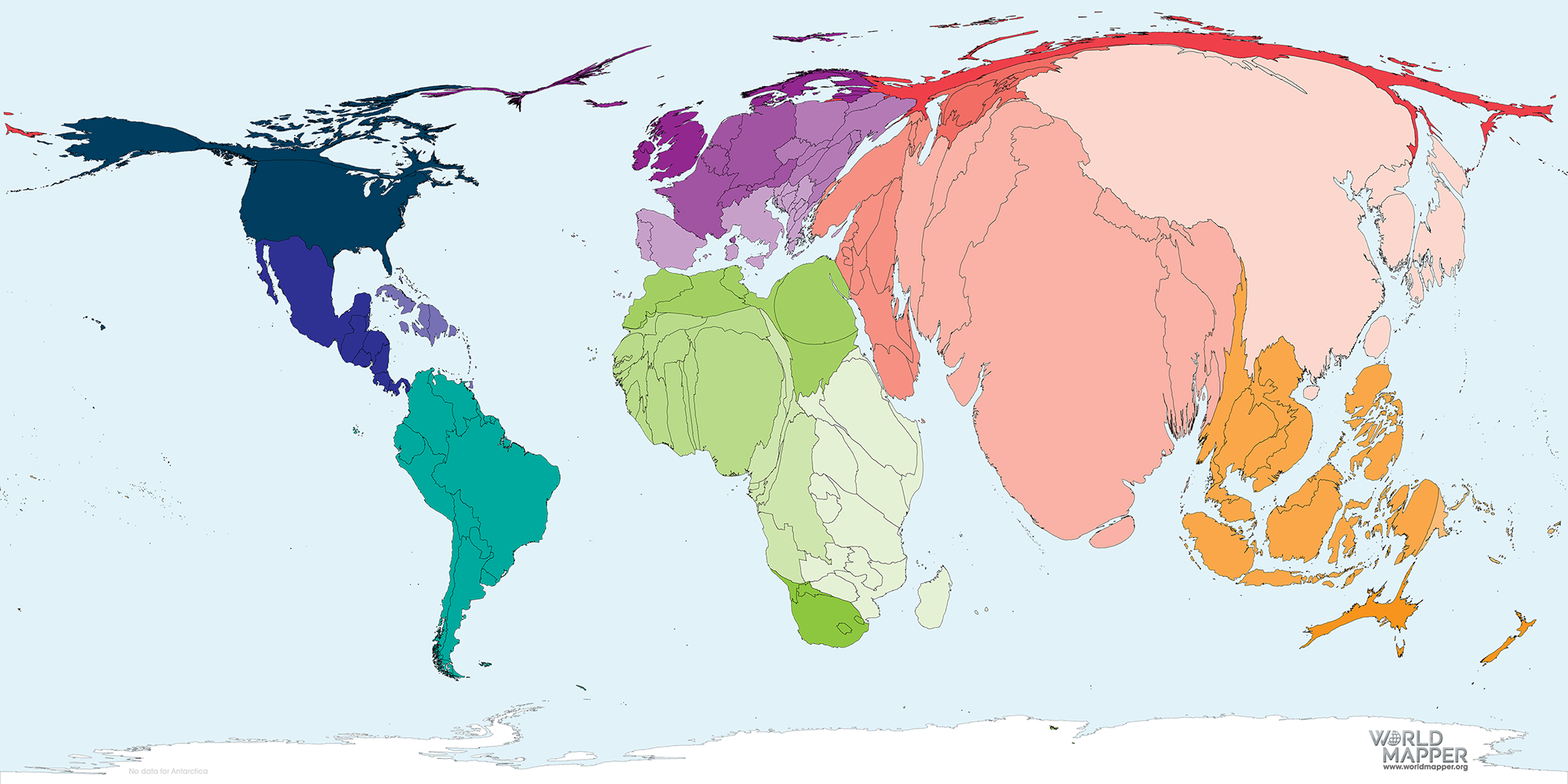
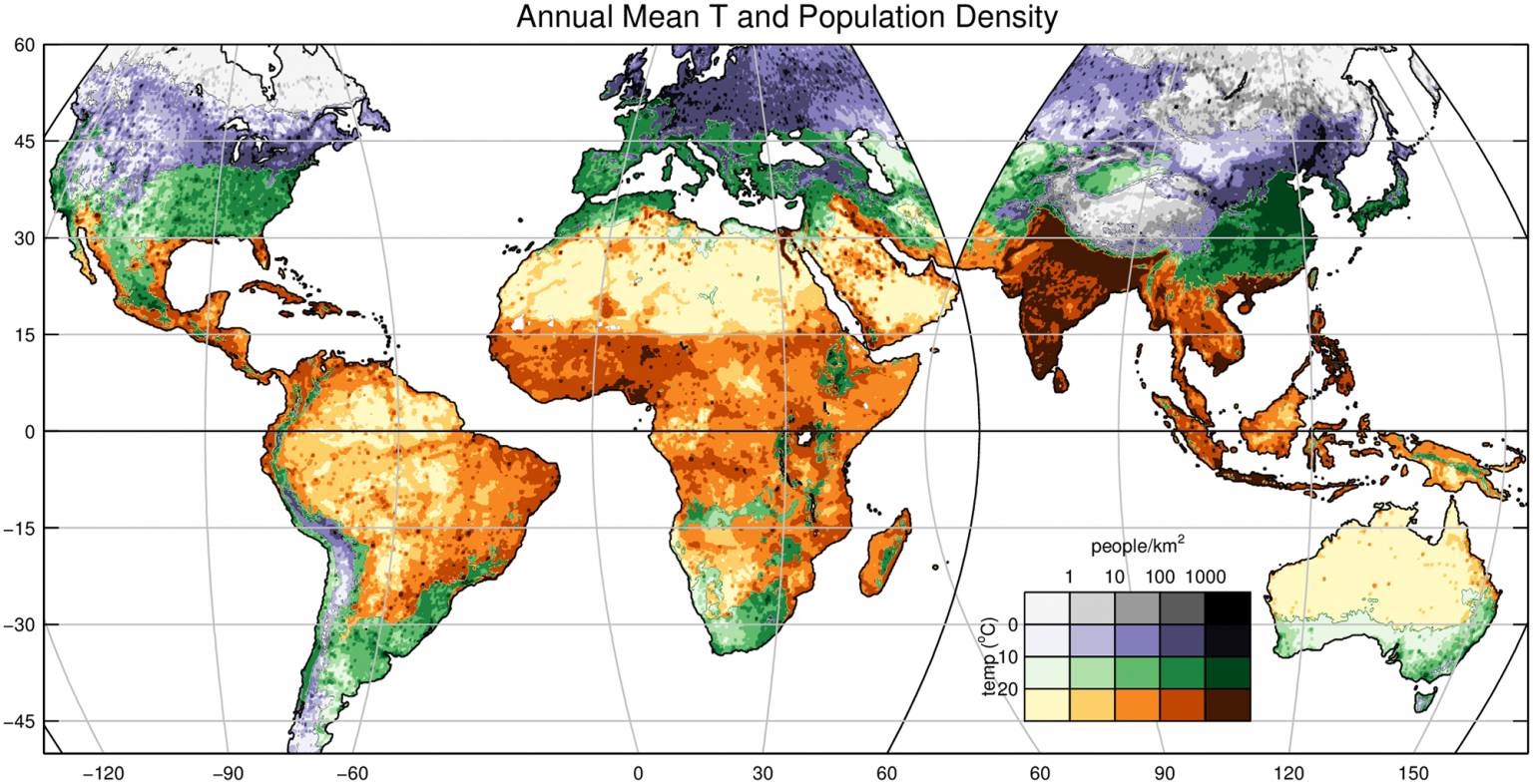



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into A Slice of the World: Analyzing International Inhabitants Distribution By Continental Pie Charts. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!