chart js full width
Associated Articles: chart js full width
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to chart js full width. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart.js Full Width: Mastering Responsive Charts for Any Display
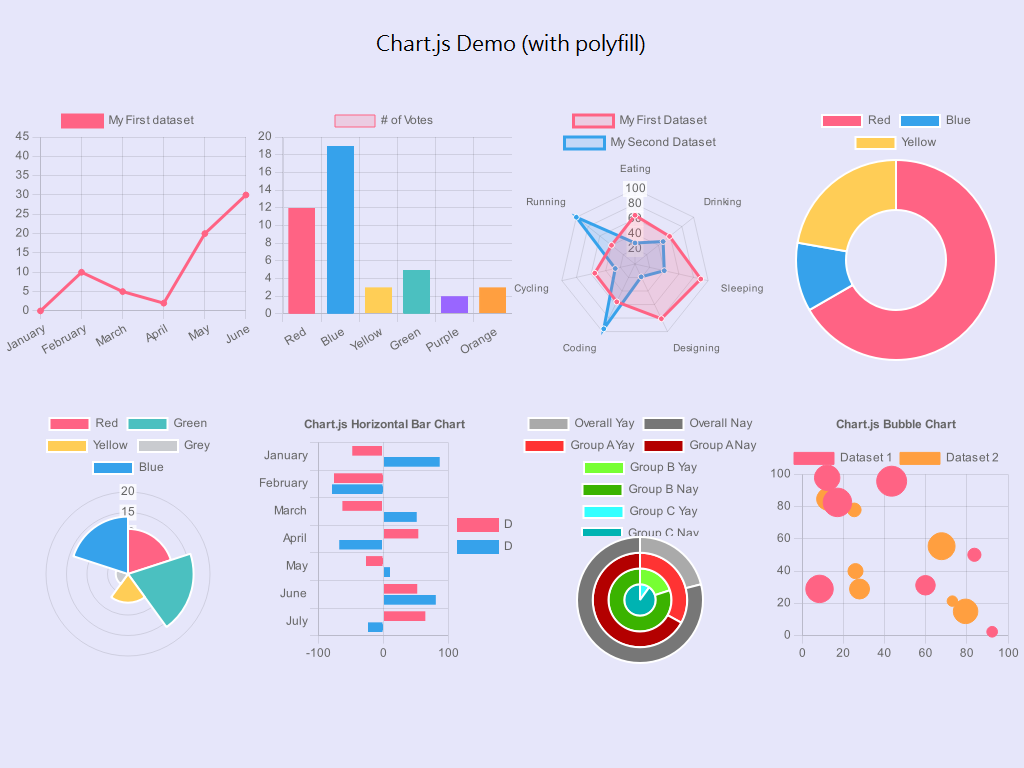
Chart.js, a well-liked and versatile JavaScript charting library, provides an easy strategy to create interactive and visually interesting charts. Nonetheless, guaranteeing your charts seamlessly adapt to totally different display screen sizes – an important facet of responsive net design – requires a deeper understanding of its configuration choices and integration with CSS. This text delves into the methods and finest practices for creating full-width Chart.js charts that gracefully scale throughout numerous units and resolutions, from tiny cell screens to expansive desktop displays.
Understanding the Problem: Mounted Width vs. Responsive Design
By default, Chart.js charts render with a hard and fast width decided by the containing factor’s dimensions. This strategy works wonderful for static layouts, nevertheless it fails spectacularly in responsive contexts. A chart designed for a desktop display screen will seem both tiny and cramped on a cell machine or will overflow its container, making a damaged structure. The secret’s to decouple the chart’s width from a hard and fast pixel worth and as a substitute hyperlink it dynamically to the accessible width of its guardian container.
Strategies for Attaining Full-Width Charts
There are a number of approaches to attain full-width Chart.js charts, every with its personal benefits and downsides:
1. Using CSS Flexbox or Grid:
That is arguably essentially the most elegant and strong methodology. Flexbox and Grid are highly effective CSS structure modules designed for creating versatile and responsive layouts. By inserting the chart’s container inside a flex or grid container, you’ll be able to leverage their inherent properties to make the chart increase to fill the accessible area.
<div class="chart-container">
<canvas id="myChart"></canvas>
</div>.chart-container
show: flex; /* Or show: grid; */
width: 100%; /* Essential for full width */
.chart-container canvas
flex: 1; /* For Flexbox. For Grid, use a related grid space definition */
width: 100%; /* Guarantee canvas takes full width */
max-width: 100%; /* Stop overflow */
This code snippet makes use of Flexbox. The .chart-container div is about to width: 100%, guaranteeing it occupies the complete accessible width. The flex: 1; property on the canvas factor tells it to take up the remaining accessible area inside the container. max-width: 100% prevents the chart from exceeding the container’s boundaries. An analogous strategy can be utilized with CSS Grid, adapting the flex property to grid-specific properties.
Benefits:
- Clear and maintainable: Separates structure issues from JavaScript logic.
- Extremely versatile: Permits for advanced layouts and responsive design patterns.
- Good efficiency: CSS structure is mostly environment friendly.
Disadvantages:
- Requires CSS data: Understanding Flexbox or Grid is important.
2. Utilizing JavaScript to Resize the Canvas:
This strategy entails dynamically adjusting the canvas factor’s width utilizing JavaScript, sometimes triggered by a window resize occasion. This methodology provides extra granular management however may be much less elegant and probably extra susceptible to efficiency points if not carried out rigorously.
const ctx = doc.getElementById('myChart').getContext('2nd');
const myChart = new Chart(ctx,
// ... your chart configuration ...
);
window.addEventListener('resize', () =>
// Get the container's width
const containerWidth = doc.querySelector('.chart-container').offsetWidth;
// Resize the canvas
ctx.canvas.width = containerWidth;
// Replace the chart (re-render)
myChart.replace();
);This code snippet listens for window resize occasions. On resize, it retrieves the container’s width utilizing offsetWidth and updates the canvas’s width accordingly. Crucially, myChart.replace() forces Chart.js to re-render the chart with the brand new dimensions.
Benefits:
- Superb-grained management: Permits for exact changes primarily based on particular situations.
Disadvantages:
- Extra advanced: Requires JavaScript code and occasion dealing with.
- Potential efficiency points: Frequent re-renders can influence efficiency on low-powered units. Optimizations (like debouncing the resize occasion) are essential.
3. Side Ratio and Responsive Width:
For sustaining constant chart proportions, you may wish to contemplate the facet ratio. As a substitute of simply setting the width to 100%, you need to use CSS to take care of a selected facet ratio, guaranteeing the chart scales proportionally.
.chart-container
place: relative;
width: 100%;
padding-bottom: 56.25%; /* 16:9 facet ratio */
top: 0;
.chart-container canvas
place: absolute;
prime: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
top: 100%;
This strategy makes use of padding-bottom to create the facet ratio. The proportion is calculated primarily based on the specified facet ratio (e.g., 56.25% for 16:9). The canvas is then positioned completely inside the container to fill the accessible area.
Greatest Practices for Responsive Chart.js Charts:
- Use a responsive CSS framework: Frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS present pre-built responsive utilities that simplify the method.
-
Debounce resize occasions: To stop efficiency points, debounce the
resizeoccasion listener to restrict the frequency of chart updates. Libraries like Lodash present useful debounce features. - Optimize chart knowledge: Giant datasets can considerably influence efficiency. Think about methods like knowledge aggregation or pagination for very massive datasets.
- Check totally: Check your charts on numerous units and display screen sizes to make sure they render accurately throughout all platforms.
- Think about chart kind: Some chart sorts are inherently higher fitted to responsive design than others. For instance, advanced charts may require extra subtle changes.
- Maintainability: Prioritize clear and well-structured code for simpler upkeep and future modifications.
Superior Methods:
- Dynamic facet ratio: Calculate the facet ratio dynamically primarily based on the chart knowledge or consumer preferences.
- Integration with JavaScript frameworks: If you happen to’re utilizing a framework like React, Angular, or Vue.js, leverage its element lifecycle strategies to handle chart resizing and updates effectively.
- Server-side rendering (SSR): For improved preliminary load instances, contemplate server-side rendering of your charts, notably for advanced charts with massive datasets.
Conclusion:
Creating full-width Chart.js charts that gracefully adapt to totally different display screen sizes is essential for a constructive consumer expertise. By combining the ability of CSS structure modules like Flexbox or Grid with considerate JavaScript integration (the place essential), you’ll be able to create responsive charts that improve the usability and visible attraction of your net functions. Bear in mind to prioritize efficiency and maintainability all through the event course of, using finest practices to make sure your charts carry out optimally throughout a variety of units and resolutions. Selecting the best strategy relies on the complexity of your mission and your familiarity with CSS and JavaScript. Nonetheless, prioritizing a clear CSS-based answer is mostly beneficial for its simplicity and maintainability.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into chart js full width. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!