Chart of Accounts Numbering: A GAAP-Compliant Method to Monetary Readability
Associated Articles: Chart of Accounts Numbering: A GAAP-Compliant Method to Monetary Readability
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Chart of Accounts Numbering: A GAAP-Compliant Method to Monetary Readability. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart of Accounts Numbering: A GAAP-Compliant Method to Monetary Readability

A well-structured chart of accounts (COA) is the spine of any sound monetary reporting system. It offers a scientific framework for recording and classifying all monetary transactions, making certain accuracy, consistency, and compliance with Usually Accepted Accounting Rules (GAAP). Inside this framework, numbering the accounts performs a vital function in facilitating environment friendly knowledge administration, evaluation, and reporting. A thoughtfully designed numbering system, aligned with GAAP, enhances the usability and reliability of monetary info. This text delves into the intricacies of chart of accounts numbering inside a GAAP-compliant context, exploring greatest practices, frequent methodologies, and the significance of sustaining a strong and adaptable system.
The Significance of a Effectively-Structured Chart of Accounts
Earlier than diving into numbering methods, it is important to know the overarching significance of a well-structured COA. A sturdy COA serves a number of crucial capabilities:
- Correct Monetary Reporting: A correctly designed COA ensures that every one transactions are recorded within the right accounts, resulting in correct monetary statements that mirror the true monetary place and efficiency of the entity.
- Improved Knowledge Evaluation: A well-organized COA simplifies knowledge evaluation, permitting for straightforward identification of tendencies, patterns, and anomalies throughout the monetary knowledge. This facilitates knowledgeable decision-making.
- Enhanced Inside Management: A structured COA contributes to stronger inside controls by offering a transparent framework for segregating duties and monitoring transactions. This reduces the chance of errors and fraud.
- GAAP Compliance: A correctly designed and maintained COA is essential for making certain compliance with GAAP. That is important for correct monetary reporting and avoiding potential authorized and regulatory points.
- Streamlined Audit Processes: A well-structured COA simplifies the audit course of, making it simpler for auditors to confirm the accuracy and completeness of monetary info.
GAAP and Chart of Accounts Design
Whereas GAAP would not prescribe a selected COA numbering system, it dictates the basic accounts that have to be included and the way they need to be categorized. The elemental accounting equation (Property = Liabilities + Fairness) types the idea for the COA construction. GAAP requires that monetary statements precisely mirror the financial substance of transactions, and a correctly designed COA is instrumental in reaching this.
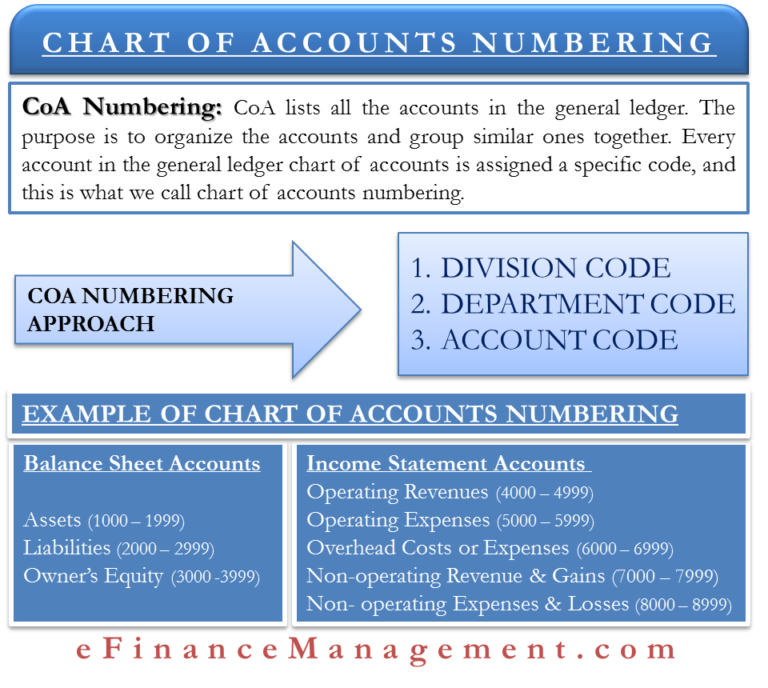
Numbering System Methodologies:
A number of numbering methodologies can be utilized to create a GAAP-compliant COA. The selection is determined by the dimensions and complexity of the group, its trade, and its particular reporting necessities. Frequent approaches embrace:
-
Decimal System: This technique makes use of decimals to create hierarchical ranges throughout the COA. For instance, 1000 would possibly signify Property, 1100 Present Property, 1110 Money, 1120 Accounts Receivable, and so forth. This enables for detailed categorization and straightforward growth because the enterprise grows. It is extremely versatile and permits for quite a lot of element.
-
Mnemonic System: This technique makes use of letters and numbers to signify account classes. For instance, "A" would possibly signify Property, "L" Liabilities, and "E" Fairness. Subcategories may very well be represented by numbers or further letters. Whereas this may be useful for memorization, it might develop into much less organized with a lot of accounts.
-
Hybrid System: Many organizations make the most of a hybrid system, combining parts of the decimal and mnemonic methods to create a system that most accurately fits their wants. This would possibly contain utilizing a decimal system for the principle account classes after which incorporating mnemonic codes for subcategories.
Key Concerns for GAAP-Compliant Numbering:
Whatever the chosen methodology, a number of key concerns guarantee GAAP compliance and efficient COA administration:
- Consistency: The numbering system have to be constantly utilized throughout all transactions and all through the group. Inconsistencies can result in errors in monetary reporting.
- Account Segmentation: The COA ought to be segmented logically to mirror the group’s enterprise actions and reporting necessities. This enables for environment friendly knowledge evaluation and reporting.
- Flexibility: The system ought to be versatile sufficient to accommodate future progress and modifications within the group’s enterprise operations. A inflexible system can develop into a bottleneck because the enterprise evolves.
- Complete Chart: The COA ought to embrace all crucial accounts to seize all related monetary transactions. Omitting important accounts can result in incomplete and inaccurate monetary statements.
- Common Evaluation and Updates: The COA ought to be usually reviewed and up to date to make sure it stays related and efficient. Adjustments in accounting requirements, enterprise operations, or reporting necessities could necessitate changes to the COA construction and numbering system.
- Documentation: Detailed documentation of the COA, together with an entire itemizing of accounts and their descriptions, is essential for inside understanding and for exterior audits.
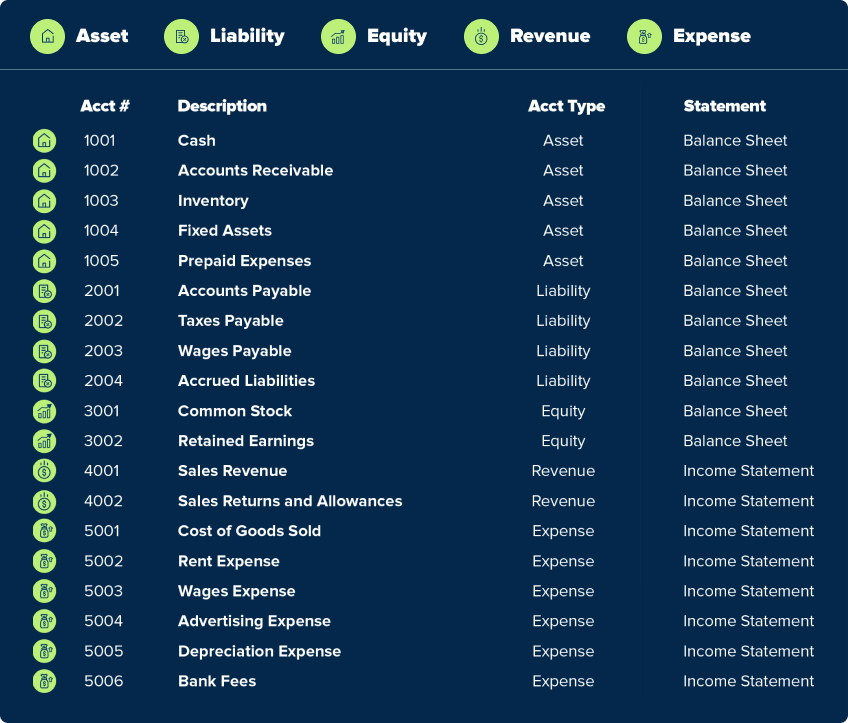
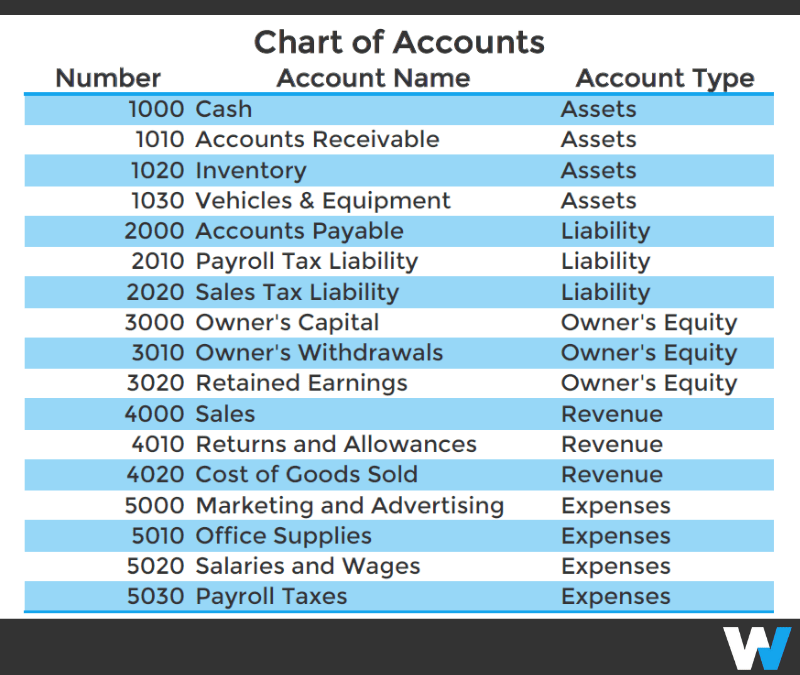
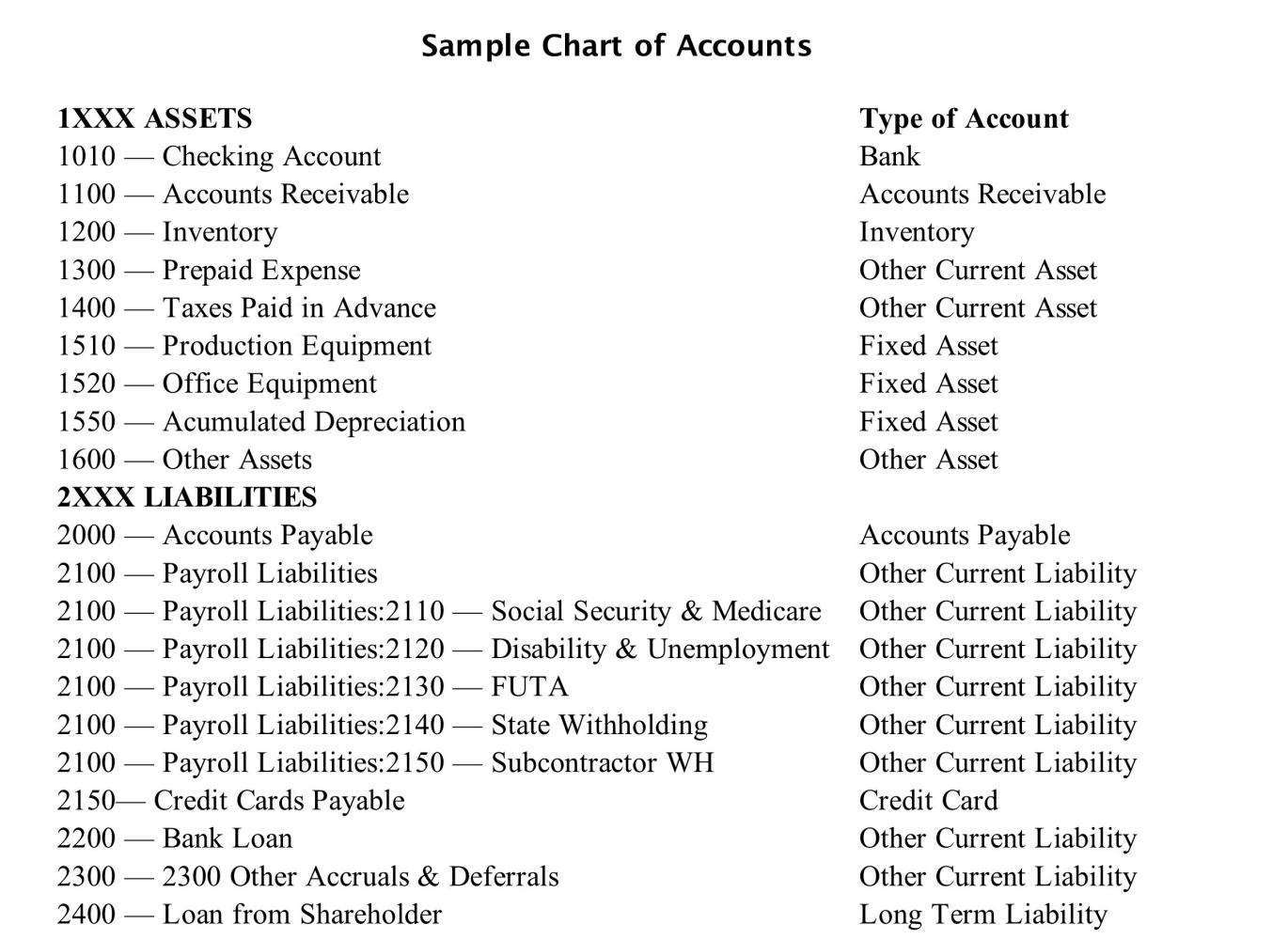
Instance of a Decimal-Primarily based COA:
The next instance illustrates a simplified decimal-based COA:
-
1000 – Property:
-
1100 – Present Property:
- 1110 – Money:
- 1120 – Accounts Receivable:
- 1130 – Stock:
-
1200 – Non-Present Property:
- 1210 – Property, Plant, and Gear (PP&E):
-
1100 – Present Property:
-
2000 – Liabilities:
-
2100 – Present Liabilities:
- 2110 – Accounts Payable:
- 2120 – Salaries Payable:
-
2200 – Non-Present Liabilities:
- 2210 – Lengthy-Time period Debt:
-
2100 – Present Liabilities:
-
3000 – Fairness:
- 3100 – Frequent Inventory:
- 3200 – Retained Earnings:
-
4000 – Income:
- 4100 – Gross sales Income:
- 4200 – Service Income:
-
5000 – Bills:
- 5100 – Value of Items Bought (COGS):
- 5200 – Promoting, Common, and Administrative Bills (SG&A):
Software program and COA Administration:
Fashionable accounting software program packages usually embrace instruments for creating, managing, and sustaining a COA. These instruments typically automate many points of COA administration, together with account creation, numbering, and reporting. Utilizing such software program considerably reduces the chance of guide errors and enhances the effectivity of the accounting course of.
Conclusion:
A well-designed and GAAP-compliant chart of accounts numbering system is significant for correct monetary reporting, efficient knowledge evaluation, and robust inside controls. By fastidiously contemplating the methodologies out there and adhering to greatest practices, organizations can set up a strong COA that helps their monetary administration wants and ensures compliance with related accounting requirements. Common overview and adaptation of the COA are key to sustaining its relevance and effectiveness because the enterprise evolves. The funding in a well-structured COA pays vital dividends by way of monetary readability, operational effectivity, and diminished threat.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Chart of Accounts Numbering: A GAAP-Compliant Method to Monetary Readability. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!