Chart Patterns: Decoding Worth Motion for Worthwhile Buying and selling
Associated Articles: Chart Patterns: Decoding Worth Motion for Worthwhile Buying and selling
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Chart Patterns: Decoding Worth Motion for Worthwhile Buying and selling. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart Patterns: Decoding Worth Motion for Worthwhile Buying and selling
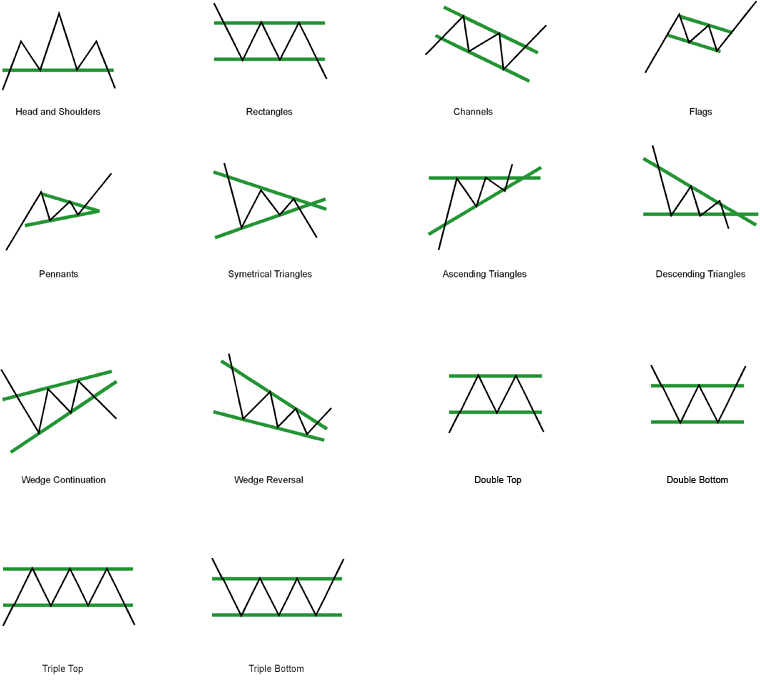
Chart patterns signify visually identifiable formations on value charts that always predict future value actions. They’re a cornerstone of technical evaluation, providing merchants beneficial insights into market sentiment and potential value reversals or continuations. Understanding and successfully using chart patterns can considerably enhance buying and selling methods, nevertheless it’s essential to keep in mind that they aren’t foolproof predictors and needs to be used together with different analytical instruments.
This text delves into the world of chart patterns, exploring their formation, interpretation, and sensible utility in value motion buying and selling. We’ll look at each reversal and continuation patterns, offering real-world examples and highlighting key issues for profitable implementation.
Understanding Worth Motion:
Earlier than diving into particular chart patterns, it is important to understand the idea of value motion. Worth motion refers back to the motion of an asset’s value over time, mirrored in candlestick charts or bar charts. Every candlestick or bar represents a particular time interval (e.g., at some point, one hour, one minute), displaying the opening, excessive, low, and shutting costs. The mix of those value factors types the visible foundation for figuring out chart patterns. Analyzing value motion includes finding out the relationships between these highs, lows, and shutting costs to know the underlying market forces at play. This consists of figuring out tendencies, assist and resistance ranges, and momentum shifts, all of which contribute to the formation and interpretation of chart patterns.
Reversal Chart Patterns:
Reversal patterns counsel a possible change within the prevailing pattern. They usually type on the finish of an uptrend (for bearish reversal patterns) or a downtrend (for bullish reversal patterns). Affirmation of the reversal is essential, usually requiring a breakout beneath or above a key assist or resistance stage, respectively.
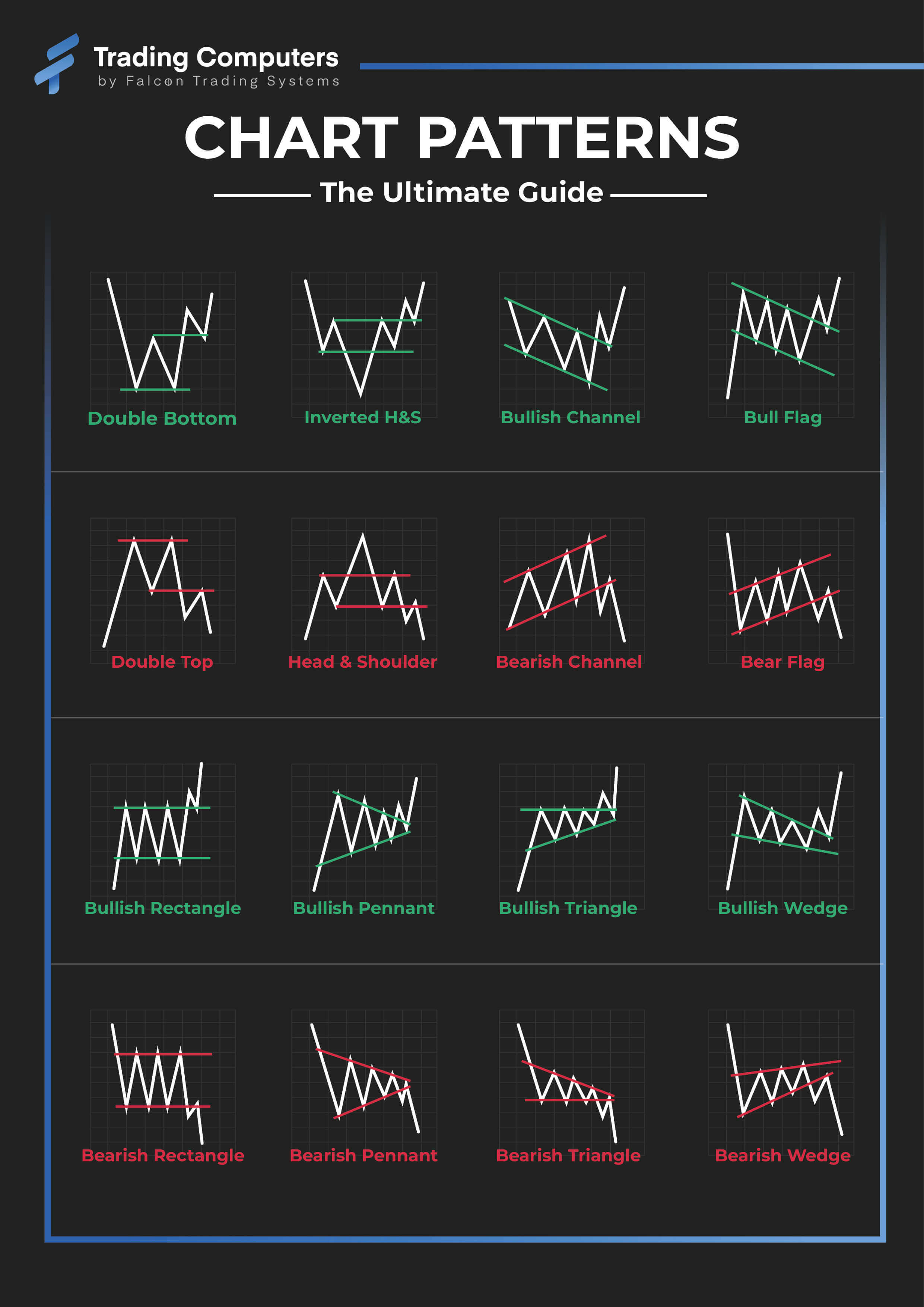
1. Head and Shoulders:
This basic reversal sample consists of three distinct peaks, resembling a head and two shoulders. The "head" is the very best peak, flanked by two decrease "shoulders." A neckline connects the troughs between the top and shoulders. A bearish breakout beneath the neckline alerts a possible reversal of the uptrend. The potential value goal is commonly measured by the gap between the top and the neckline, projected downwards from the breakout level.
2. Inverse Head and Shoulders:
The mirror picture of the top and shoulders sample, this bullish reversal sample types throughout a downtrend. It options three troughs, with the central trough being the bottom ("head"). A neckline connects the peaks between the troughs. A bullish breakout above the neckline suggests a possible uptrend reversal. The value goal is calculated equally to the top and shoulders sample, projecting upwards from the breakout level.
3. Double High/Double Backside:
These patterns are characterised by two related value peaks (double prime) or troughs (double backside). They point out a possible lack of momentum within the prevailing pattern, suggesting a potential reversal. A breakout beneath the neckline of a double prime or above the neckline of a double backside confirms the reversal. The value goal is commonly measured from the neckline to the very best/lowest level of the sample.
4. Triple High/Triple Backside:
Just like double tops/bottoms, however with three distinct peaks or troughs. The extra peaks/troughs, the stronger the potential reversal sign. Breakouts beneath/above the neckline verify the reversal.
Continuation Chart Patterns:
Continuation patterns counsel a brief pause within the prevailing pattern earlier than the pattern resumes in the identical path. They usually seem during times of consolidation or sideways motion.
1. Triangles:
Triangles are characterised by converging trendlines, forming a triangle form on the chart. There are three major sorts: symmetrical, ascending, and descending. Symmetrical triangles counsel a continuation with no clear bias; ascending triangles point out a bullish continuation; and descending triangles level to a bearish continuation. A breakout above the higher trendline (for ascending and symmetrical) or beneath the decrease trendline (for descending and symmetrical) confirms the continuation.
2. Flags and Pennants:
These patterns are characterised by a pointy value transfer adopted by a interval of consolidation, forming a flag or pennant form. Flags are characterised by parallel trendlines, whereas pennants have converging trendlines. A breakout within the path of the preliminary value transfer confirms the continuation.
3. Rectangles:
Rectangles are characterised by horizontal assist and resistance ranges, creating an oblong form on the chart. The value consolidates inside these ranges earlier than a breakout within the path of the prevailing pattern. Breakouts above the resistance stage verify a bullish continuation, whereas breakouts beneath the assist stage verify a bearish continuation.
4. Wedges:
Wedges are just like triangles however have sloping trendlines that converge in direction of some extent. Ascending wedges are usually bearish, whereas descending wedges are often bullish. The path of the breakout confirms the pattern continuation or reversal (relying on the wedge sort).
Affirmation and Threat Administration:
Whereas chart patterns present beneficial insights, they shouldn’t be utilized in isolation. Affirmation from different technical indicators (e.g., transferring averages, RSI, MACD) and elementary evaluation can considerably improve the reliability of buying and selling selections primarily based on chart patterns.
Threat administration is paramount. All the time use stop-loss orders to restrict potential losses, and solely danger a small share of your buying and selling capital on any single commerce. Moreover, contemplate the general market context, information occasions, and financial indicators that might affect the value motion.
Sensible Utility:
Figuring out chart patterns requires observe and expertise. Start by specializing in just a few key patterns and mastering their identification and interpretation. Use historic information to research previous value actions and take a look at your sample recognition expertise. Backtesting your buying and selling methods utilizing simulated trades may help refine your method and establish potential weaknesses.
Conclusion:
Chart patterns provide a robust instrument for analyzing value motion and making knowledgeable buying and selling selections. By understanding the varied varieties of reversal and continuation patterns, and by combining sample recognition with different technical and elementary evaluation strategies, merchants can improve their buying and selling methods and doubtlessly enhance their profitability. Nonetheless, keep in mind that no technique is foolproof. Steady studying, disciplined danger administration, and endurance are important for achievement in utilizing chart patterns for value motion buying and selling. The secret is to mix sample recognition with a complete understanding of market dynamics and a sturdy danger administration plan. Constant observe and a willingness to adapt to altering market situations will in the end decide your success on this discipline.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Chart Patterns: Decoding Worth Motion for Worthwhile Buying and selling. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!