Chart Viewer Persuasion: The Artwork and Science of Influencing with Information
Associated Articles: Chart Viewer Persuasion: The Artwork and Science of Influencing with Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Chart Viewer Persuasion: The Artwork and Science of Influencing with Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart Viewer Persuasion: The Artwork and Science of Influencing with Information

Information visualization is not a mere presentation device; it is a highly effective instrument of persuasion. Chart viewers, the viewers deciphering your charts, should not passive recipients of data. They’re lively contributors, participating along with your knowledge primarily based on their pre-existing data, biases, and expectations. Understanding how one can craft persuasive charts that resonate along with your viewers is essential for efficient communication and attaining your required consequence, whether or not it is securing funding, advocating for a coverage change, or driving gross sales. This text delves into the artwork and science of chart viewer persuasion, exploring the psychological ideas and design issues that rework knowledge into compelling narratives.
Understanding Your Viewers: The Basis of Persuasion
Earlier than even contemplating chart design, understanding your audience is paramount. Completely different viewers possess various ranges of information literacy, material experience, and motivations. A chart efficient for a bunch of seasoned analysts is likely to be fully incomprehensible to a lay viewers. Think about these key features:
-
Information Literacy: Tailor the complexity of your chart to your viewers’s understanding. Keep away from jargon and overly technical representations in case your viewers lack statistical experience. Go for easier chart varieties like bar charts or pie charts for much less skilled audiences, reserving extra complicated visualizations like heatmaps or community graphs for these with stronger analytical abilities.
-
Prior Information: Account to your viewers’s current data of the subject material. If they’re already acquainted with the info, you possibly can concentrate on highlighting key developments and insights. Nevertheless, if they’re encountering the knowledge for the primary time, you will want to supply extra context and background info.
-
Motivations and Targets: What are your viewers hoping to achieve from this knowledge? Are they on the lookout for options to an issue, making a call, or just gaining a greater understanding of a scenario? Tailor your message and chart design to resonate with their particular motivations. As an illustration, if they’re on the lookout for options, spotlight actionable insights. If they’re making a call, emphasize the important thing components influencing their selection.
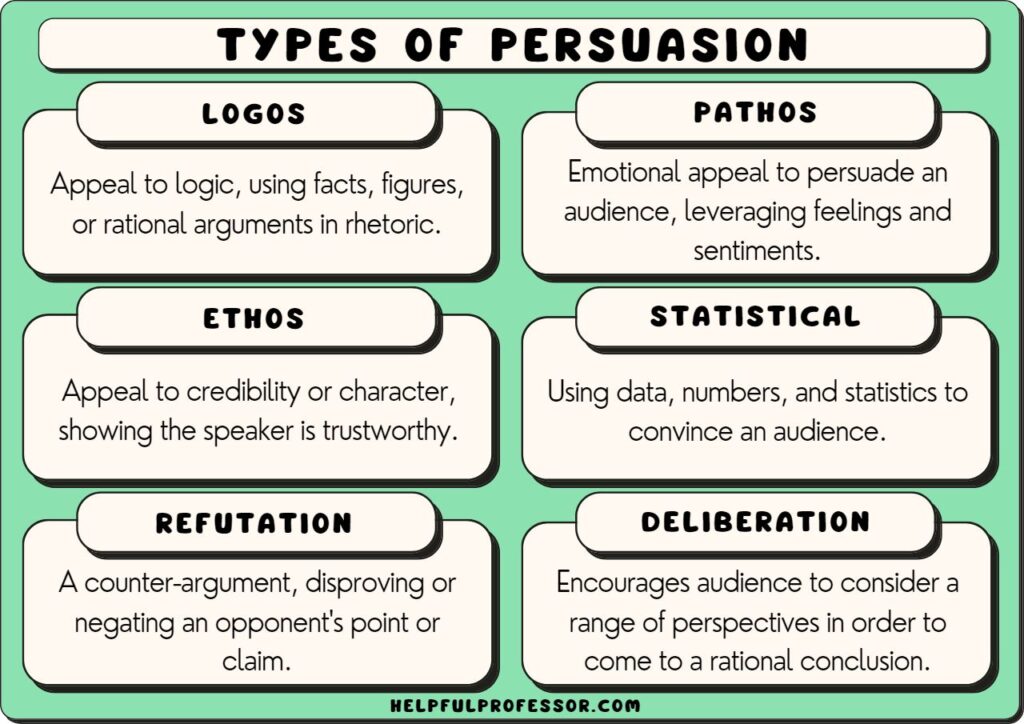
The Psychology of Persuasion in Chart Design
Persuasive chart design goes past merely displaying knowledge precisely. It includes leveraging psychological ideas to affect viewers’ interpretations and conclusions. Listed below are some key issues:
-
Anchoring Bias: The primary piece of data introduced usually acts as an anchor, influencing subsequent judgments. Strategically place your key findings early in your presentation or chart to ascertain a powerful preliminary impression.
-
Availability Heuristic: Folks are likely to overestimate the chance of occasions which might be simply recalled. Visually outstanding knowledge factors or hanging patterns in your chart can be extra readily remembered and affect viewers’ perceptions.
-
Framing Impact: The way you current the info can considerably affect its interpretation. Highlighting optimistic features or specializing in potential positive aspects can result in extra favorable responses than emphasizing destructive outcomes or potential losses.
-
Affirmation Bias: Folks are likely to favor info that confirms their current beliefs. Whilst you can not fully remove this bias, you possibly can try and current knowledge objectively and acknowledge potential counterarguments.
-
Visible Hierarchy: Information the viewer’s eye by means of the chart utilizing measurement, shade, and place to emphasise key findings and de-emphasize much less necessary particulars. Use clear labels and annotations to forestall misinterpretations.
Chart Sorts and Their Persuasive Energy
Completely different chart varieties are higher suited to conveying particular messages and influencing viewers specifically methods. Think about the next:
-
Bar Charts: Wonderful for evaluating discrete classes and highlighting variations in magnitude. Their simplicity makes them extremely accessible and simply comprehensible.
-
Line Charts: Very best for showcasing developments and adjustments over time. They successfully illustrate development, decline, and cyclical patterns.
-
Pie Charts: Helpful for exhibiting proportions of an entire. Nevertheless, they’re much less efficient for evaluating a number of classes, particularly when proportions are comparable.
-
Scatter Plots: Reveal correlations and relationships between two variables. They can be utilized to determine patterns and outliers.
-
Heatmaps: Efficient for displaying giant datasets and highlighting areas of excessive or low focus. They’re visually hanging and may reveal complicated patterns.
-
Maps: Very best for displaying geographical knowledge and illustrating spatial patterns. They’re notably efficient for speaking location-based info.
Design Rules for Persuasive Charts
Past selecting the best chart sort, the visible design itself performs a vital function in persuasion. Think about these design ideas:
-
Simplicity: Keep away from litter and pointless particulars. A clear, uncluttered chart is simpler to grasp and extra persuasive.
-
Readability: Use clear and concise labels, titles, and legends. Be sure that the info is well interpretable.
-
Shade: Use shade strategically to focus on key info and information the viewer’s eye. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, which will be overwhelming and distracting.
-
Typography: Select a legible font and applicable font sizes. Be sure that all textual content is well readable.
-
Whitespace: Use whitespace successfully to create visible respiratory room and enhance readability.
-
Information Integrity: Be sure that your knowledge is correct and ethically introduced. Keep away from manipulating knowledge to help a predetermined conclusion.
Moral Issues in Persuasive Chart Design
Whereas persuasion is a official objective, it is essential to take care of moral requirements. Keep away from:
-
Cherry-picking knowledge: Deciding on solely knowledge factors that help your argument whereas ignoring contradictory proof.
-
Manipulating scales: Distorting the visible illustration of information to magnify or downplay variations.
-
Deceptive labels or annotations: Utilizing ambiguous or misleading language to affect the viewer’s interpretation.
-
Lack of transparency: Failing to reveal knowledge sources or methodologies.
Conclusion: The Energy of Persuasive Information Visualization
Mastering the artwork of chart viewer persuasion is a vital talent in immediately’s data-driven world. By understanding your viewers, leveraging psychological ideas, and using efficient design methods, you possibly can rework knowledge into compelling narratives that affect choices, drive motion, and obtain your communication targets. Bear in mind, persuasive knowledge visualization is just not about manipulating your viewers; it is about speaking your message clearly, precisely, and ethically, empowering your viewers to make knowledgeable judgments primarily based on the proof you current. The important thing lies find the fragile stability between efficient persuasion and unwavering integrity.

![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Chart Viewer Persuasion: The Artwork and Science of Influencing with Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!