Selecting the Proper Chart: A Knowledge Visualization Information
Associated Articles: Selecting the Proper Chart: A Knowledge Visualization Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Selecting the Proper Chart: A Knowledge Visualization Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Selecting the Proper Chart: A Knowledge Visualization Information

Knowledge visualization is essential for successfully speaking insights. Nonetheless, selecting the unsuitable chart kind can obfuscate your message, resulting in misinterpretations and missed alternatives. This text serves as a complete information to deciding on the suitable chart in your knowledge, guaranteeing your visualizations are clear, correct, and impactful. We’ll discover numerous chart varieties, their strengths, weaknesses, and finest use circumstances, empowering you to make knowledgeable choices when presenting your knowledge.
I. Understanding Your Knowledge and Your Targets:
Earlier than deciding on a chart, you have to perceive two key features: your knowledge and your communication objectives.
-
Knowledge Sort: What sort of knowledge are you working with? Is it categorical (e.g., colours, manufacturers, areas), numerical (e.g., gross sales figures, temperatures), or a mixture of each? Is your knowledge displaying adjustments over time (temporal knowledge)? Understanding your knowledge’s traits is paramount.
-
Communication Targets: What message are you attempting to convey? Are you aiming to indicate developments, evaluate values, spotlight outliers, reveal correlations, or inform a narrative? Your goal dictates one of the best visualization technique.
II. Chart Sorts and Their Purposes:
Let’s delve into numerous chart varieties and their very best functions:
A. Charts for Evaluating Values:
-
Bar Chart: Glorious for evaluating discrete classes. Vertical bars characterize the magnitude of every class. Ideally suited for evaluating gross sales throughout totally different areas, product efficiency, or survey responses. Variations embrace grouped bar charts (for evaluating a number of variables inside classes) and stacked bar charts (for displaying the composition of an entire).
- Strengths: Straightforward to grasp, efficient for comparisons, good for highlighting variations.
- Weaknesses: Can change into cluttered with many classes, not very best for displaying developments over time.
-
Column Chart: Just like bar charts, however with horizontal bars. Helpful when class labels are lengthy or if you need to emphasize the magnitude of values extra instantly.
- Strengths: Straightforward to learn, good for evaluating values, handles lengthy labels effectively.
- Weaknesses: Will be cluttered with many classes, not appropriate for temporal knowledge.
-
Pie Chart: Exhibits the proportion of every class to the entire. Efficient for illustrating the composition of a single dataset. Nonetheless, overuse can result in difficulties in evaluating segments precisely, particularly with many slices.
- Strengths: Visually interesting, simply exhibits proportions.
- Weaknesses: Troublesome to check segments exactly, not appropriate for a lot of classes.
-
Dot Plot: A easy chart displaying particular person knowledge factors alongside a single axis. Helpful for displaying the distribution of information and figuring out outliers.
- Strengths: Easy, clear, exhibits particular person knowledge factors, highlights outliers.
- Weaknesses: Can change into cluttered with giant datasets, not very best for displaying developments.
B. Charts for Exhibiting Tendencies Over Time:
-
Line Chart: Ideally suited for displaying developments and adjustments over time. Connects knowledge factors to disclose patterns and fluctuations. Efficient for displaying gross sales figures over months, web site site visitors over time, or inventory costs.
- Strengths: Clearly exhibits developments, straightforward to interpret temporal adjustments.
- Weaknesses: Will be cluttered with a number of traces, not very best for evaluating discrete classes.
-
Space Chart: Just like line charts, however fills the realm below the road. Emphasizes the magnitude of adjustments over time and the cumulative impact.
- Strengths: Exhibits developments and magnitudes, highlights cumulative values.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with a number of traces, not very best for exact comparisons.
C. Charts for Exhibiting Relationships Between Variables:
-
Scatter Plot: Shows the connection between two numerical variables. Every level represents an information level, and the sample of factors reveals correlations. Helpful for figuring out relationships between promoting spend and gross sales, or peak and weight.
- Strengths: Exhibits correlations between variables, identifies outliers.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with giant datasets, would not present causality.
-
Bubble Chart: An extension of scatter plots, the place the scale of every bubble represents a 3rd variable. Helpful for displaying relationships between three variables concurrently.
- Strengths: Exhibits relationships between three variables, highlights magnitude.
- Weaknesses: Will be cluttered with many knowledge factors, tough to interpret with overlapping bubbles.
-
Heatmap: Makes use of colour depth to characterize the magnitude of information in a matrix. Helpful for visualizing correlations between many variables or displaying geographical knowledge.
- Strengths: Visually interesting, exhibits patterns in giant datasets.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with advanced knowledge, requires cautious colour scaling.
D. Different Helpful Chart Sorts:
-
Field Plot (Field and Whisker Plot): Summarizes the distribution of a dataset, displaying median, quartiles, and outliers. Helpful for evaluating distributions throughout totally different teams.
- Strengths: Exhibits distribution, median, quartiles, and outliers.
- Weaknesses: Will be much less intuitive than different charts for non-statistical audiences.
-
Histogram: Exhibits the frequency distribution of a numerical variable. Helpful for understanding the form of the info and figuring out clusters.
- Strengths: Exhibits knowledge distribution, identifies clusters and outliers.
- Weaknesses: Will be delicate to bin dimension choice.
-
Treemap: Represents hierarchical knowledge utilizing nested rectangles. The scale of every rectangle represents the magnitude of the info. Helpful for displaying market share, web site site visitors sources, or file system buildings.
- Strengths: Exhibits hierarchical knowledge successfully, visually interesting.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with many ranges of hierarchy.
-
Community Graph: Illustrates relationships between entities. Nodes characterize entities, and edges characterize connections. Helpful for visualizing social networks, organizational buildings, or web site hyperlinks.
- Strengths: Exhibits advanced relationships, visually interesting.
- Weaknesses: Can change into cluttered with many nodes and edges.
III. Finest Practices for Knowledge Visualization:
- Maintain it Easy: Keep away from muddle and pointless particulars. Deal with the important thing message.
- Select Acceptable Scales: Use applicable scales in your axes to keep away from deceptive interpretations.
- **Use Clear Labels and


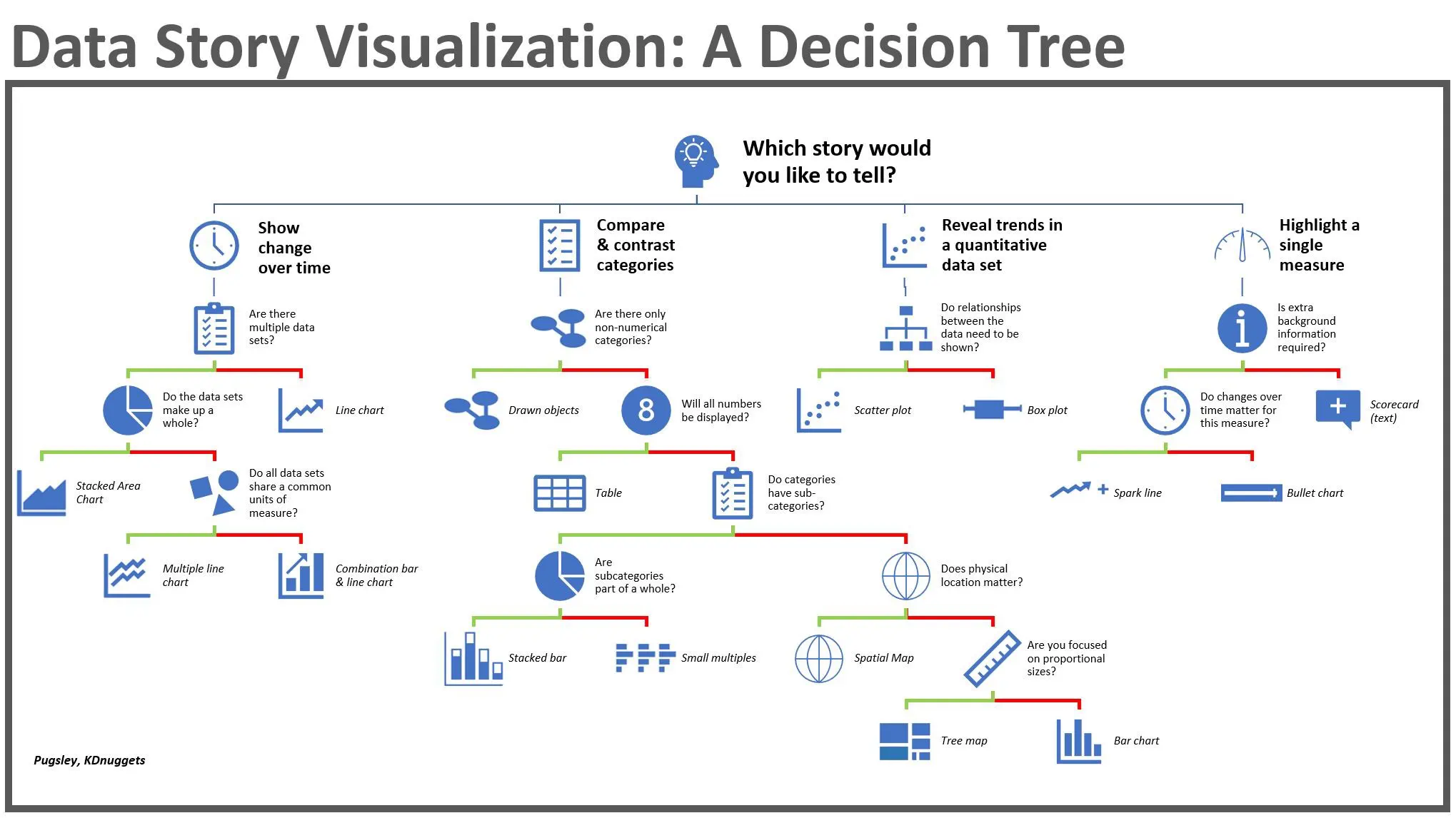
![How to Choose the Right Chart Type [Infographic] - DataScienceCentral.com](https://www.datasciencecentral.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/1226131201.jpg)
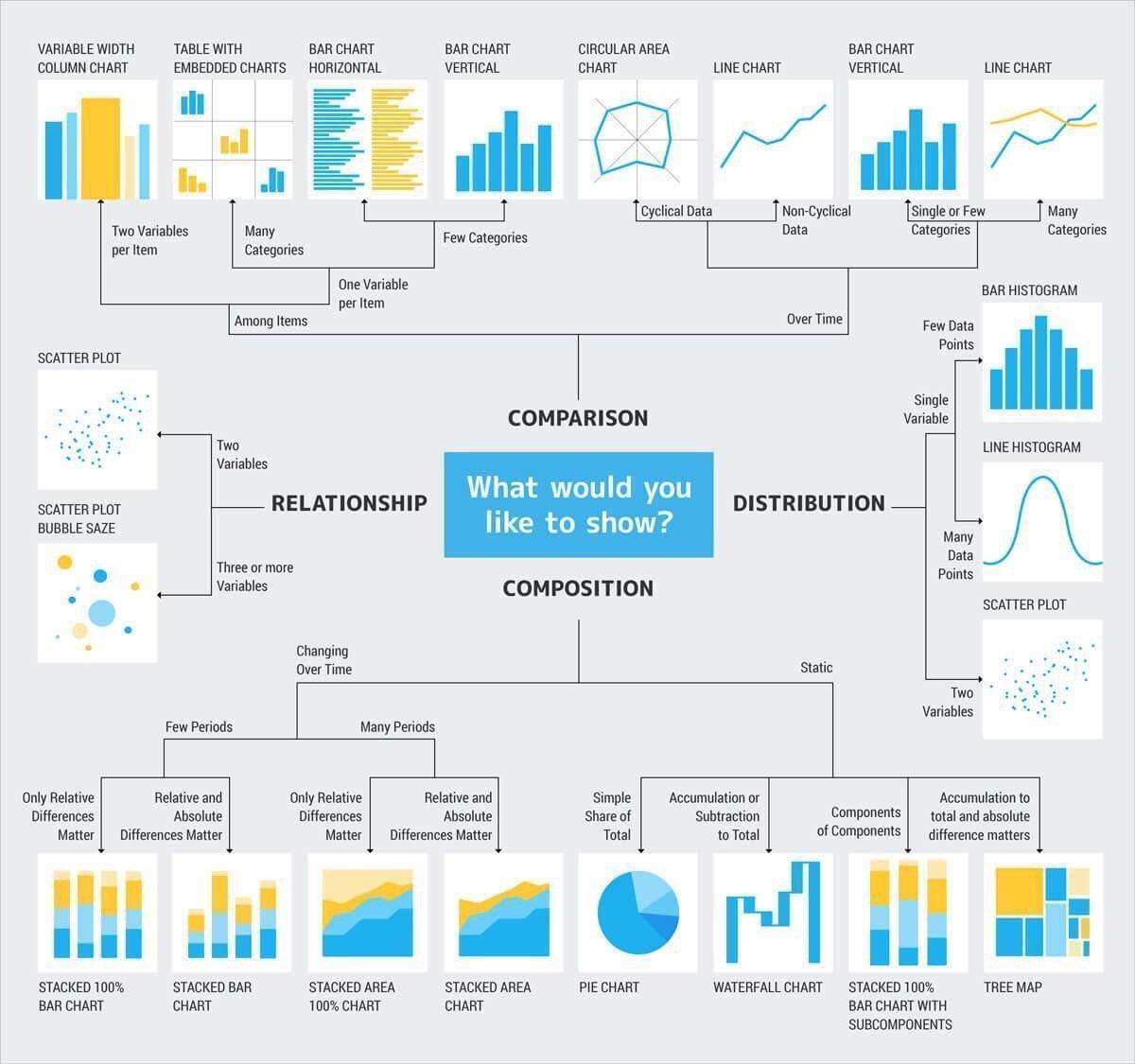
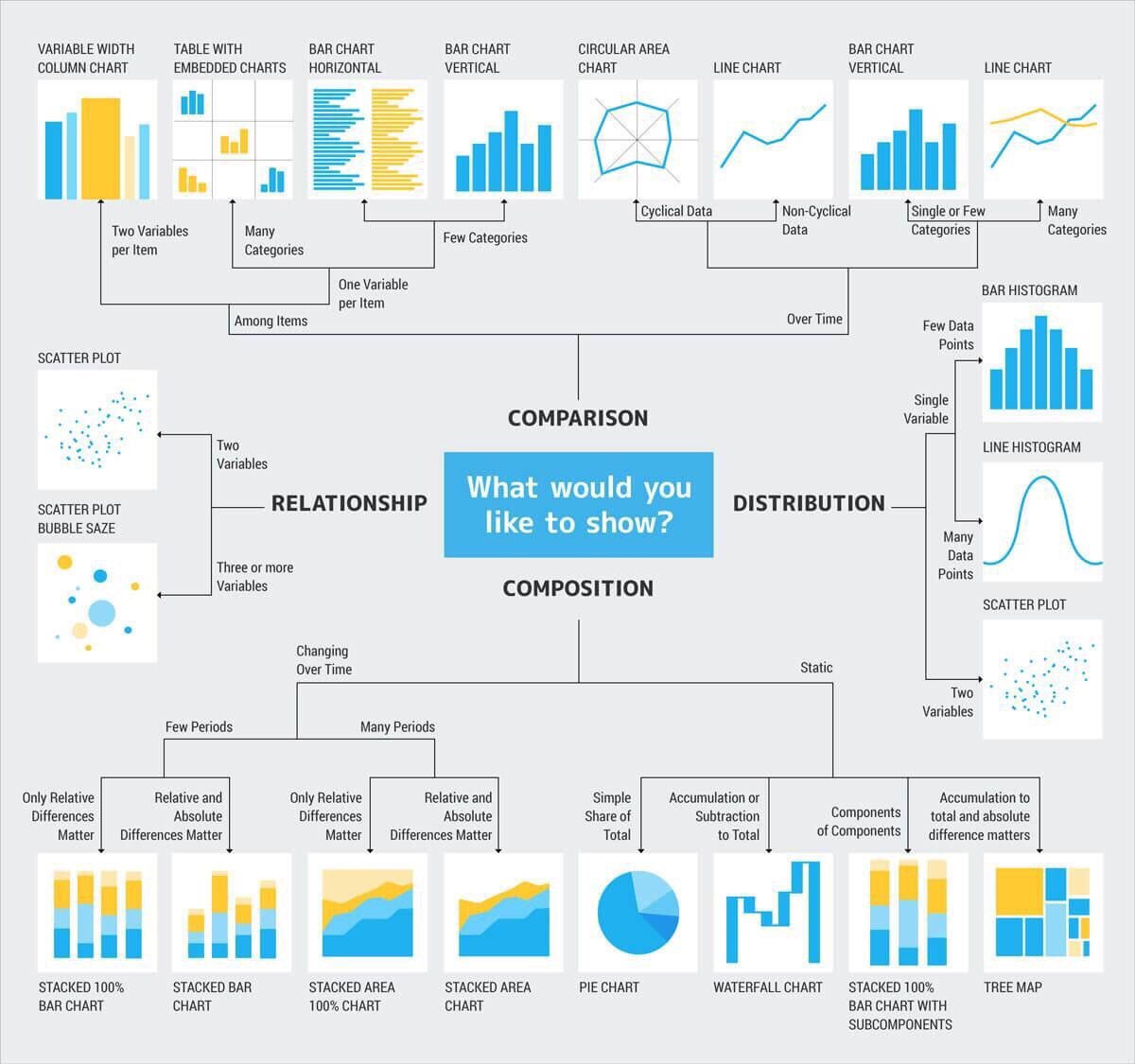


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Selecting the Proper Chart: A Knowledge Visualization Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!