Selecting the Proper Chart for Two Measures: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Selecting the Proper Chart for Two Measures: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Selecting the Proper Chart for Two Measures: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Selecting the Proper Chart for Two Measures: A Complete Information

Knowledge visualization is essential for efficient communication and insightful evaluation. When coping with two measures, the selection of chart considerably impacts the readability and understanding of the offered data. Deciding on the suitable chart relies upon closely on the kind of knowledge, the connection between the measures, and the story you goal to inform. This text delves into numerous chart sorts appropriate for visualizing two measures, offering detailed explanations, examples, and steering on making knowledgeable selections.
Understanding Your Knowledge: The Basis of Chart Choice
Earlier than diving into particular chart sorts, it is essential to know the character of your two measures. Are they each numerical (steady or discrete)? Is one categorical and the opposite numerical? Do you need to present the connection between them, evaluate them, or observe their modifications over time? These questions will information your alternative.
1. Each Measures are Numerical:
This state of affairs opens up a variety of charting choices, every with its strengths and weaknesses.
-
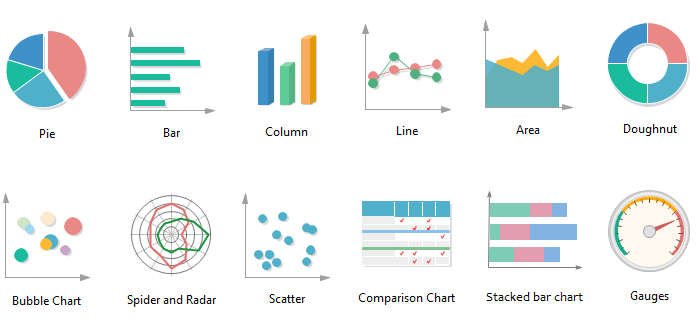
Scatter Plot: Perfect for exploring the connection between two steady numerical variables. Every knowledge level is represented as a dot on a two-dimensional aircraft, with one measure on the x-axis and the opposite on the y-axis. Scatter plots successfully reveal correlations (optimistic, detrimental, or no correlation), clusters, and outliers. They’re notably helpful for figuring out potential traits and patterns. Nevertheless, they develop into much less efficient with very giant datasets, because the factors can overlap and obscure particulars. Including shade or dimension to the factors can characterize a 3rd variable, enhancing the visualization’s richness.
-
Line Chart: Appropriate for visualizing the development of two measures over time or a steady variable. Every measure is represented by a separate line, permitting for straightforward comparability of their trajectories. Line charts are wonderful for displaying modifications, figuring out peaks and valleys, and highlighting development or decline. They’re much less efficient for evaluating absolutely the values of the 2 measures at particular factors. A number of strains could be troublesome to interpret if too many are included.
-
Space Chart: Just like a line chart, however the space beneath every line is stuffed with shade. This emphasizes the magnitude of every measure over time. Space charts are efficient for displaying the relative contribution of every measure to a complete. Nevertheless, overlapping areas could make it troublesome to tell apart particular person measures, notably when the values are shut. Like line charts, they’re finest fitted to time-series knowledge or knowledge ordered alongside a steady variable.
-
Bubble Chart: An extension of the scatter plot, the place the dimensions of every bubble represents the magnitude of a 3rd variable. This permits for the visualization of three measures concurrently. Bubble charts are efficient for highlighting the relative significance of various knowledge factors primarily based on all three measures. Nevertheless, they will develop into cluttered with giant datasets and could also be troublesome to interpret if the bubble sizes aren’t clearly differentiated.
-
Heatmap: Represents knowledge as a grid of coloured cells, the place the colour depth corresponds to the worth of the measure. Whereas sometimes used for a single measure throughout a number of classes, heatmaps could be tailored to point out two measures by utilizing completely different shade scales for every measure, or by representing one measure as rows and the opposite as columns. Heatmaps are efficient for figuring out patterns and clusters throughout a number of classes. Nevertheless, they’re much less efficient for displaying exact values.
2. One Measure is Categorical, the Different is Numerical:
This example requires completely different chart sorts that successfully characterize the explicit variable and the numerical variable’s distribution inside every class.
-
Bar Chart: A basic alternative for evaluating the numerical measure throughout completely different classes. Every bar represents a class, and its top corresponds to the numerical worth. Bar charts are easy, straightforward to know, and efficient for highlighting variations between classes. Grouped bar charts can be utilized to check the numerical measure throughout a number of classes concurrently. Stacked bar charts present the contribution of every class to a complete.
-
Column Chart: Primarily a rotated bar chart, with classes on the x-axis and the numerical measure on the y-axis. Column charts are notably helpful when class labels are lengthy or if you need to emphasize the numerical values extra prominently.
-
Field Plot (Field and Whisker Plot): Illustrates the distribution of a numerical measure for every class. It exhibits the median, quartiles, and outliers, offering a abstract of the information’s central tendency and variability. Field plots are efficient for evaluating the distribution of the numerical measure throughout completely different classes and figuring out potential outliers. They’re much less efficient for displaying the exact values of particular person knowledge factors.
-
Violin Plot: Just like a field plot, nevertheless it additionally exhibits the chance density of the information at completely different values. This supplies a extra detailed view of the information’s distribution than a field plot. Violin plots are efficient for highlighting the form and unfold of the information inside every class.
3. Issues for Massive Datasets (e.g., > 1000 knowledge factors):
For very giant datasets, some chart sorts can develop into overwhelming or lose their effectiveness. Take into account these methods:
- Sampling: Cut back the dataset dimension by randomly choosing a consultant subset.
- Aggregation: Group knowledge into bins or classes to scale back the variety of knowledge factors.
- Interactive Charts: Use interactive charts that enable customers to zoom, pan, and filter the information to discover particular areas of curiosity.
- Small Multiples: Create a number of smaller charts, every displaying a subset of the information.
Selecting the Proper Chart: A Choice Matrix
To summarize, the next matrix can help in choosing the suitable chart kind:
| Knowledge Kind | Chart Kind | Function | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical, Numerical | Scatter Plot | Discover relationship, determine correlation | Reveals patterns, outliers | Cluttered with giant datasets |
| Numerical, Numerical | Line Chart | Present traits over time | Straightforward to check traits | Much less efficient for evaluating absolute values |
| Numerical, Numerical | Space Chart | Present traits and relative contributions | Emphasizes magnitude over time | Overlapping areas could be troublesome to interpret |
| Numerical, Numerical | Bubble Chart | Present three measures concurrently | Highlights relative significance | Cluttered with giant datasets, troublesome to learn |
| Numerical, Numerical | Heatmap | Present patterns throughout classes | Identifies clusters | Much less efficient for exact values |
| Categorical, Numerical | Bar Chart | Examine numerical values throughout classes | Easy, straightforward to know | Will be cluttered with many classes |
| Categorical, Numerical | Column Chart | Examine numerical values throughout classes | Just like bar chart, emphasizes numerical values | Will be cluttered with many classes |
| Categorical, Numerical | Field Plot | Present distribution of numerical knowledge | Reveals median, quartiles, outliers | Much less efficient for displaying particular person knowledge factors |
| Categorical, Numerical | Violin Plot | Present distribution of numerical knowledge | Reveals detailed distribution | Will be advanced to interpret |
Conclusion:
Deciding on the proper chart for visualizing two measures is a vital step in efficient knowledge communication. By understanding the character of your knowledge and the story you want to inform, you may select a chart that successfully conveys your insights and facilitates knowledgeable decision-making. Bear in mind to think about the dataset dimension and select acceptable methods for dealing with giant datasets. The objective is to create a transparent, concise, and visually interesting illustration of your knowledge that enhances understanding and drives motion.
![How to Choose the Right Chart Type [Infographic] - DataScienceCentral.com](https://www.datasciencecentral.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/1226131201.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Selecting the Proper Chart for Two Measures: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!