Selecting the Proper Chart Kind for Your Information: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Selecting the Proper Chart Kind for Your Information: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Selecting the Proper Chart Kind for Your Information: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Selecting the Proper Chart Kind for Your Information: A Complete Information
![How to Choose the Right Chart Type [Infographic] - DataScienceCentral.com](https://www.datasciencecentral.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/1226131201.jpg)
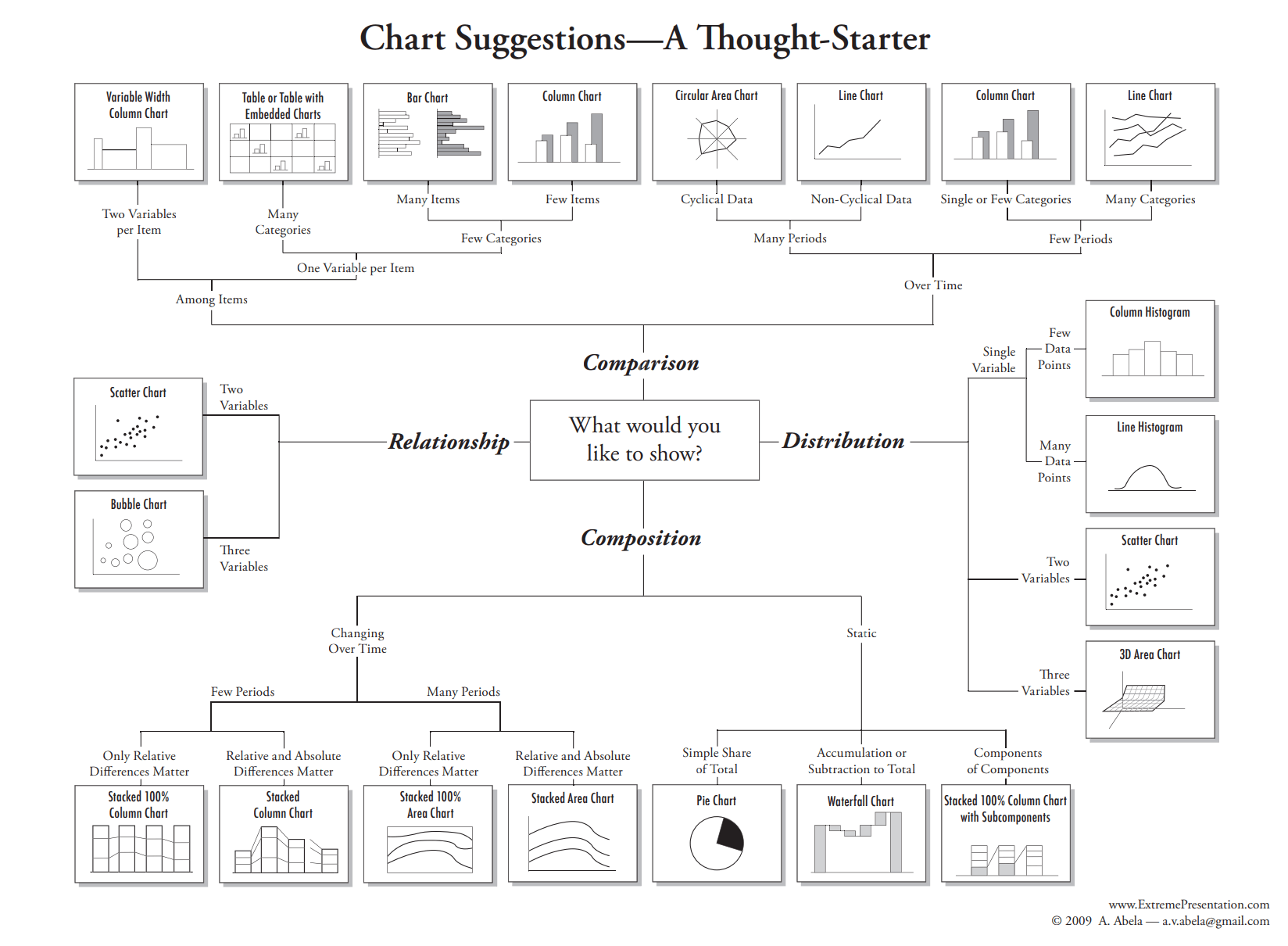
Information visualization is paramount in at the moment’s data-driven world. A well-chosen chart can immediately talk advanced info, revealing traits, patterns, and outliers which may in any other case stay hidden inside uncooked information. Conversely, a poorly chosen chart can obfuscate which means, resulting in misinterpretations and flawed conclusions. The important thing to efficient information visualization lies in choosing the suitable chart sort to match your information and the message you goal to convey. This complete information explores numerous chart sorts, their strengths and weaknesses, and supplies sensible recommendation on selecting the most effective match in your particular wants.
Understanding Your Information: The Basis of Efficient Visualization
Earlier than diving into the plethora of chart sorts obtainable, it is essential to grasp your information. Think about the next:
-
Kind of Information: Is your information categorical (e.g., colours, names, classes) or numerical (e.g., age, weight, temperature)? Categorical information usually entails counts or proportions, whereas numerical information can characterize steady or discrete values. Understanding this distinction is foundational for choosing an acceptable chart.
-
Variety of Variables: What number of variables are you making an attempt to characterize? A single variable may require a easy histogram, whereas evaluating two or extra variables may necessitate a scatter plot or bar chart.
-
Information Distribution: Is your information usually distributed, skewed, or bimodal? The distribution of your information will affect the selection of chart; some charts are higher suited to deal with skewed information than others.
-
Viewers: Who’s your meant viewers? A chart appropriate for a technical viewers could be overly advanced for a basic viewers. Think about their stage of understanding and the message you wish to convey.
-
Goal: What story are you making an attempt to inform together with your information? Are you highlighting traits, evaluating teams, displaying correlations, or figuring out outliers? Your goal will instantly inform your chart choice.
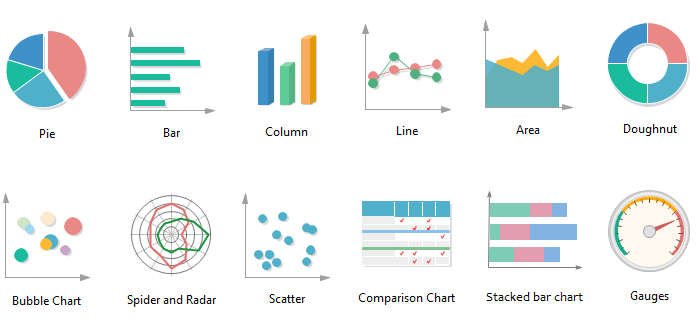
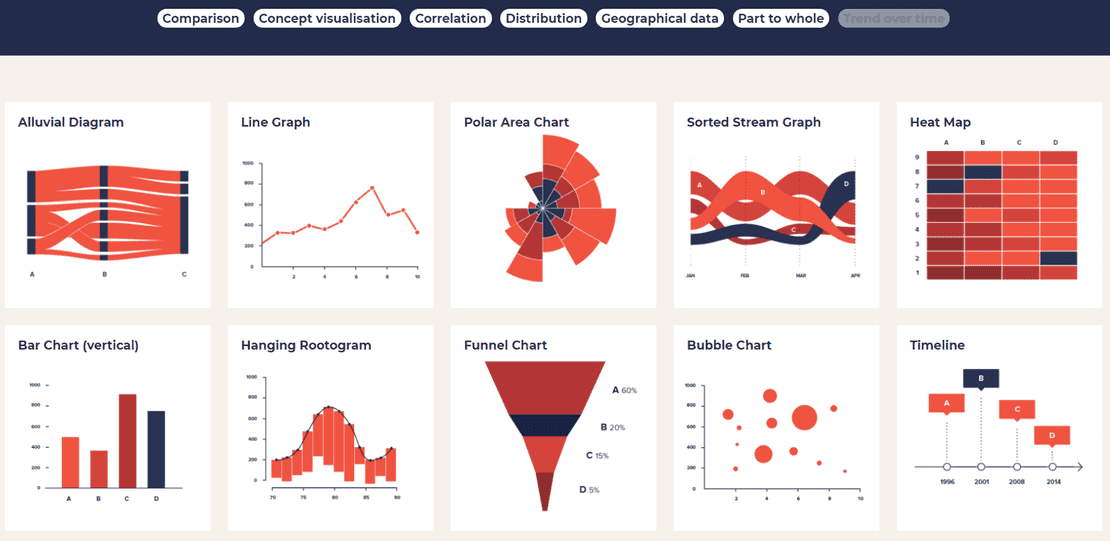
Frequent Chart Varieties and Their Purposes:
Let’s discover some frequent chart sorts and their greatest functions:
1. Bar Charts: Ideally suited for evaluating categorical information throughout totally different teams. They visually characterize the magnitude of every class utilizing the peak or size of bars.
- Strengths: Easy to grasp, efficient for comparisons, can deal with each small and huge datasets.
- Weaknesses: Can develop into cluttered with too many classes, not appropriate for displaying traits over time.
- Greatest for: Evaluating gross sales figures throughout totally different areas, displaying the frequency of various classes, presenting survey outcomes.
2. Column Charts: Much like bar charts, however with bars oriented vertically. They serve the identical function however might be extra visually interesting relying on the context.
- Strengths: Simple to grasp, efficient for comparisons, appropriate for giant datasets.
- Weaknesses: Can develop into cluttered with many classes, not superb for displaying traits.
- Greatest for: Evaluating efficiency metrics throughout totally different time intervals, showcasing finances allocations, illustrating survey responses.
3. Line Charts: Wonderful for visualizing traits and modifications over time. They join information factors with traces, revealing patterns and fluctuations.
- Strengths: Successfully reveals traits, highlights modifications over time, simple to interpret.
- Weaknesses: Not superb for evaluating distinct classes, can develop into cluttered with many information sequence.
- Greatest for: Exhibiting inventory costs over time, monitoring web site site visitors, illustrating progress patterns.
4. Space Charts: Much like line charts, however the space beneath the road is full of coloration. They emphasize the magnitude of change over time.
- Strengths: Highlights the cumulative impact over time, emphasizes modifications in magnitude, visually interesting.
- Weaknesses: Could be tough to interpret with many information sequence, not superb for exact comparisons.
- Greatest for: Exhibiting web site site visitors over time, illustrating cumulative gross sales, visualizing inhabitants progress.
5. Pie Charts: Used to point out the proportion of various classes inside an entire. Every slice represents a class’s share.
- Strengths: Easy to grasp, successfully reveals proportions, good for highlighting the dominant classes.
- Weaknesses: Troublesome to match small slices, not appropriate for a lot of classes, might be deceptive if not correctly labeled.
- Greatest for: Exhibiting market share, illustrating finances allocation, representing demographic breakdowns.
6. Scatter Plots: Used to discover the connection between two numerical variables. Every level represents an information level, with its place decided by the values of the 2 variables.
- Strengths: Reveals correlations between variables, identifies outliers, helpful for exploratory information evaluation.
- Weaknesses: Could be tough to interpret with many information factors, does not present causation.
- Greatest for: Exploring the connection between age and earnings, analyzing the correlation between promoting spend and gross sales, figuring out outliers in a dataset.
7. Histograms: Used to show the distribution of a single numerical variable. They group information into bins and present the frequency of information factors inside every bin.
- Strengths: Reveals the distribution of information, reveals skewness and modality, helpful for understanding information patterns.
- Weaknesses: Could be delicate to bin dimension choice, not superb for evaluating a number of variables.
- Greatest for: Exhibiting the distribution of age, illustrating the frequency of check scores, understanding the unfold of information.
8. Field Plots (Field and Whisker Plots): Present the distribution of a numerical variable by means of quartiles, median, and outliers. They’re glorious for evaluating distributions throughout totally different teams.
- Strengths: Successfully reveals the unfold and central tendency of information, highlights outliers, helpful for evaluating distributions throughout teams.
- Weaknesses: Could be much less intuitive than different charts, not superb for displaying detailed information patterns.
- Greatest for: Evaluating the distribution of earnings throughout totally different demographics, analyzing the variability of check scores throughout totally different colleges, figuring out outliers in a dataset.
9. Heatmaps: Use coloration depth to characterize the magnitude of information in a matrix. They’re efficient for visualizing massive datasets with a number of variables.
- Strengths: Successfully shows massive datasets, highlights patterns and correlations, visually interesting.
- Weaknesses: Could be tough to interpret with many variables, not superb for displaying exact values.
- Greatest for: Visualizing correlation matrices, displaying geographical information, illustrating buyer segmentation.
10. Geographic Maps (Choropleth Maps): Use coloration shading to characterize information throughout geographical areas. They’re glorious for visualizing spatial information.
- Strengths: Successfully reveals geographical patterns, highlights regional variations, simple to grasp.
- Weaknesses: Could be deceptive if not correctly scaled, not superb for displaying exact values.
- Greatest for: Exhibiting inhabitants density, illustrating election outcomes, visualizing illness outbreaks.
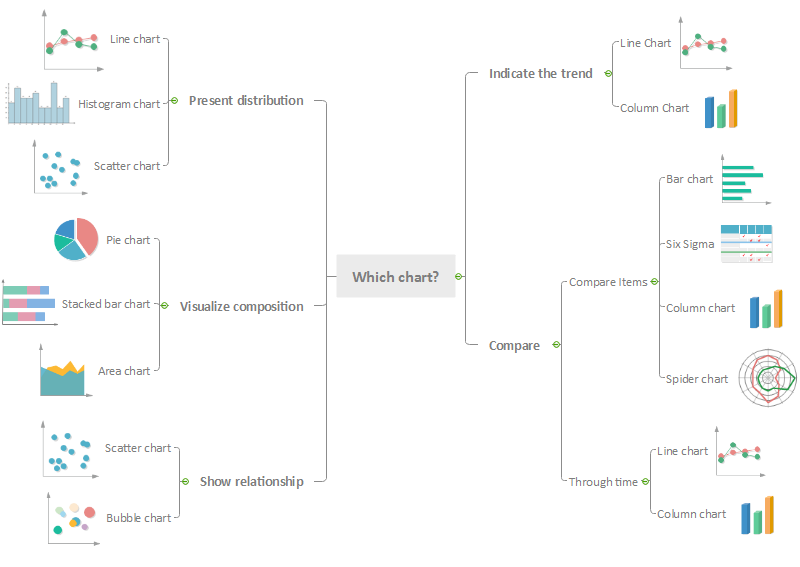
Selecting the Proper Chart: A Sensible Method
The collection of the suitable chart sort must be a deliberate course of. Think about the next steps:
- Outline your goal: What message do you wish to convey?
- Determine your variables: What information are you working with?
- Think about your information sort: Is it categorical or numerical?
- Assess your information distribution: Is it regular, skewed, or bimodal?
- Select probably the most acceptable chart sort: Based mostly in your solutions above, choose the chart that most closely fits your wants.
- Take a look at and refine: Create your chart and consider its effectiveness. Make changes as wanted to make sure readability and accuracy.
By fastidiously contemplating these components and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various chart sorts, you possibly can create efficient information visualizations that talk your message clearly and precisely, main to higher knowledgeable choices and insights. Bear in mind, the last word objective is to translate advanced information into simply digestible and actionable info.

![How to Choose the Right Chart Type [Infographic] : r/Infographics](https://preview.redd.it/fbsimd38kbj21.png?auto=webpu0026s=b74cf97f38c194a5045c9a9acdfbe3af6838b69d)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Selecting the Proper Chart Kind for Your Information: A Complete Information. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!