Decoding the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts and Their Purposes
Associated Articles: Decoding the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts and Their Purposes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts and Their Purposes. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts and Their Purposes

Pie charts, these ubiquitous round diagrams sliced into segments, are a staple of information visualization. Their easy, intuitive design makes them readily comprehensible, even for audiences with restricted statistical data. Nevertheless, their obvious simplicity belies a nuanced software that requires cautious consideration of information choice, design selections, and moral implications. This text delves deep into the world of pie charts, exploring their strengths and weaknesses, offering examples throughout various fields, and providing steering on efficient implementation.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
A pie chart represents proportions of a complete. Every slice represents a class, with its measurement instantly proportional to its contribution to the entire. All the circle represents 100% of the information, with every slice’s space akin to its share. This visible illustration permits for fast comparisons between classes and rapid identification of the biggest and smallest contributors.
Instance 1: Market Share Evaluation
Contemplate a hypothetical market evaluation for smartphones. For instance now we have information in the marketplace share of 4 main manufacturers: Model A (45%), Model B (30%), Model C (15%), and Model D (10%). A pie chart completely illustrates this distribution.
[Imagine a pie chart here with four slices: A (largest, 45%), B (second largest, 30%), C (medium, 15%), and D (smallest, 10%). Each slice should be clearly labelled with the brand name and its percentage.]
This straightforward visualization immediately communicates the dominance of Model A, the robust second place of Model B, and the comparatively smaller shares of Manufacturers C and D. An viewers can rapidly grasp the aggressive panorama while not having to sift by numerical information.
Instance 2: Finances Allocation
Pie charts are extraordinarily efficient in depicting budgetary breakdowns. Think about an organization’s annual price range of $1 million. The price range could be allotted as follows: Analysis & Improvement (30%), Advertising (25%), Operations (20%), Gross sales (15%), and Administration (10%).
[Imagine a pie chart here with five slices representing R&D (30%), Marketing (25%), Operations (20%), Sales (15%), and Administration (10%). Each slice should be labelled with the department and its percentage of the budget.]
This pie chart gives a transparent visible illustration of the place the corporate’s assets are directed. It permits stakeholders to rapidly assess the proportion of funds allotted to every division and determine potential areas for adjustment or optimization. The visible nature makes it simpler to know the price range allocation in comparison with a easy desk of numbers.
Instance 3: Demographic Breakdown
Pie charts are often used as an instance demographic information. As an example, contemplate the age distribution of an internet site’s consumer base: 18-25 (20%), 26-35 (35%), 36-45 (25%), 46-55 (15%), and 55+ (5%).
[Imagine a pie chart here with five slices representing the age groups: 18-25 (20%), 26-35 (35%), 36-45 (25%), 46-55 (15%), and 55+ (5%). Each slice should be labelled with the age range and its percentage.]
This pie chart clearly exhibits the dominant age group (26-35) and the relative proportions of different age segments. This info is essential for focused advertising campaigns and web site design changes to cater to the first consumer demographics.
Instance 4: Reason behind Buyer Churn
In enterprise analytics, pie charts can successfully visualize the explanations behind buyer churn. For instance an organization analyzed buyer suggestions and recognized the next contributing elements: Poor customer support (40%), Excessive pricing (30%), Lack of options (20%), and Competitors (10%).
[Imagine a pie chart here with four slices representing: Poor customer service (40%), High pricing (30%), Lack of features (20%), and Competition (10%). Each slice should be labelled with the reason and its percentage.]
This pie chart helps the corporate prioritize its efforts to enhance buyer retention. The big slice representing "Poor customer support" instantly highlights the necessity for enhancements on this space.
Limitations of Pie Charts:
Whereas pie charts are efficient for easy comparisons, they’ve limitations:
- Problem evaluating small slices: When coping with quite a few classes or classes with small percentages, it turns into difficult to visually differentiate between the slices.
- Restricted precision: Pie charts usually are not appropriate for exact comparisons. It is troublesome to precisely choose the distinction between, say, 25% and 28% based mostly solely on the visible illustration.
- Ineffective with many classes: Pie charts turn out to be cluttered and troublesome to interpret after they comprise greater than 5 to seven classes.
- Deceptive with unequal angles: Whereas the world of every slice ought to symbolize the share, inaccurate illustration can mislead the viewers.
Alternate options to Pie Charts:
For conditions the place pie charts are much less efficient, different visualizations could be extra acceptable:
- Bar charts: Glorious for evaluating the magnitude of various classes.
- Treemaps: Helpful for hierarchical information, displaying proportions inside subcategories.
- Stacked bar charts: Appropriate for displaying the composition of a number of teams.
Moral Issues:
Creating correct and unbiased pie charts is essential. Manipulating the information or design components to misrepresent the data is unethical. For instance, exaggerating the scale of a specific slice or utilizing deceptive labels can distort the viewers’s understanding.
Conclusion:
Pie charts are a helpful software for information visualization, significantly when illustrating proportions of a complete. Their simplicity and intuitive design make them simply accessible to a large viewers. Nevertheless, it is important to know their limitations and select the suitable visualization method based mostly on the information and the supposed viewers. By fastidiously contemplating information choice, design selections, and moral implications, we will successfully leverage pie charts to speak advanced info clearly and precisely. Keep in mind to at all times try for readability, accuracy, and moral illustration to make sure that your pie charts successfully talk the supposed message with out deceptive the viewers. The ability of a pie chart lies not solely in its visible enchantment but additionally in its capability to facilitate understanding and knowledgeable decision-making.


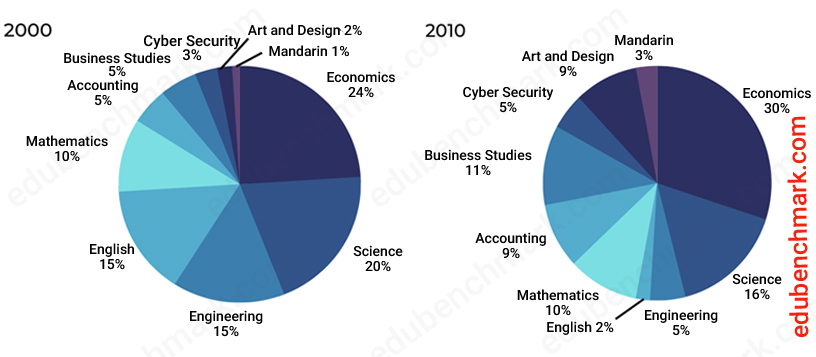
![Electricity Pie Chart [Sample IELTS Essay] - TED IELTS](https://ted-ielts.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Learn-How-to-Describe-Pie-Charts-for-IELTS.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Decoding the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts and Their Purposes. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!