Decoding the ECG: A Complete Information to Regular Readings
Associated Articles: Decoding the ECG: A Complete Information to Regular Readings
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the ECG: A Complete Information to Regular Readings. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the ECG: A Complete Information to Regular Readings

The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a cornerstone of cardiovascular diagnostics, offering a non-invasive window into {the electrical} exercise of the center. This text will delve into the interpretation of a traditional ECG, explaining the assorted parts, their significance, and the underlying physiological processes they symbolize. Understanding a traditional ECG is essential for recognizing abnormalities and appreciating the diagnostic energy of this important device.
I. The Fundamentals: Lead Placement and Electrical Conduction
Earlier than diving into the interpretation, it is vital to grasp the elemental ideas. An ECG information {the electrical} exercise of the center utilizing electrodes positioned on the pores and skin’s floor. These electrodes are linked to a machine that amplifies and shows {the electrical} alerts as waveforms on a graph. Commonplace ECGs make the most of 12 leads, every offering a unique perspective of the center’s electrical exercise. These leads are categorized into limb leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF) and precordial leads (V1-V6).
The center’s electrical conduction system initiates and coordinates the rhythmic contraction of the center muscle. The method begins within the sinoatrial (SA) node, the center’s pure pacemaker, positioned in the proper atrium. {The electrical} impulse spreads by the atria, inflicting atrial contraction. The impulse then travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, an important gateway controlling the speed of impulse transmission to the ventricles. From the AV node, the impulse travels down the bundle of His, dividing into the proper and left bundle branches, and eventually reaching the Purkinje fibers, which distribute the impulse all through the ventricles, resulting in ventricular contraction.
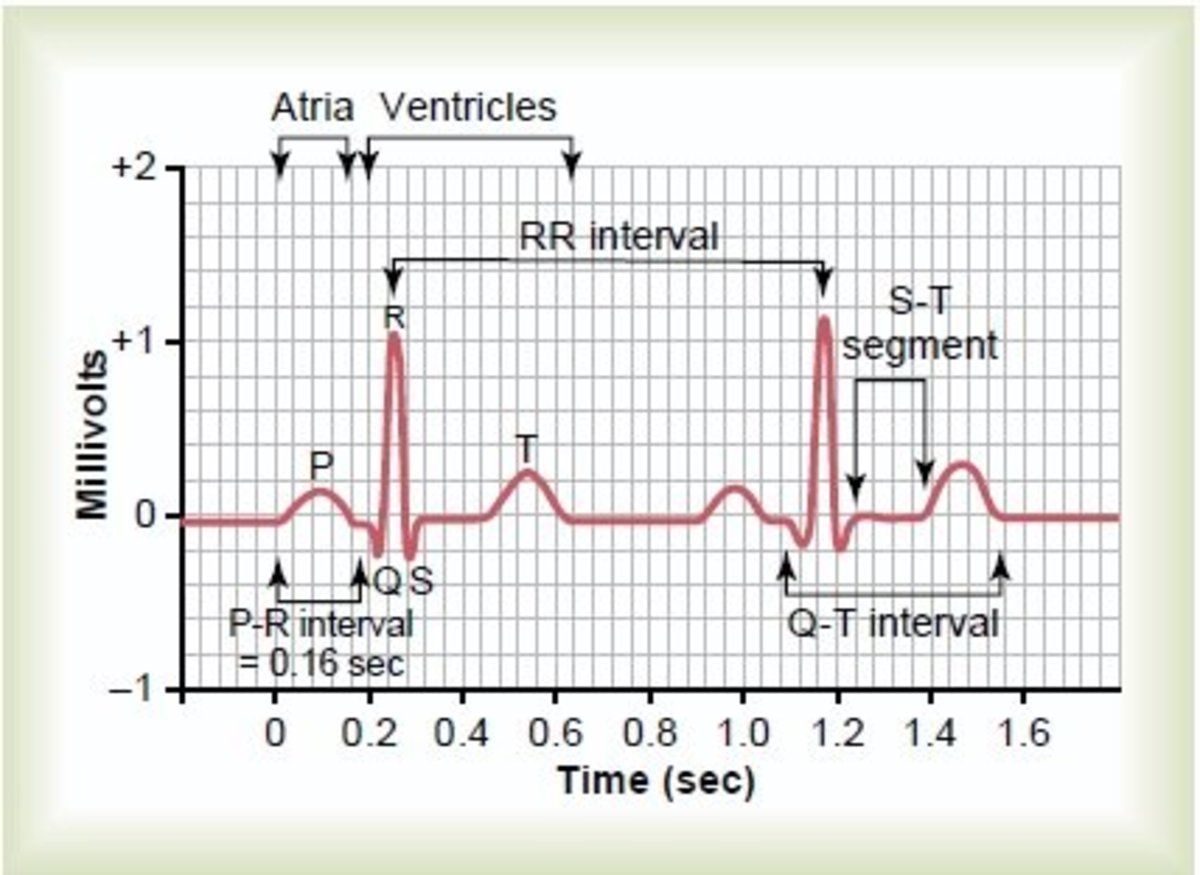
II. Elements of a Regular ECG Waveform
A traditional ECG waveform consists of a number of key parts, every representing a selected section of the cardiac cycle:
-
P wave: This small, rounded upward deflection represents atrial depolarization, {the electrical} activation of the atria previous their contraction. In a traditional ECG, the P wave is upright in leads I, II, and aVF, and its period is often lower than 0.12 seconds.
-
PR interval: This phase represents the time it takes for {the electrical} impulse to journey from the SA node by the atria, the AV node, and the His-Purkinje system to the ventricles. It is measured from the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS advanced. A traditional PR interval ranges from 0.12 to 0.20 seconds. Prolongation signifies a delay in AV nodal conduction, whereas shortening suggests accelerated conduction.
-
QRS advanced: This advanced represents ventricular depolarization, {the electrical} activation of the ventricles. It is sometimes composed of three deflections: a downward deflection (Q wave), an upward deflection (R wave), and a downward deflection (S wave). The QRS advanced is normally lower than 0.12 seconds in period. Widening of the QRS advanced suggests a delay in ventricular conduction, doubtlessly resulting from bundle department blocks or different conduction abnormalities.
-
ST phase: This isoelectric (flat) phase represents the early section of ventricular repolarization, {the electrical} restoration of the ventricles. It is essential in figuring out ischemia or infarction, as elevation or melancholy of the ST phase can point out myocardial damage. In a traditional ECG, the ST phase is normally isoelectric, inside ± 1 mm of the baseline.
-
T wave: This rounded wave represents ventricular repolarization, the ultimate section of ventricular electrical restoration. It sometimes follows the identical route as the primary QRS deflection in most leads. Adjustments within the T wave morphology (form and amplitude) can replicate electrolyte imbalances, myocardial ischemia, or different cardiac situations.
-
QT interval: This interval represents the entire period of ventricular depolarization and repolarization. It is measured from the start of the QRS advanced to the top of the T wave. The QT interval is influenced by coronary heart charge and varies with age and intercourse. Prolongation of the QT interval can improve the chance of torsades de pointes, a doubtlessly life-threatening arrhythmia.
-
U wave: A small, rounded wave that typically follows the T wave. Its actual physiological significance remains to be debated, nevertheless it’s considered associated to repolarization of the Purkinje fibers or papillary muscular tissues. Distinguished U waves could be related to electrolyte imbalances (hypokalemia) or bradycardia.
III. Deciphering a Regular ECG: A Step-by-Step Method
Analyzing an ECG entails a scientific method:
-
Coronary heart Price: The center charge could be simply calculated from the ECG. A number of strategies exist, together with counting the variety of QRS complexes in a 6-second strip and multiplying by 10, or utilizing specialised ECG software program. A traditional resting coronary heart charge sometimes ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
-
Rhythm: Assess the regularity of the center rhythm. Is the gap between consecutive R waves constant? Irregularity can point out numerous arrhythmias. In a traditional sinus rhythm, the P waves are upright, constant, and precede every QRS advanced.
-
P wave evaluation: Study the P waves for his or her morphology, amplitude, and period. Are they upright and constant in leads I, II, and aVF? Are they current earlier than every QRS advanced? Irregular P waves can recommend atrial enlargement or different atrial abnormalities.
-
PR interval measurement: Measure the PR interval to evaluate AV nodal conduction. A traditional PR interval is between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds.
-
QRS advanced evaluation: Measure the period of the QRS advanced. A traditional QRS advanced is lower than 0.12 seconds. Widening signifies a delay in ventricular conduction. Study the amplitude and morphology of the QRS advanced in several leads.
-
ST phase and T wave evaluation: Assess the ST phase for elevation or melancholy. Analyze the T wave for its morphology and amplitude. Vital deviations can point out ischemia, infarction, or electrolyte imbalances.
-
QT interval measurement: Measure the QT interval and assess for prolongation. Prolongation can improve the chance of torsades de pointes.
IV. Variations in Regular ECGs
It is essential to notice that "regular" ECG findings can range barely relying on components resembling age, intercourse, physique habitus, and athletic coaching. For instance, athletes usually have decrease resting coronary heart charges and will exhibit delicate adjustments in ECG morphology. Moreover, sure physiological states, resembling being pregnant, can even affect ECG readings. Due to this fact, interpretation ought to at all times contemplate the person’s scientific context.
V. Conclusion:
The ECG stays an important device within the analysis and administration of cardiovascular illnesses. Understanding the parts of a traditional ECG, their physiological significance, and a scientific method to interpretation is important for healthcare professionals. Whereas this text offers a complete overview, it is essential to keep in mind that ECG interpretation requires expertise and scientific judgment. This data shouldn’t be used for self-diagnosis, and any considerations relating to coronary heart well being needs to be addressed with a professional healthcare skilled. They will present a correct interpretation of your ECG together with your medical historical past and bodily examination, making certain correct analysis and applicable administration. Steady studying and apply are obligatory for mastering the artwork of ECG interpretation.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Decoding the ECG: A Complete Information to Regular Readings. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!