Decoding the World Gasoline Value Chart: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook
Associated Articles: Decoding the World Gasoline Value Chart: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the World Gasoline Value Chart: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the World Gasoline Value Chart: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook

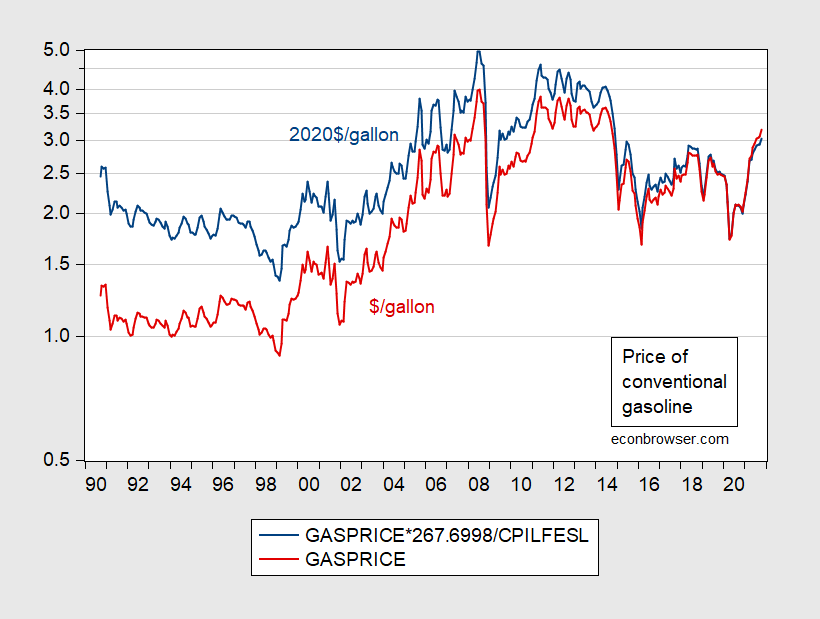
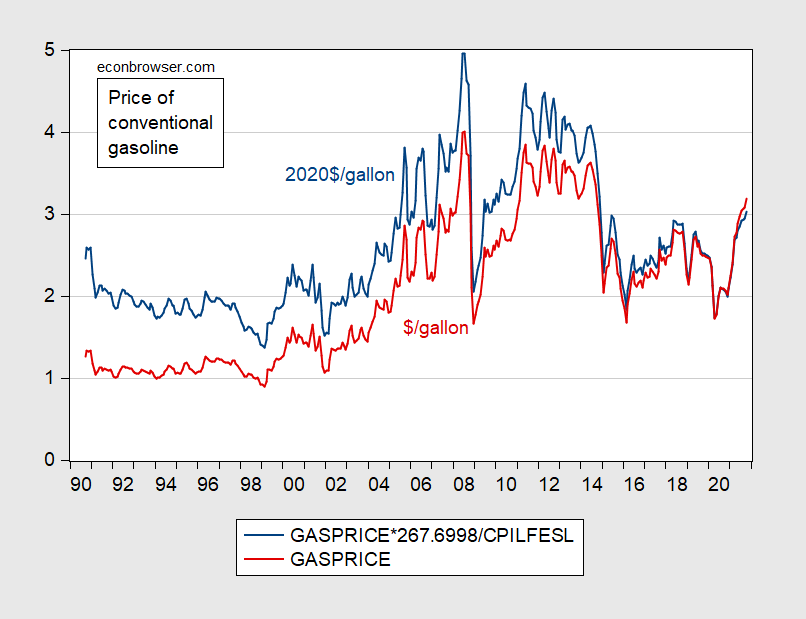
The worldwide gasoline value chart is a posh tapestry woven from threads of geopolitical occasions, financial fluctuations, technological developments, and environmental considerations. Over the previous twenty years, this chart has exhibited dramatic swings, reflecting a risky market prone to a large number of interconnected elements. Understanding these elements is essential for customers, governments, and companies alike, as gasoline stays a cornerstone of the worldwide financial system and a big driver of inflation and client spending.
A Historic Overview: From Stability to Volatility
The early 2000s witnessed a comparatively steady interval in world gasoline costs. Whereas fluctuations occurred, they had been typically contained inside a predictable vary. This stability was partly attributed to comparatively steady oil manufacturing ranges, constant world financial development, and a much less pronounced consciousness of local weather change’s influence on vitality coverage. Nevertheless, the seeds of future volatility had been already sown.
The mid-2000s marked a big turning level. A number of elements converged to drive costs sharply upwards. The speedy financial development of China and India fueled a surge in world oil demand, outpacing provide will increase. Concurrently, geopolitical instability within the Center East, a significant oil-producing area, created uncertainty and provide disruptions. Hurricane Katrina in 2005 additional exacerbated the state of affairs, damaging essential oil refining infrastructure in the US and driving up costs globally.
The following years noticed a interval of utmost value volatility. Costs soared to report highs, impacting transportation prices, inflation, and client spending worldwide. Governments responded with a spread of insurance policies, from strategic petroleum reserves releases to gas effectivity requirements, making an attempt to mitigate the influence on their economies and residents.
The worldwide monetary disaster of 2008 introduced a brief reprieve, as diminished financial exercise led to decrease oil demand and consequently, decrease costs. Nevertheless, this was short-lived. As the worldwide financial system recovered, so did oil demand, and costs started to climb once more.
The interval from 2010 to 2014 noticed a mixture of upward and downward tendencies, influenced by elements similar to the continued restoration from the monetary disaster, the shale oil increase in the US, and fluctuating geopolitical tensions. The shale oil revolution, specifically, considerably impacted the worldwide oil market, rising provide and exerting downward strain on costs.
The dramatic plunge in oil costs in 2014 and 2015, pushed largely by elevated US shale oil manufacturing and diminished OPEC manufacturing quotas, offered a distinct set of challenges. Whereas customers benefited from decrease gasoline costs, oil-producing nations confronted financial hardship, resulting in renewed geopolitical complexities.
The next years witnessed a gradual value restoration, punctuated by occasional spikes resulting from elements similar to OPEC manufacturing cuts, geopolitical occasions (e.g., the Iran nuclear deal and subsequent sanctions), and surprising provide disruptions.
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused an unprecedented collapse in world oil demand as lockdowns and journey restrictions severely curtailed financial exercise. This led to a dramatic fall in oil and gasoline costs, even briefly turning unfavorable in some markets. Nevertheless, the next financial restoration, coupled with OPEC+ manufacturing cuts, led to a pointy rebound in costs, reaching new highs in 2022. The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 additional exacerbated the state of affairs, creating vital provide disruptions and driving costs to unprecedented ranges.
Key Elements Influencing World Gasoline Costs
Analyzing the worldwide gasoline value chart requires understanding the interaction of a number of key elements:
-
Crude Oil Costs: The value of crude oil is essentially the most vital determinant of gasoline costs. Crude oil is the uncooked materials from which gasoline is refined, and its value fluctuations instantly influence the ultimate price on the pump.
-
Refining Prices: The method of refining crude oil into gasoline includes vital prices, together with vitality, labor, and capital funding. These prices can range relying on technological developments, environmental rules, and the geographic location of refineries.
-
Geopolitical Occasions: Political instability in main oil-producing areas, sanctions, wars, and different geopolitical occasions can considerably disrupt oil provide and drive up costs. The Center East, specifically, stays a essential area influencing world oil markets.
-
Financial Progress: World financial development considerably impacts oil demand. Sturdy financial development usually results in elevated vitality consumption and better oil costs, whereas financial downturns can result in decrease demand and decrease costs.
-
Provide and Demand: The elemental ideas of provide and demand govern the oil market. A scarcity of provide relative to demand will push costs increased, whereas an oversupply will result in decrease costs.
-
Foreign money Fluctuations: The worth of the US greenback, by which oil is primarily traded, considerably impacts oil costs. A stronger greenback makes oil costlier for patrons utilizing different currencies, whereas a weaker greenback has the alternative impact.
-
Authorities Laws and Insurance policies: Authorities insurance policies, together with taxes, subsidies, environmental rules, and strategic reserves administration, can affect gasoline costs. Carbon taxes, for instance, can enhance the worth of gasoline, whereas subsidies can decrease it.
-
Technological Developments: Technological developments in oil extraction, refining, and different vitality sources can influence oil provide and demand, influencing costs. The shale oil revolution is a primary instance of how technological developments can considerably alter the market dynamics.
The Way forward for World Gasoline Costs: Uncertainties and Predictions
Predicting future gasoline costs is inherently difficult because of the multitude of interconnected elements at play. Nevertheless, a number of tendencies and potential eventualities might be thought of:
-
The Transition to Renewable Vitality: The worldwide shift in direction of renewable vitality sources, similar to photo voltaic, wind, and hydroelectric energy, is anticipated to progressively scale back the demand for gasoline over the long run. Nevertheless, the tempo of this transition stays unsure and can considerably affect future gasoline costs.
-
Electrical Automobiles: The rising adoption of electrical automobiles (EVs) is one other issue that might considerably influence gasoline demand. As EVs grow to be extra inexpensive and accessible, their market share is anticipated to extend, doubtlessly resulting in a decline in gasoline consumption.
-
Geopolitical Dangers: Geopolitical instability stays a big wildcard that might considerably influence future oil and gasoline costs. Conflicts, sanctions, and provide disruptions in main oil-producing areas might result in value spikes.
-
Technological Developments in Oil Manufacturing: Continued developments in oil extraction applied sciences, similar to enhanced oil restoration methods, might enhance oil provide and exert downward strain on costs.
-
Financial Progress and World Demand: The longer term trajectory of worldwide financial development will considerably affect oil demand and, consequently, gasoline costs. Sturdy financial development in creating nations might result in elevated oil consumption, whereas a worldwide financial slowdown might scale back demand.
Conclusion:
The worldwide gasoline value chart is a dynamic reflection of a posh and interconnected world. Understanding the historic tendencies, key influencing elements, and potential future eventualities is essential for navigating the uncertainties of this risky market. Whereas the long-term outlook suggests a possible decline in gasoline demand because of the transition to renewable vitality and the adoption of EVs, short-term value fluctuations will proceed to be influenced by a large number of things, together with geopolitical occasions, financial development, and technological developments. Cautious monitoring of those elements is important for each customers and policymakers to successfully handle the impacts of gasoline value volatility on the worldwide financial system.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Decoding the World Gasoline Value Chart: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!