Decoding the Grid: A Complete Information to Graph Paper Sizes and Their Functions
Associated Articles: Decoding the Grid: A Complete Information to Graph Paper Sizes and Their Functions
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Grid: A Complete Information to Graph Paper Sizes and Their Functions. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Grid: A Complete Information to Graph Paper Sizes and Their Functions

Graph paper, with its exact grid of traces, is a ubiquitous instrument for an enormous array of purposes, from engineering and structure to artwork and arithmetic. Nonetheless, the seemingly easy world of graph paper is surprisingly nuanced, with quite a lot of sizes and codecs catering to various wants. Understanding these variations is essential for choosing the precise paper to your particular job. This text offers a complete information to graph paper sizes, exploring their dimensions, widespread makes use of, and the way to decide on one of the best match to your mission.
Normal Sizes and Their Variations:
Whereas there is no single, universally standardized system for graph paper sizes, sure dimensions have change into prevalent throughout completely different areas and industries. These are sometimes based mostly on widespread paper sizes like A-series (ISO 216) or US letter/authorized sizes, with the grid superimposed. Nonetheless, the grid itself introduces one other layer of variation, in regards to the spacing between traces (e.g., 5mm, 2mm, 1mm, and so on.) and the kind of grid (sq., isometric, polar, and so on.).
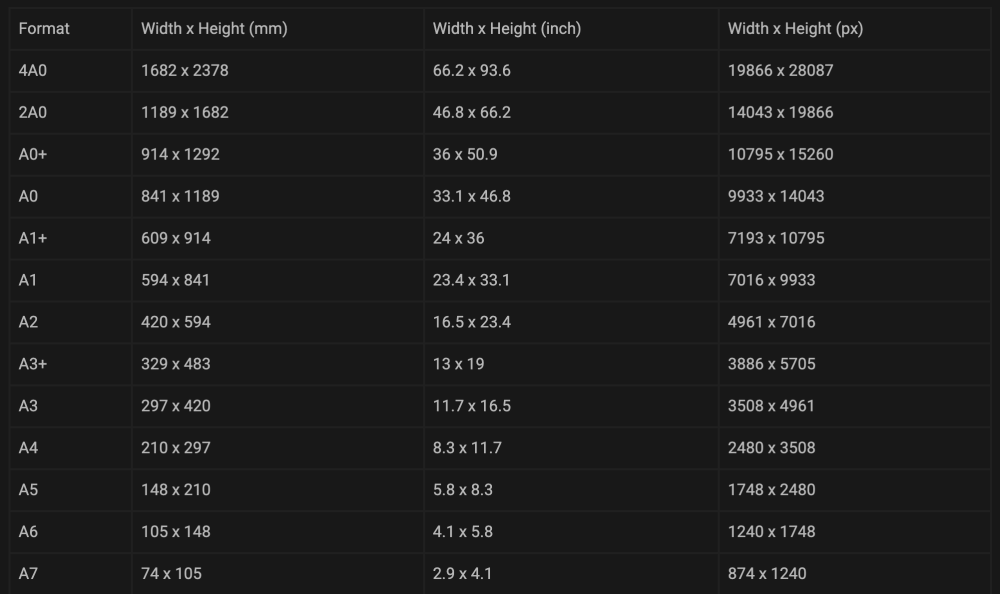
1. A-Sequence Graph Paper:
The A-series, a globally acknowledged paper measurement normal, typically varieties the premise for graph paper dimensions. A4 (210 x 297 mm) is the most typical measurement, steadily used for on a regular basis duties, faculty assignments, and smaller engineering drawings. Bigger sizes like A3 (297 x 420 mm) and A2 (420 x 594 mm) are employed for bigger drawings and shows. Inside every A-size, the grid spacing can fluctuate significantly. For example, you would possibly discover A4 graph paper with a 5mm grid, a 2mm grid, or perhaps a 1mm grid, relying on the meant use.
2. US Letter and Authorized Measurement Graph Paper:
In america and another international locations, graph paper is commonly based mostly on US Letter (8.5 x 11 inches) and Authorized (8.5 x 14 inches) sizes. Much like A-series, the grid spacing varies, starting from giant grids for sketching to very nice grids for detailed technical drawings. The selection between Letter and Authorized measurement will depend on the required drawing space and the dimensions of the mission. Authorized measurement offers extra vertical area, making it appropriate for longer drawings or paperwork.
3. Customized Sizes and Specialised Codecs:
Past the usual sizes, custom-sized graph paper is available, typically tailor-made to particular industries or purposes. These can vary from giant roll codecs utilized in architectural drafting to smaller, specialised sizes for particular duties. Moreover, the grid itself will be personalized. Isometric graph paper, as an illustration, includes a grid of equilateral triangles, perfect for three-dimensional drawings. Polar graph paper makes use of concentric circles and radial traces, appropriate for plotting polar coordinates. Logarithmic graph paper makes use of logarithmic scales on one or each axes, helpful for visualizing exponential relationships.
Grid Spacing and its Significance:
The spacing between the traces on graph paper is a important issue influencing its suitability for various purposes. Bigger grid spacing (e.g., 5mm or 10mm) is good for:
- Sketching and brainstorming: The bigger areas enable for freehand drawing and fast sketching of concepts with out being constrained by overly nice traces.
- Giant-scale drawings: Bigger grids are appropriate for drawings the place precision is not paramount, however a transparent visible illustration of the general format is critical.
- Early-stage design work: The broader traces enable for simple revisions and modifications throughout the preliminary phases of design.
Smaller grid spacing (e.g., 1mm, 2mm) is healthier fitted to:
- Exact technical drawings: The finer grid permits for correct measurements and detailed illustration of elements.
- Engineering and architectural drawings: These fields require excessive precision, and a nice grid facilitates correct scaling and dimensioning.
- Mathematical graphing: Smaller grids are crucial for plotting correct graphs and diagrams with exact information factors.
- Detailed illustrations: Effective grids assist create intricate illustrations with excessive ranges of element.
Selecting the Proper Graph Paper:
Deciding on the suitable graph paper requires cautious consideration of a number of elements:
- Supposed use: What’s going to you be utilizing the graph paper for? Sketching, technical drawing, mathematical graphing, or one thing else?
- Required precision: How a lot accuracy is required in your drawings or graphs? Will a bigger grid suffice, or do you want a nice grid for exact measurements?
- Paper measurement: What measurement paper will greatest accommodate your mission? Will a normal A4 or US Letter measurement be adequate, or do you want a bigger format?
- Grid kind: Do you want a normal sq. grid, or a specialised grid like isometric or polar?
- Paper high quality: The paper’s thickness, weight, and floor texture will affect the drawing expertise and the longevity of your work. Take into account whether or not you want a paper that may face up to erasing or heavy ink utilization.
Functions Throughout Various Fields:
Graph paper’s versatility extends throughout a variety of disciplines:
- Engineering: Used for creating detailed technical drawings, schematics, and diagrams.
- Structure: Important for creating ground plans, elevations, and web site plans.
- Arithmetic: Used for plotting graphs, charts, and diagrams to visualise mathematical features and information.
- Science: Used for recording information, creating graphs, and visualizing experimental outcomes.
- Artwork and Design: Used for creating sketches, illustrations, and patterns.
- Stitching and Quilting: Used for creating patterns and diagrams.
- Recreation Design: Used for mapping sport worlds and designing sport mechanics.
- Training: Utilized in colleges and universities for varied academic functions.
Digital Alternate options:
Whereas bodily graph paper stays a well-liked alternative, digital alternate options have emerged, providing flexibility and comfort. Quite a few software program purposes and on-line instruments present digital graph paper with customizable grids, sizes, and options. These digital choices enable for simple enhancing, sharing, and collaboration, making them engaging alternate options for sure purposes. Nonetheless, the tactile expertise of working with bodily graph paper stays most popular by many.
Conclusion:
The world of graph paper is richer and extra various than its seemingly easy look suggests. Understanding the assorted sizes, grid spacings, and specialised codecs is essential for choosing the precise instrument for any given job. By fastidiously contemplating the elements outlined on this article, you possibly can select the proper graph paper to satisfy your particular wants, whether or not you are an engineer creating exact technical drawings, an artist sketching intricate designs, or a pupil plotting mathematical features. The fitting graph paper can considerably improve the accuracy, effectivity, and total high quality of your work.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the Grid: A Complete Information to Graph Paper Sizes and Their Functions. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!