Decoding the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts
Associated Articles: Decoding the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts

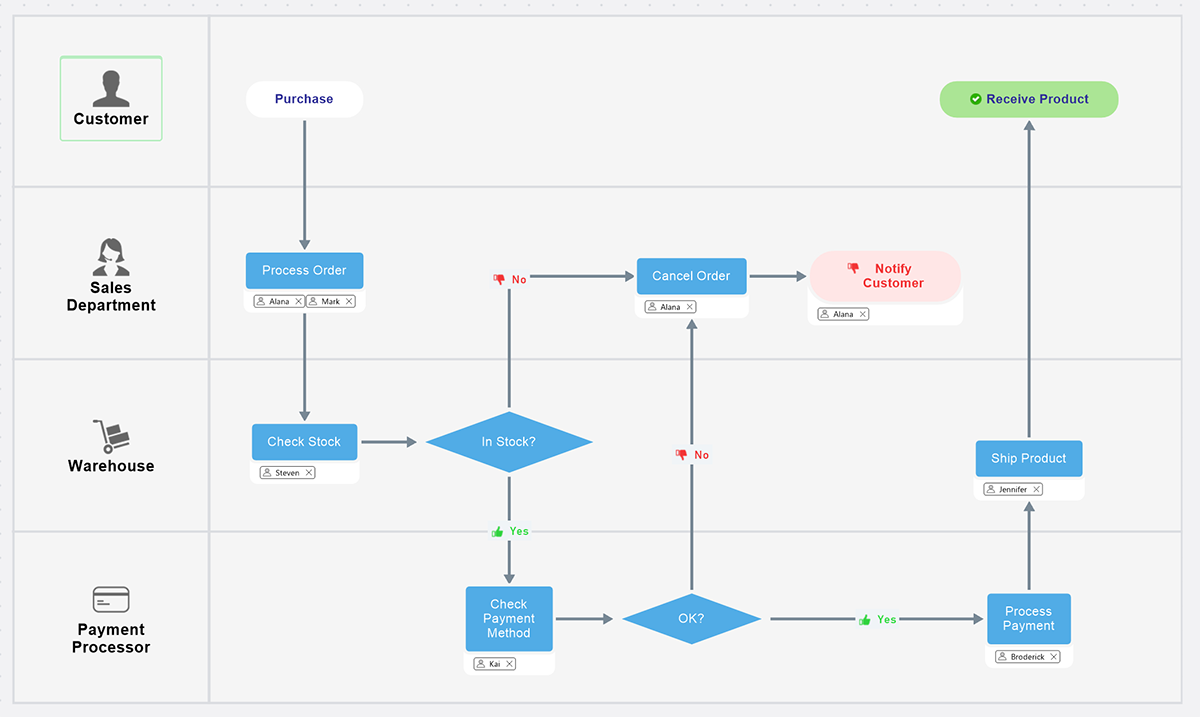
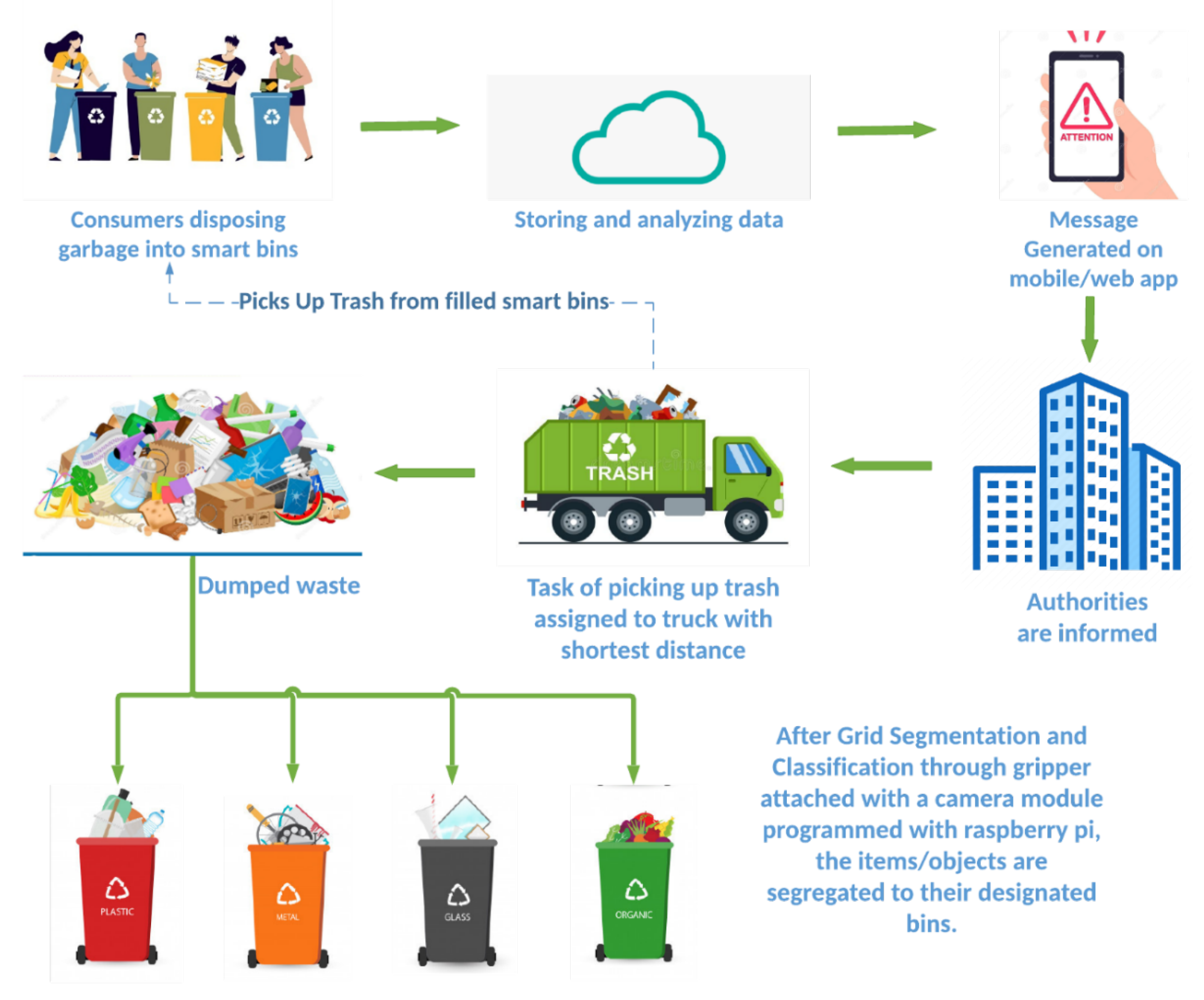
Stable waste administration (SWM) is a multifaceted problem going through communities worldwide. From the discarded banana peel to the discarded equipment, the sheer quantity and numerous nature of waste necessitate a well-defined and environment friendly system for its assortment, processing, and disposal. Understanding this technique is essential for efficient environmental safety and public well being. A strong waste administration flowchart serves as a visible roadmap, outlining the intricate journey of waste from its level of era to its ultimate vacation spot. This text delves into the complexities of SWM flowcharts, exploring differing types, their elements, and their significance in reaching sustainable waste administration practices.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Elements of a SWM Flowchart
A typical SWM flowchart depicts the sequential steps concerned in managing waste. Whereas the particular steps may range relying on the context (e.g., residential, business, industrial), a number of core elements are constantly current:
-
Waste Technology: That is the start line, representing the origin of waste from varied sources like households, companies, industries, and building websites. The flowchart may additional categorize waste based mostly on its sort (natural, recyclable, hazardous, and many others.).
-
Waste Assortment: This stage includes the gathering of waste from its supply. It contains varied strategies like curbside assortment, communal bins, door-to-door assortment, and specialised assortment for hazardous waste. The flowchart would illustrate the completely different assortment routes, frequencies, and varieties of automobiles used.
-
Waste Transportation: As soon as collected, waste must be transported to processing services or disposal websites. The flowchart would present the transportation routes, the varieties of automobiles used (vans, containers), and the space lined. This stage is essential for minimizing environmental influence, contemplating gas consumption and potential spills.
-
Waste Processing: This can be a essential step encompassing varied strategies aimed toward decreasing waste quantity and maximizing useful resource restoration. Frequent processing strategies embody:
- Recycling: Separating and processing recyclable supplies like paper, plastic, glass, and steel for reuse. The flowchart may element the sorting course of, materials restoration services (MRFs), and the end-users of recycled supplies.
- Composting: Decomposing natural waste (meals scraps, yard waste) right into a nutrient-rich soil modification. The flowchart would illustrate the composting strategies (e.g., in-vessel, windrow) and the end-use of compost.
- Incineration: Burning waste at excessive temperatures to cut back its quantity and generate power. The flowchart would element the incineration course of, emission management measures, and ash administration.
- Landfilling: The ultimate disposal methodology for non-recyclable and non-compostable waste. The flowchart would illustrate landfill design, leachate administration, and fuel assortment methods.
-
Waste Disposal: This stage represents the ultimate vacation spot of waste, whether or not it is a landfill, incineration ash disposal website, or a delegated space for handled compost. The flowchart ought to emphasize environmental safety measures at this stage.
-
Monitoring and Analysis: An important, typically ignored, element. The flowchart ought to incorporate suggestions loops to observe the effectivity of the system, establish bottlenecks, and observe environmental efficiency indicators (e.g., landfill fuel emissions, recycling charges).
Forms of SWM Flowcharts
The complexity of a SWM flowchart is dependent upon the size and scope of the system. A number of sorts exist:
-
Easy Flowcharts: These present a fundamental overview of the SWM course of, highlighting the primary phases with out delving into intricate particulars. They’re helpful for offering a basic understanding of the system.
-
Detailed Flowcharts: These present a complete illustration of the SWM course of, together with particular applied sciences, tools, and procedures used at every stage. They’re important for planning, implementation, and operational administration.
-
Sector-Particular Flowcharts: These give attention to a particular sector, like residential, business, or industrial waste administration, offering tailor-made representations of the method inside that sector.
-
Built-in Flowcharts: These embody your entire SWM system, together with completely different sectors and applied sciences, displaying the interconnections and interactions between varied elements. They’re essential for built-in waste administration methods.
-
Hierarchical Flowcharts: These use a hierarchical construction to characterize the completely different ranges of the SWM system, from the general technique all the way down to particular person operations. This strategy facilitates a transparent understanding of the system’s construction and decision-making processes.
The Significance of SWM Flowcharts
SWM flowcharts serve a number of important functions:
-
Visible Illustration: They supply a transparent and concise visible illustration of a fancy system, making it simpler to know for stakeholders with numerous backgrounds.
-
Course of Optimization: By figuring out bottlenecks and inefficiencies, flowcharts allow the optimization of the SWM course of, resulting in value financial savings and improved environmental efficiency.
-
Planning and Design: They’re important instruments for planning and designing new SWM methods or upgrading current ones. They assist make sure that all points of the system are thought of and built-in successfully.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Flowcharts facilitate communication and collaboration amongst stakeholders, together with authorities companies, waste administration corporations, and the general public.
-
Coaching and Training: They’re useful instruments for coaching and educating personnel concerned in SWM operations.
-
Efficiency Monitoring: They supply a framework for monitoring and evaluating the efficiency of the SWM system, enabling steady enchancment.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Flowcharts can assist guarantee compliance with related laws and requirements associated to waste administration.
Challenges and Future Instructions
Regardless of their significance, creating and implementing efficient SWM flowcharts face a number of challenges:
-
Knowledge Availability: Correct and dependable information on waste era, composition, and processing are essential for growing reasonable flowcharts. Knowledge gaps can hinder the effectiveness of the system.
-
Technological Developments: The fast tempo of technological developments in waste administration requires steady updating of flowcharts to mirror new applied sciences and processes.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Efficient implementation of SWM methods requires energetic participation from all stakeholders. Failure to have interaction stakeholders can result in resistance and implementation challenges.
-
Monetary Constraints: Enough funding is important for growing and implementing sturdy SWM methods. Monetary limitations can compromise the effectiveness of the system.
The way forward for SWM flowcharts lies in embracing digital applied sciences and incorporating information analytics. Good waste administration methods, utilizing sensors and IoT units, can present real-time information on waste era, assortment, and processing, enabling dynamic changes to the SWM course of. Integration of Geographic Info Programs (GIS) can additional improve the visualization and evaluation of spatial points of waste administration. Finally, the aim is to create sustainable and resilient SWM methods that reduce environmental influence and promote useful resource restoration. By way of cautious design, implementation, and steady enchancment, SWM flowcharts will play an important position in reaching this aim. By understanding the intricacies of those flowcharts, we will navigate the labyrinth of waste administration and pave the best way for a cleaner, more healthy future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!