Decoding the Snellen Chart: A Deep Dive into Visible Acuity at 20 Ft
Associated Articles: Decoding the Snellen Chart: A Deep Dive into Visible Acuity at 20 Ft
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Snellen Chart: A Deep Dive into Visible Acuity at 20 Ft. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Snellen Chart: A Deep Dive into Visible Acuity at 20 Ft

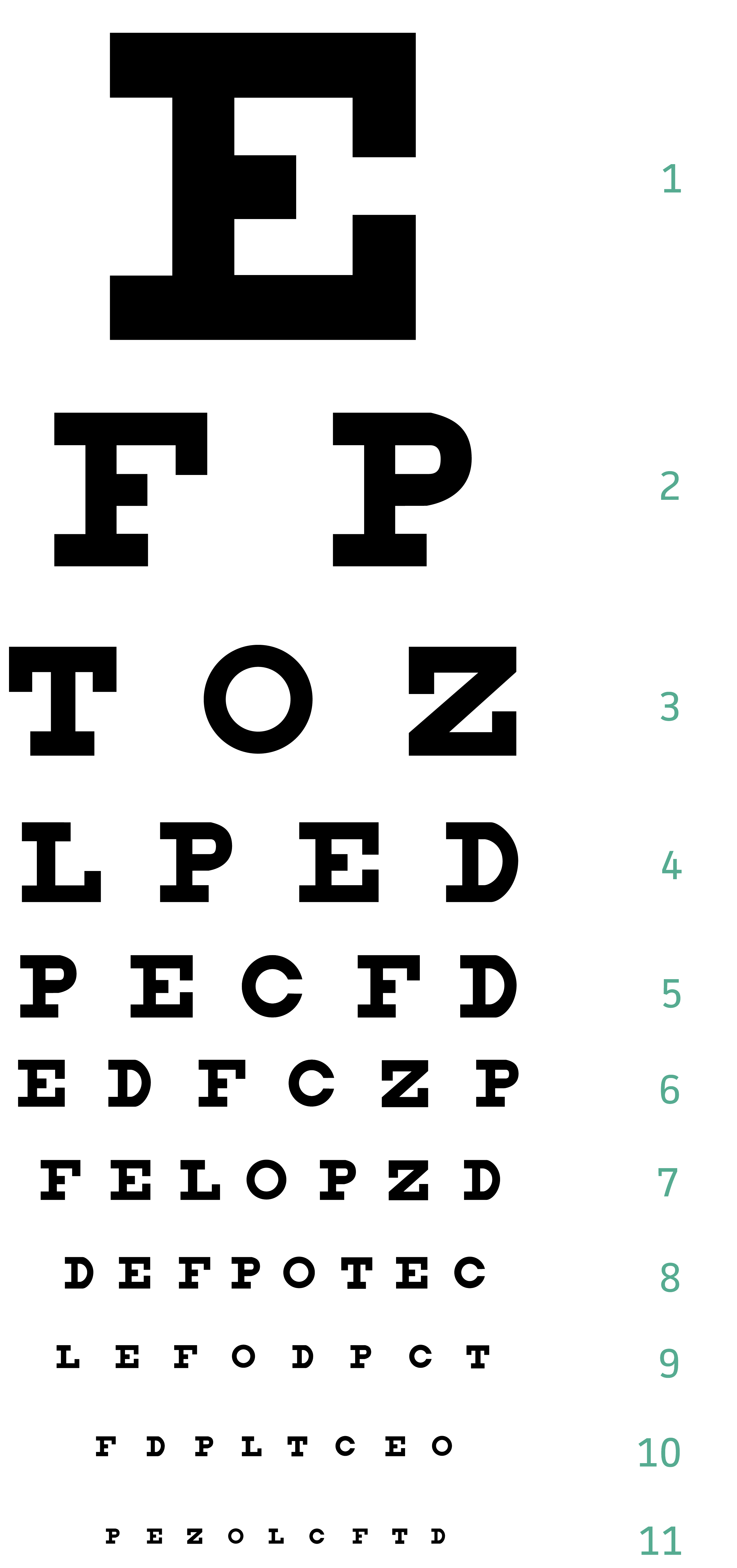
The Snellen chart, with its seemingly easy association of letters, numbers, and symbols, is a cornerstone of ophthalmology. For over a century, this iconic chart, considered from a standardized 20-foot distance, has served as the first software for assessing visible acuity, a vital measure of somebody’s capacity to see clearly. This text will delve into the intricacies of the Snellen chart at 20 ft, exploring its historical past, methodology, interpretation, limitations, and its ongoing relevance in fashionable optometry.
A Temporary Historical past of the Snellen Chart:
Hermann Snellen, a Dutch ophthalmologist, developed the chart in 1862. His progressive method addressed the necessity for a standardized and quantifiable methodology to evaluate visible acuity, transferring away from subjective descriptions of imaginative and prescient. Snellen’s genius lay in his understanding of visible angle – the angle subtended by an object on the eye. He designed the chart so that every letter or image subtended a visible angle of 5 minutes of arc on the prescribed viewing distance (initially 20 meters, or roughly 66 ft, later standardized to twenty ft). The person parts of every letter additional subtended one minute of arc, guaranteeing a constant stage of element for correct evaluation.
The unique Snellen chart used quite a lot of symbols, however the fashionable model predominantly options uppercase letters, chosen for his or her familiarity and relative ease of recognition. The dimensions of the letters progressively decreases down the chart, representing completely different ranges of visible acuity.
Methodology of the 20-Foot Snellen Take a look at:
The 20-foot Snellen take a look at is remarkably easy in its execution, but requires precision to make sure correct outcomes. The process sometimes entails the next steps:
-
Standardized Distance: The affected person stands 20 ft away from the chart, guaranteeing correct distance is essential for correct outcomes. A marked line on the ground typically aids in sustaining this distance.
-
One Eye at a Time: The take a look at is performed monocularly (one eye at a time), with the opposite eye lined to stop binocular imaginative and prescient from influencing the outcomes. This enables for the impartial evaluation of every eye’s visible acuity.
-
Occlusion: An acceptable occluder, reminiscent of an opaque card or eye patch, ought to be used to successfully cowl the non-tested eye, stopping peeking.
-
Studying the Chart: The affected person is instructed to learn the letters aloud, ranging from the highest of the chart and progressing downwards. The smallest line the affected person can precisely learn is recorded.
-
Recording the Outcomes: The outcomes are expressed as a fraction, for example, 20/20, 20/40, or 20/200. The numerator (20) represents the testing distance (20 ft), whereas the denominator represents the space at which an individual with regular imaginative and prescient may learn the identical line.
Decoding the Snellen Fraction:
-
20/20: This means regular visible acuity. The affected person can see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 20 ft.
-
20/40: This implies the affected person can see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 40 ft. This means a reasonable stage of visible impairment.
-
20/200: This represents a big visible impairment. The affected person can see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 200 ft. That is typically thought of legally blind.
-
Numerator Higher Than Denominator (e.g., 20/15): This means better-than-average visible acuity. The affected person can see at 20 ft what an individual with regular imaginative and prescient can see at 15 ft.
Past the Commonplace Chart: Variations and Concerns:
Whereas the usual Snellen chart is extensively used, variations exist to cater to particular wants:
-
Youngsters’s Charts: Charts that includes photos or symbols as an alternative of letters are used for younger kids who can’t but learn. The Allen chart is a standard instance.
-
Charts for Low Imaginative and prescient: For people with extreme visible impairment, bigger charts or specialised near-vision charts could also be employed.
-
Digital Charts: Digital Snellen charts provide benefits reminiscent of adjustable brightness and font dimension, making them extra adaptable to particular person wants.
Limitations of the Snellen Chart:
Regardless of its widespread use, the Snellen chart has limitations:
-
Restricted Evaluation: It primarily assesses visible acuity, neglecting different essential elements of imaginative and prescient, reminiscent of distinction sensitivity, coloration imaginative and prescient, and peripheral imaginative and prescient.
-
Subjectivity: The take a look at depends on the affected person’s self-reporting, which will be influenced by components like fatigue, nervousness, or malingering.
-
Cultural Bias: Using letters would possibly drawback people unfamiliar with the Roman alphabet.
-
Doesn’t assess visible area: The Snellen chart solely assesses central imaginative and prescient, neglecting peripheral imaginative and prescient which can also be vital for protected navigation and every day actions.
The Snellen Chart within the Context of Trendy Optometry:
Whereas the Snellen chart stays a elementary software, fashionable optometry makes use of a extra complete method to visible evaluation. The Snellen chart is usually complemented by different exams, together with:
-
Refraction: Figuring out the refractive error (myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism) utilizing phoropters and retinoscopy.
-
Automated Perimetry: Assessing the visible area, figuring out any blind spots or peripheral imaginative and prescient deficits.
-
Distinction Sensitivity Testing: Measuring the power to tell apart objects with various ranges of distinction.
-
Colour Imaginative and prescient Testing: Evaluating the power to understand colours precisely.
Conclusion:
The Snellen chart, considered from 20 ft, represents a big milestone within the historical past of ophthalmology. Its simplicity and standardization have made it an indispensable software for assessing visible acuity for over a century. Nevertheless, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations and perceive that it kinds just one part of a complete eye examination. Trendy optometry incorporates a multifaceted method, using the Snellen chart alongside different superior strategies to offer an entire and correct evaluation of a affected person’s visible well being. The 20/20 imaginative and prescient commonplace, whereas a handy benchmark, is just one side of general visible operate, and sustaining good eye well being requires common complete eye examinations past merely attaining this particular measurement. Common eye exams, incorporating the Snellen chart and different diagnostic instruments, are very important for early detection and administration of eye circumstances, guaranteeing optimum imaginative and prescient all through life.





/silver-ballpoint-pen-pointing-to-letter-in-eyesight-check-table-526850744-5a9745bf1d640400379bb245.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into Decoding the Snellen Chart: A Deep Dive into Visible Acuity at 20 Ft. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!