Decoding the Energy: A Complete Information to Fastener Grade Charts
Associated Articles: Decoding the Energy: A Complete Information to Fastener Grade Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Energy: A Complete Information to Fastener Grade Charts. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Energy: A Complete Information to Fastener Grade Charts
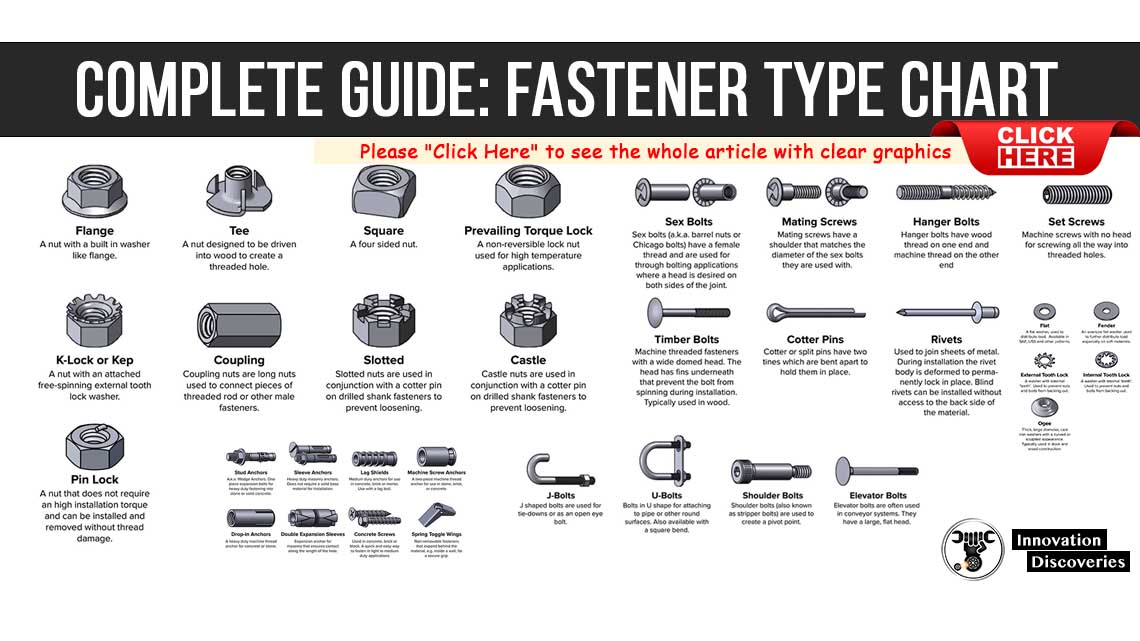
Fasteners, these seemingly insignificant items of {hardware} – bolts, screws, nuts, washers – are the spine of numerous constructions and machines. Their seemingly easy perform belies a posh world of fabric science, manufacturing processes, and efficiency specs. Understanding fastener grade charts is essential for engineers, contractors, and anybody concerned in choosing {hardware} for essential functions. A improper alternative can result in catastrophic failure, jeopardizing security and inflicting important monetary losses. This text offers a complete overview of fastener grade charts, explaining their significance, deciphering their markings, and highlighting the essential variations between varied grades.
The Significance of Fastener Grades:
Fastener grades are standardized classifications that outline the fabric properties and tensile energy of a fastener. Tensile energy, the utmost stress a fabric can stand up to earlier than breaking underneath rigidity, is a essential parameter in figuring out a fastener’s suitability for a selected utility. Increased grade fasteners possess superior tensile energy, yield energy (the stress at which the fabric begins to deform completely), and fatigue resistance (skill to resist repeated stress cycles). These properties straight affect the fastener’s skill to reliably safe elements underneath varied load circumstances.
Choosing the suitable grade is paramount for guaranteeing structural integrity and security. Utilizing a lower-grade fastener than required can result in untimely failure, probably leading to:
- Structural collapse: In buildings, bridges, and different essential constructions, insufficiently sturdy fasteners can result in catastrophic failures with devastating penalties.
- Tools malfunction: In equipment and automobiles, fastener failure could cause malfunction, downtime, and potential damage.
- Product recollects: Utilizing substandard fasteners can lead to product recollects, resulting in important monetary losses and reputational harm.
- Security hazards: Failure of fasteners in safety-critical functions can straight result in damage and even dying.
Understanding Fastener Grade Markings:
Fastener grade markings fluctuate relying on the fabric and the related commonplace (e.g., SAE, ISO, ASTM). These markings are sometimes stamped or etched onto the fastener’s head and supply important details about its properties. Let’s discover some widespread marking programs:
1. SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Grades:
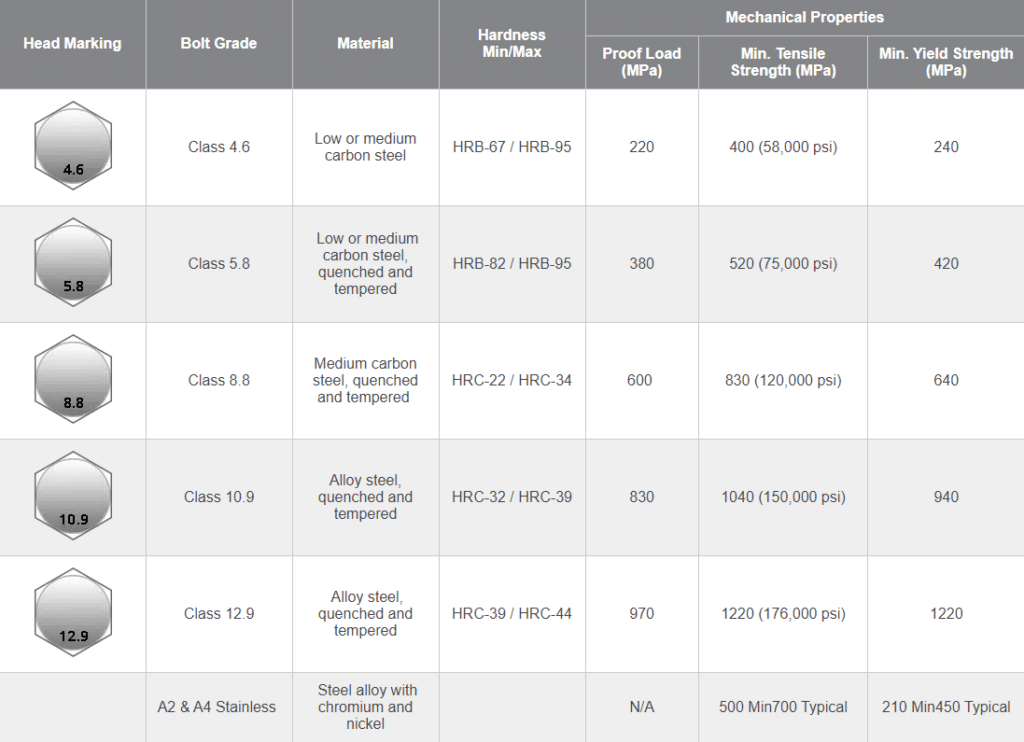
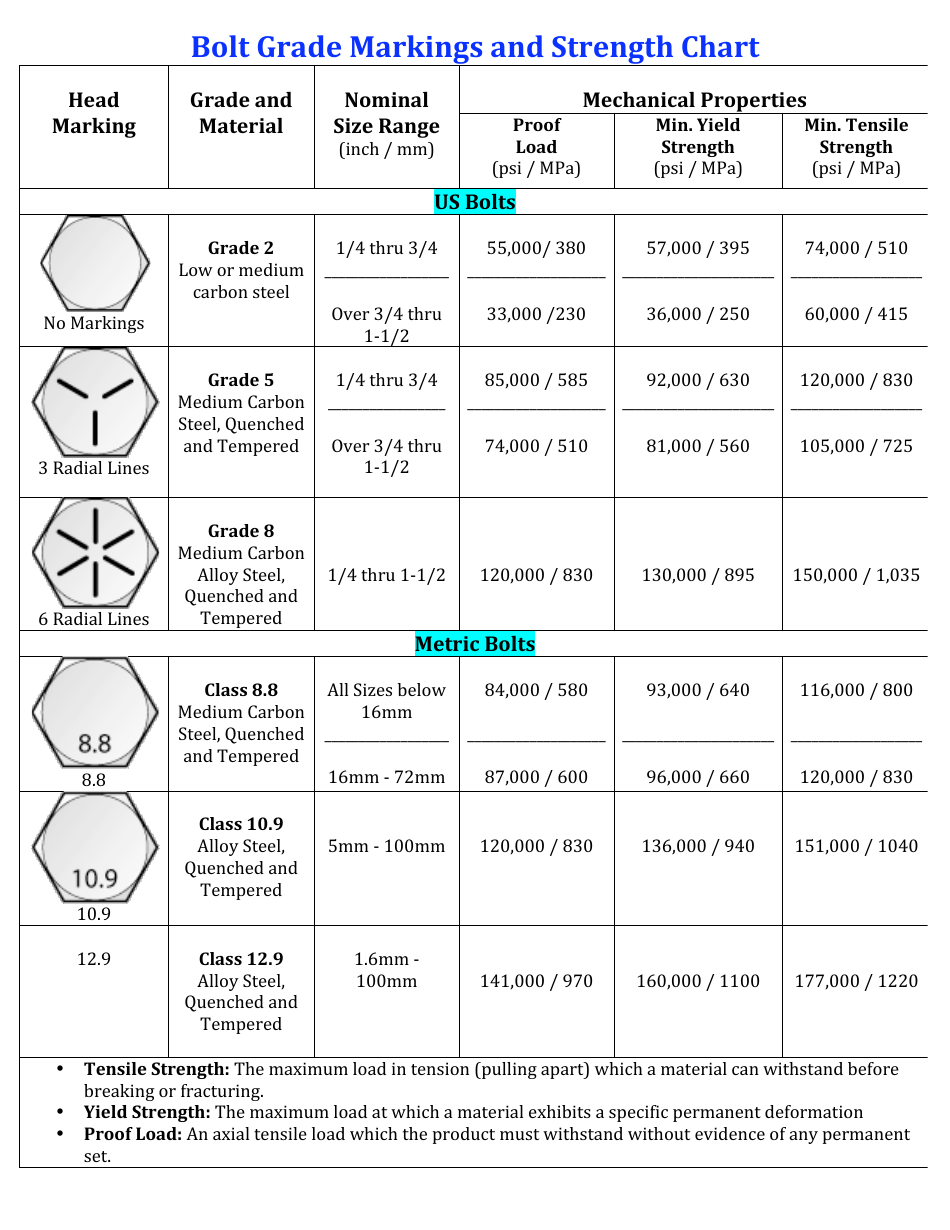
SAE grades are generally used for metal bolts and screws in automotive and mechanical functions. They’re sometimes recognized by a numerical grade designation adopted by a letter (e.g., 5, 8, 10). Increased numbers point out larger tensile energy. This is a quick overview:
- Grade 2: Low-strength fasteners, appropriate for low-stress functions.
- Grade 5: Medium-strength fasteners, broadly used basically functions.
- Grade 8: Excessive-strength fasteners, appropriate for demanding functions requiring larger tensile energy and fatigue resistance.
- Grade 10: Additional-high-strength fasteners, designed for very high-stress functions. These fasteners usually have a singular marking, usually a "10.9" marking indicating their metric equal.
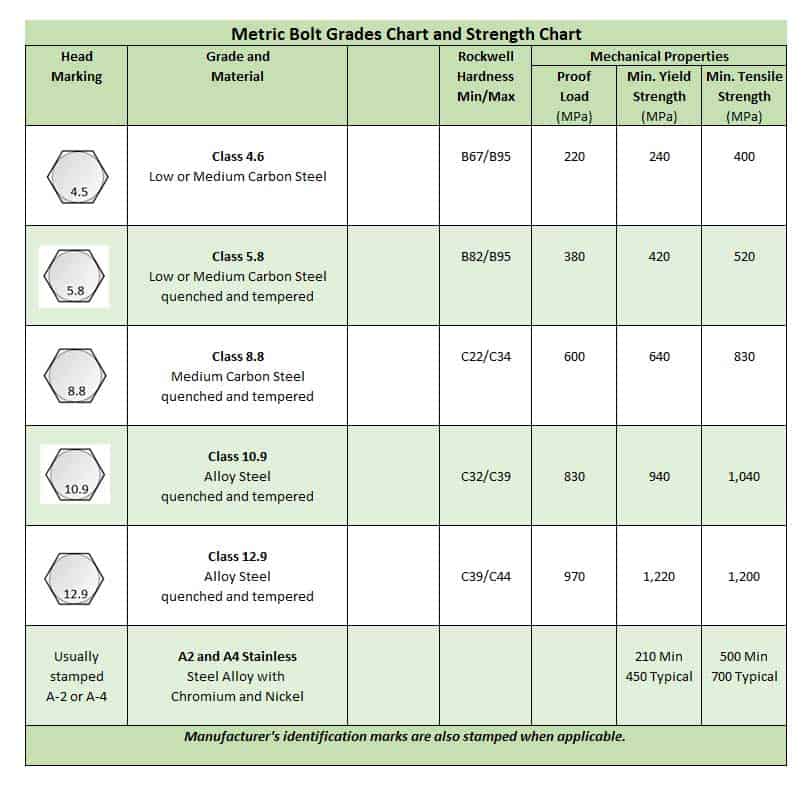
2. ISO (Worldwide Group for Standardization) Grades:
ISO grades are internationally acknowledged and broadly used for metric fasteners. They’re represented by a three-digit quantity (e.g., 4.6, 5.8, 8.8, 10.9). The primary digit represents the tensile energy in a whole lot of megapascals (MPa), whereas the second digit represents the yield energy as a share of the tensile energy. For instance:
- 4.6: Decrease-strength fastener.
- 5.8: Medium-strength fastener.
- 8.8: Excessive-strength fastener.
- 10.9: Additional-high-strength fastener, equal to SAE Grade 10. This grade is often utilized in high-stress structural functions.
3. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Supplies) Grades:
ASTM grades are used for varied supplies, together with metal, stainless-steel, and different alloys. The precise marking system varies relying on the fabric and utility. As an illustration, ASTM A325 and A490 are widespread grades for high-strength metal bolts utilized in structural functions.
4. Materials Designations:
Past the grade markings, fasteners usually have markings indicating the fabric composition. Frequent materials designations embrace:
- Metal: Varied grades of metal are used, with properties various relying on the alloying components and warmth remedy.
- Stainless Metal: Affords superior corrosion resistance in comparison with carbon metal. Completely different grades of stainless-steel exist, every with various energy and corrosion resistance properties.
- Aluminum: Light-weight and corrosion-resistant, however usually decrease in energy than metal.
- Brass: Affords good corrosion resistance and machinability.
- Different Alloys: Varied different alloys are used for particular functions, providing distinctive properties like excessive temperature resistance or enhanced energy.
Deciphering the Grade Chart: A Sensible Instance
Let’s think about a sensible situation. An engineer is designing a bridge and wishes to pick out bolts for connecting structural members. The design calculations point out a required tensile energy of 1200 MPa. Referring to a fastener grade chart, the engineer would search for a grade that meets or exceeds this requirement. A ten.9 grade bolt (with a tensile energy of 1000 MPa) would probably be inadequate. They would wish to think about higher-strength bolts or different fastening strategies. This highlights the essential position of the grade chart in guaranteeing secure and dependable design.
Components Affecting Fastener Choice Past Grade:
Whereas the grade is a essential issue, different features affect fastener choice:
- Thread Sort: Completely different thread varieties (e.g., coarse, tremendous) impression the holding energy and utility.
- Head Type: Varied head types (e.g., hex, button, pan) are designed for particular functions and torque necessities.
- End: Coatings and finishes (e.g., zinc plating, galvanizing) improve corrosion resistance and look.
- Size and Diameter: Correct sizing is essential for guaranteeing enough engagement and cargo distribution.
- Software-Particular Necessities: Components like temperature, vibration, and chemical publicity affect fastener choice.
Conclusion:
Understanding fastener grade charts is crucial for choosing the suitable {hardware} for any utility. Ignoring the grade can result in catastrophic failures, compromising security and inflicting important financial losses. By rigorously contemplating the required tensile energy, yield energy, and different properties, engineers and contractors can make sure the structural integrity and reliability of their tasks. This text offers a basis for understanding fastener grades and encourages additional exploration of particular requirements and materials properties for a deeper understanding of this essential side of engineering and development. All the time seek the advice of related requirements and producer specs to make sure the right collection of fasteners in your particular utility. Security ought to at all times be the paramount consideration when selecting fasteners.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding the Energy: A Complete Information to Fastener Grade Charts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!