Decoding the Threads: A Complete Information to Screw Chart Varieties
Associated Articles: Decoding the Threads: A Complete Information to Screw Chart Varieties
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Threads: A Complete Information to Screw Chart Varieties. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Threads: A Complete Information to Screw Chart Varieties

Screws, seemingly easy fasteners, signify a surprisingly numerous world of designs, every tailor-made to particular purposes and supplies. Understanding the nuances of screw sorts is essential for anybody concerned in building, manufacturing, engineering, and even DIY tasks. This complete information delves into the assorted chart sorts used to categorise screws, exploring their traits, purposes, and the elements influencing their choice.
The time period "screw chart" is not a standardized, universally acknowledged time period like "screw sort". As a substitute, it refers back to the varied methods we categorize and signify screw data, usually visually via charts or tables. These charts sometimes element key screw traits, permitting for fast identification and choice based mostly on utility necessities. The data offered can differ drastically relying on the supply and supposed viewers.
We are able to broadly categorize screw chart sorts based mostly on the knowledge they prioritize:
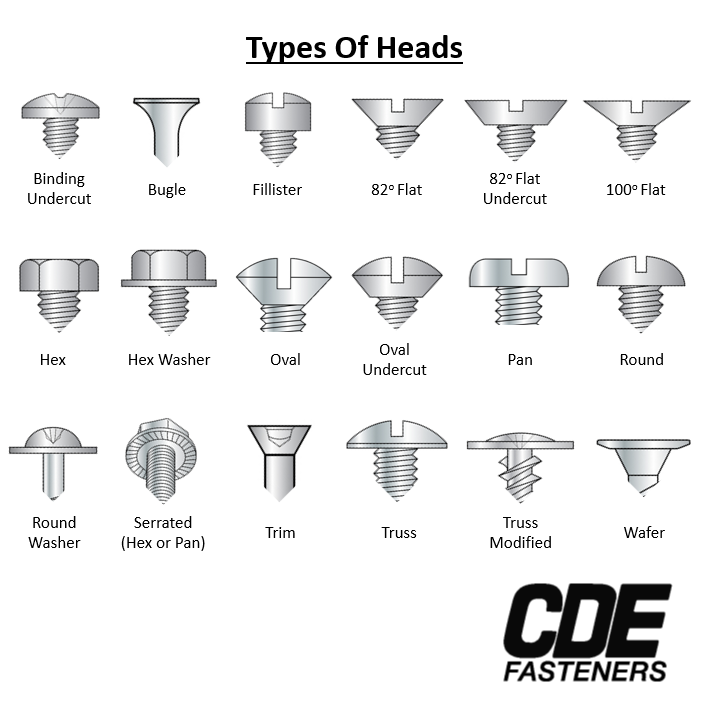
I. Charts Based mostly on Head Sort:
That is arguably the most typical strategy, specializing in the screw’s head design. The top dictates how the screw is pushed and infrequently influences its aesthetic enchantment. A typical chart would possibly embody photos and descriptions of the next head sorts:
-
Slotted Head: The oldest and easiest design, that includes a single, longitudinal slot for a flat-head screwdriver. These are typically much less most popular for high-torque purposes because of the danger of cam-out (the screwdriver slipping out of the slot). They’re usually present in much less demanding purposes or older designs.
-
Phillips Head: A cross-shaped recess, offering higher torque transmission than slotted heads because of the self-centering motion of the screwdriver bit. The cross-shaped design additionally helps forestall cam-out, making them extra environment friendly for mass manufacturing. Completely different sizes and variations (e.g., Phillips #0, #1, #2, and many others.) exist, impacting the driving force bit dimension required.
-
Pozidriv Head: Just like Phillips, however with further smaller recesses inside the principle cross. This design affords superior torque switch and resistance to cam-out in comparison with Phillips, lowering the danger of damaging the screw head.
-
Torx Head: Encompasses a six-pointed star-shaped recess. Torx drivers present glorious torque switch and resistance to cam-out, even beneath excessive stress. They’re generally utilized in automotive and industrial purposes the place energy and precision are paramount. Variations embody Torx Plus, which additional enhances efficiency.
-
Sq. Head: A easy, square-shaped recess, providing good torque switch and resistance to cam-out. These are sometimes present in purposes requiring excessive torque and the place a exact match is important.
-
Hex Head (or Socket Head): Encompasses a hexagonal recess designed to be used with a hex wrench or socket. These are extraordinarily strong and supply glorious torque transmission, making them excellent for high-strength purposes. They’re continuously utilized in equipment and structural elements.
-
Robertson Head (Sq. Drive): A sq. recess, much like the sq. head however designed for a selected driver. This design gives distinctive torque switch and is much less liable to cam-out than different designs. It is standard in some areas, significantly Canada.
-
Clutch Head: A variation of the Phillips design, with a extra pronounced cam-out prevention characteristic. The top is designed to slide when extreme torque is utilized, stopping injury to the screw or the pushed materials.
-
Tri-Wing Head: A 3-winged recess, providing good torque transmission and resistance to cam-out. These are sometimes utilized in electronics and safety purposes the place tampering is a priority.
II. Charts Based mostly on Drive Sort:
This strategy focuses on the kind of driver required to put in the screw. Whereas carefully associated to move sort, this classification might be extra nuanced, significantly when contemplating specialised drivers. A chart would possibly cowl:
- Slotted Drive: Makes use of a flat-head screwdriver.
- Phillips Drive: Makes use of a Phillips head screwdriver.
- Pozidriv Drive: Makes use of a Pozidriv screwdriver.
- Torx Drive: Makes use of a Torx driver.
- Hex Drive: Makes use of a hex key or socket wrench.
- Robertson Drive: Makes use of a Robertson screwdriver.
- Sq. Drive: Makes use of a sq. drive screwdriver (usually interchangeable with Robertson).
- Clutch Drive: Makes use of a selected clutch head driver.
- Tri-Wing Drive: Makes use of a tri-wing driver.
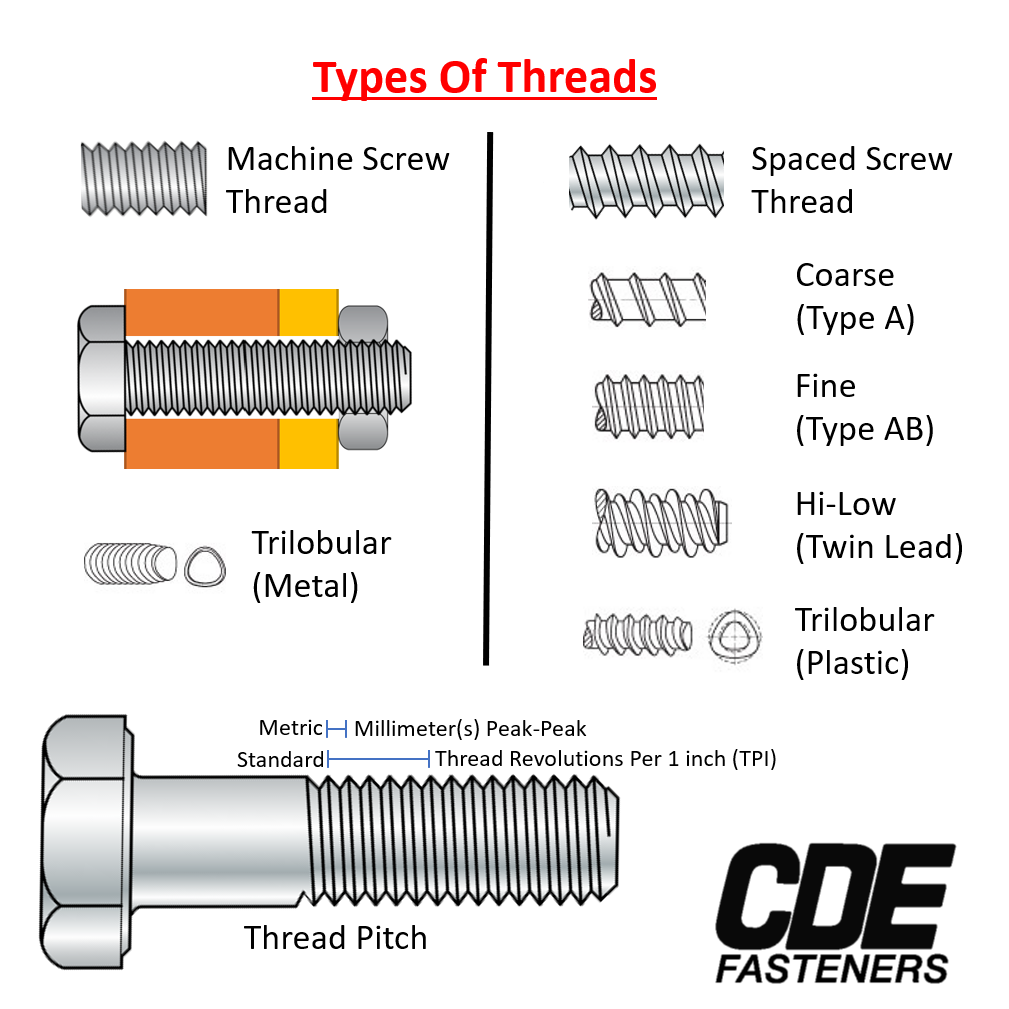
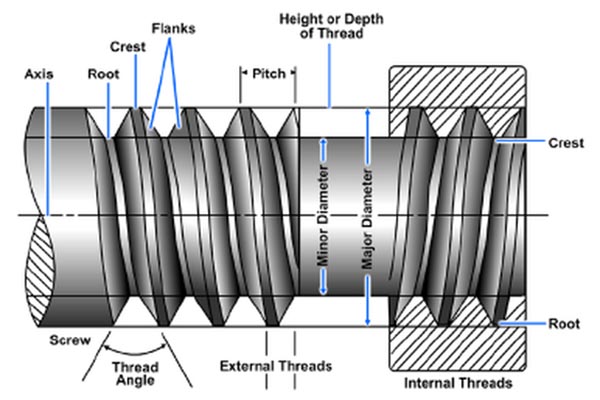
III. Charts Based mostly on Thread Sort:
That is essential for understanding the screw’s holding energy and suitability for various supplies. A complete chart would come with:
- Coarse Thread: Options broadly spaced threads, offering a sooner driving pace however probably much less holding energy in softer supplies.
- Wonderful Thread: Options carefully spaced threads, providing larger holding energy and elevated resistance to vibration, however requiring extra time to drive.
- Self-Tapping: These screws create their very own threads as they’re pushed into the fabric, eliminating the necessity for pre-drilled holes. They’re generally utilized in softer supplies like wooden or plastic.
- Machine Screw: Designed to be used with pre-drilled and tapped holes, offering exact and powerful fastening.
- Wooden Screw: Particularly designed to be used in wooden, usually that includes a sharper level and coarser threads for simpler penetration.
- Sheet Metallic Screw: Designed to be used in skinny sheet steel, usually that includes a self-tapping design and a pointy level for simple penetration.
- Drywall Screw: Particularly designed for drywall, usually that includes a fantastic thread and a self-tapping design.
IV. Charts Based mostly on Materials:
The fabric of the screw considerably impacts its energy, corrosion resistance, and total lifespan. A chart would possibly embody:
- Metal: A standard and powerful materials, however inclined to corrosion except handled. Numerous metal grades supply various ranges of energy and hardness.
- Stainless Metal: Extremely corrosion-resistant, providing glorious sturdiness in harsh environments. Completely different grades (e.g., 304, 316) supply various ranges of corrosion resistance.
- Brass: Corrosion-resistant and aesthetically pleasing, usually utilized in ornamental purposes.
- Aluminum: Light-weight and corrosion-resistant, usually utilized in aerospace and automotive purposes.
- Zinc-Plated Metal: Supplies further corrosion safety to metal screws.
V. Mixed Charts:
Essentially the most informative charts usually mix a number of of the above classes, offering a complete overview of screw traits. These charts would possibly embody columns for head sort, drive sort, thread sort, materials, size, diameter, and different related specs. Such charts are invaluable for engineers, contractors, and anybody needing to pick the correct screw for a selected utility.
Selecting the Proper Screw:
Deciding on the suitable screw entails cautious consideration of a number of elements:
- Materials being fixed: Completely different supplies require screws with totally different thread sorts and holding energy.
- Power necessities: The screw should be sturdy sufficient to resist the anticipated load.
- Environmental situations: Corrosion resistance is essential in harsh environments.
- Aesthetic issues: The top sort and materials can affect the general look.
- Accessibility: The placement and accessibility of the fastening level could affect the selection of head sort and driver.
By understanding the assorted chart sorts and the knowledge they convey, you’ll be able to confidently choose the correct screw in your challenge, making certain a safe, dependable, and aesthetically pleasing consequence. Consulting complete screw charts and datasheets from respected producers is essential for making knowledgeable choices and avoiding potential failures. The seemingly easy act of selecting a screw turns into a exact engineering determination when the correct data is at hand.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Decoding the Threads: A Complete Information to Screw Chart Varieties. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!