Decoding the Z-Chart: A Deep Dive into Constructive Z-Scores and Their Functions
Associated Articles: Decoding the Z-Chart: A Deep Dive into Constructive Z-Scores and Their Functions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Z-Chart: A Deep Dive into Constructive Z-Scores and Their Functions. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Z-Chart: A Deep Dive into Constructive Z-Scores and Their Functions
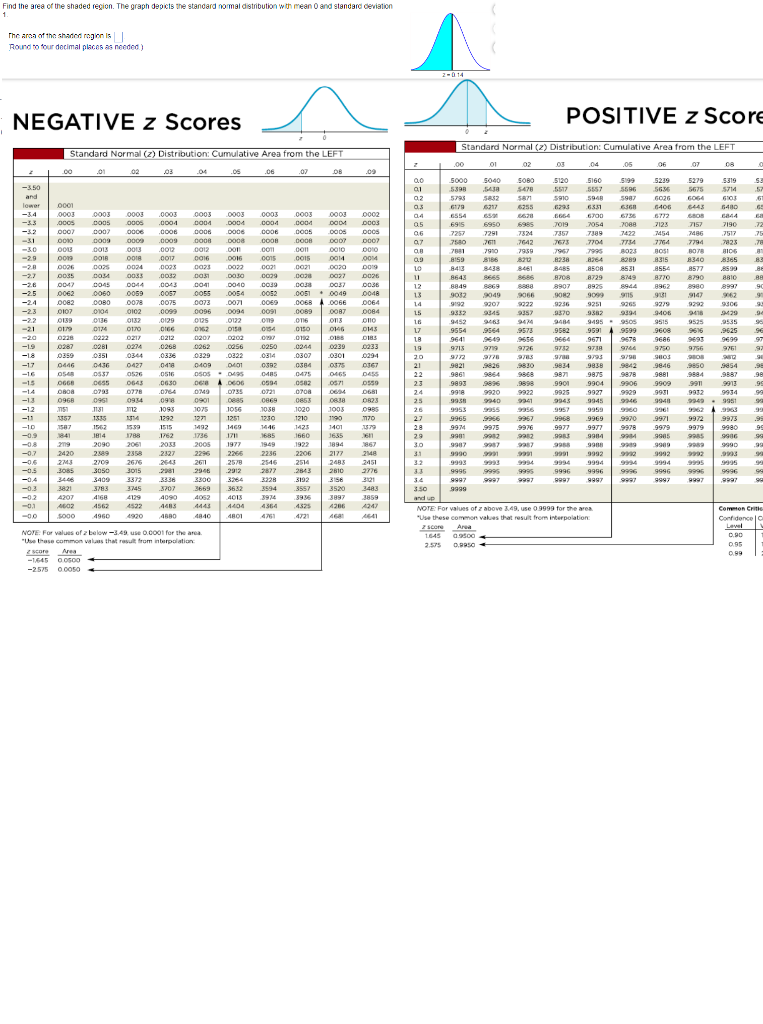
The Z-chart, a visible illustration of the usual regular distribution, is a cornerstone of statistical evaluation. It permits us to grasp the likelihood related to any given information level inside a usually distributed dataset. Whereas your complete Z-chart encompasses each constructive and destructive Z-scores, this text will focus particularly on the implications and purposes of constructive Z-scores. We’ll discover their which means, calculation, interpretation, and numerous makes use of throughout varied fields.
Understanding the Normal Regular Distribution and Z-Scores
Earlier than delving into constructive Z-scores, it is essential to know the basics of the usual regular distribution. This distribution is a bell-shaped curve with a imply (common) of 0 and a normal deviation of 1. The world beneath this curve represents likelihood, with the entire space equaling 1 (or 100%).
A Z-score, often known as a normal rating, quantifies what number of commonplace deviations a specific information level lies away from the imply of the distribution. A constructive Z-score signifies that the information level is above the imply, whereas a destructive Z-score signifies that it is beneath the imply. The magnitude of the Z-score displays the gap from the imply – a bigger absolute worth signifies a higher distance.
Calculating Constructive Z-Scores
The method for calculating a Z-score is simple:
Z = (X – μ) / σ
The place:
- Z is the Z-score
- X is the person information level
- μ is the inhabitants imply
- σ is the inhabitants commonplace deviation
For instance, if a scholar scored 85 on a take a look at with a imply of 75 and a normal deviation of 10, their Z-score can be:
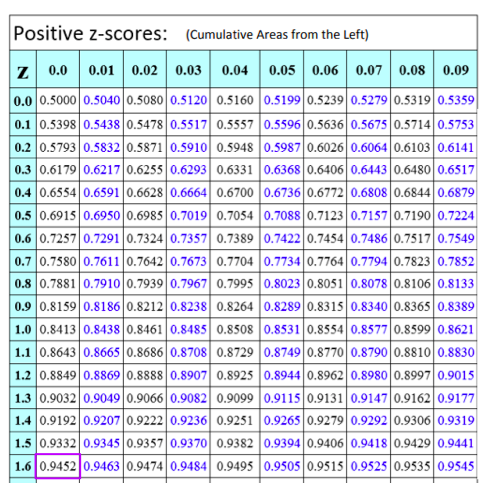
Z = (85 – 75) / 10 = 1
This means that the scholar’s rating is one commonplace deviation above the imply. A constructive Z-score, on this context, implies a efficiency above common.
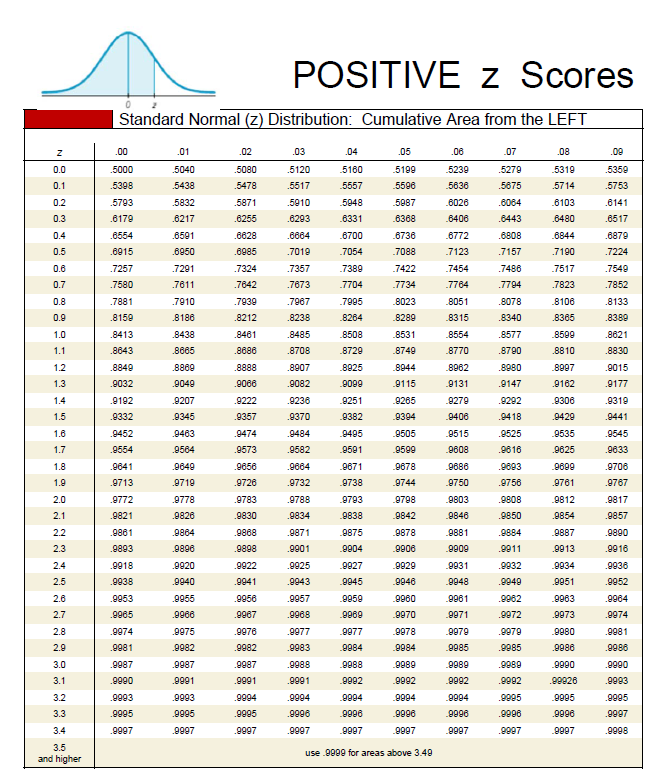
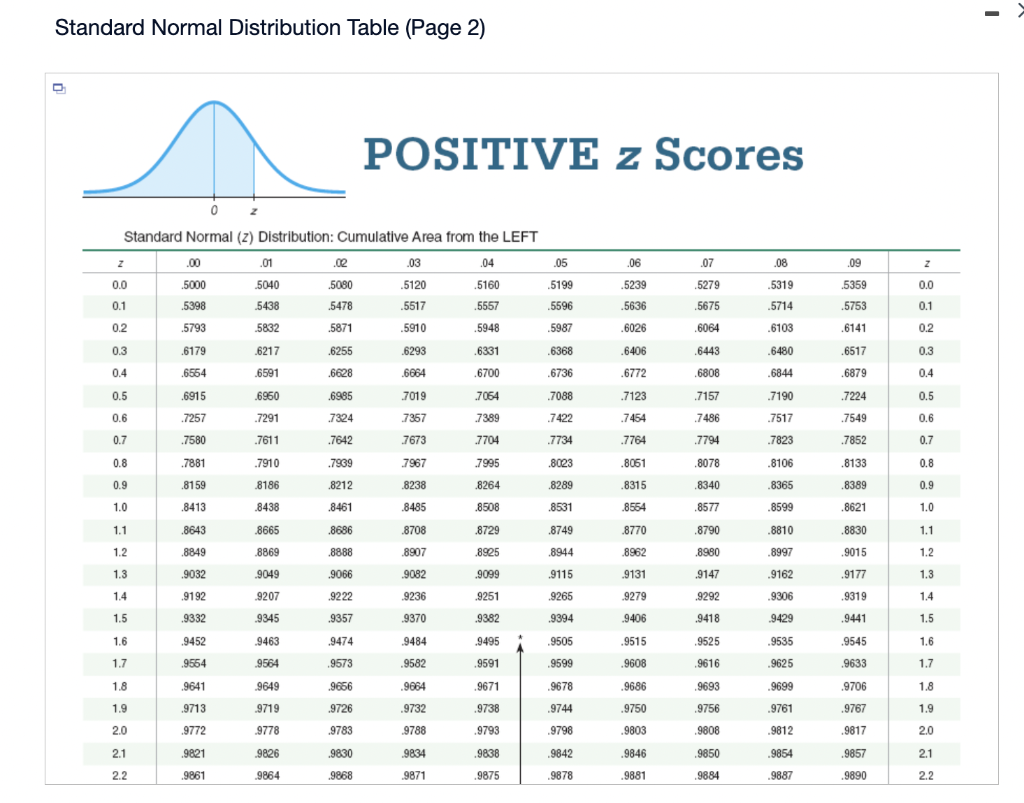
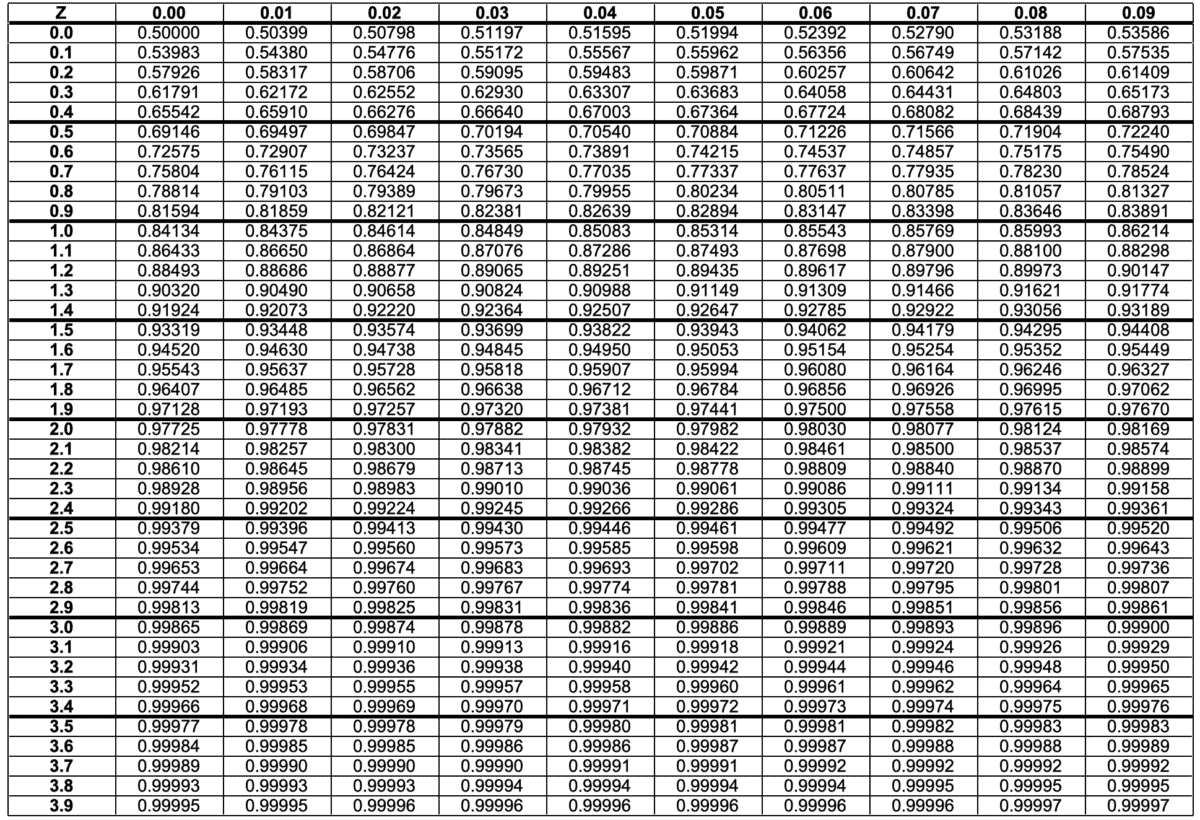
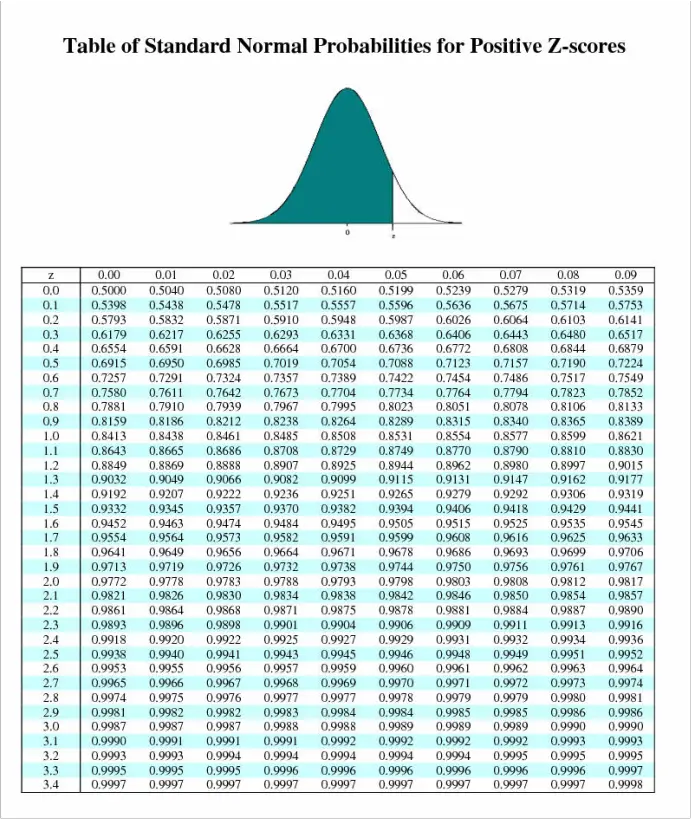
Decoding Constructive Z-Scores utilizing the Z-Chart
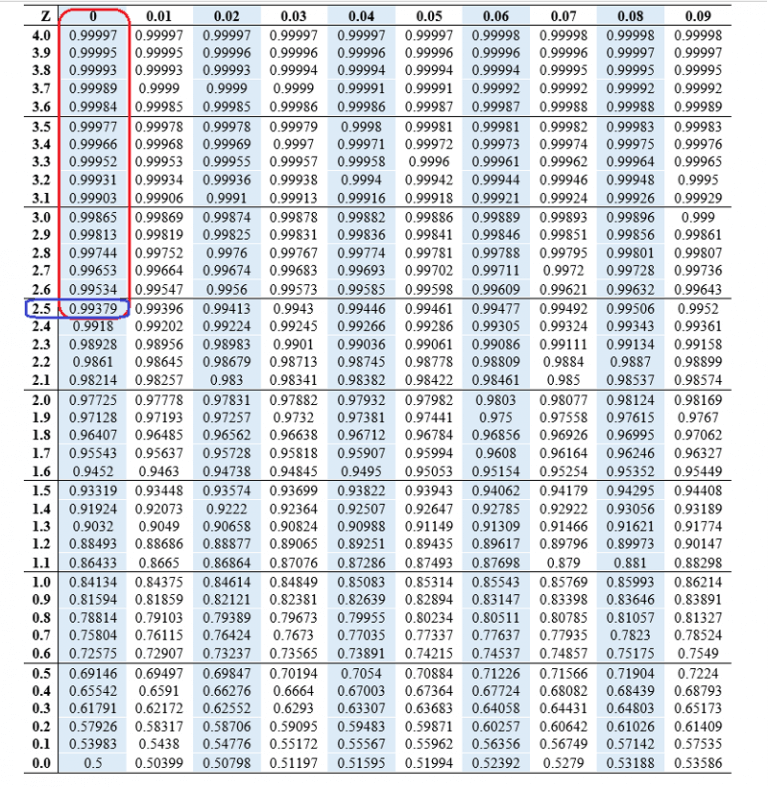
The Z-chart (or Z-table) is an important software for deciphering Z-scores. It supplies the cumulative likelihood of acquiring a Z-score lower than or equal to a given worth. For constructive Z-scores, this represents the world beneath the usual regular curve to the left of the Z-score. This space corresponds to the likelihood of observing a knowledge level lower than or equal to the worth related to that Z-score.
For example, a Z-score of 1.0 has a cumulative likelihood of roughly 0.8413. This implies there’s an 84.13% likelihood of observing a knowledge level with a Z-score lower than or equal to 1. To seek out the likelihood of observing a knowledge level higher than a selected constructive Z-score, we subtract the cumulative likelihood from 1. On this case, the likelihood of observing a knowledge level higher than a Z-score of 1 is 1 – 0.8413 = 0.1587, or 15.87%.
Functions of Constructive Z-Scores Throughout Numerous Fields
Constructive Z-scores discover widespread software in quite a few fields, together with:
1. Schooling: As illustrated within the earlier instance, Z-scores are incessantly used to standardize take a look at scores, permitting for comparisons throughout totally different assessments and cohorts. A constructive Z-score signifies above-average efficiency.
2. Finance: In finance, Z-scores are utilized to evaluate the creditworthiness of debtors. A better Z-score (typically calculated utilizing Altman’s Z-score mannequin) suggests a decrease threat of default. Constructive Z-scores, on this context, point out a more healthy monetary standing.
3. High quality Management: In manufacturing and high quality management, Z-scores assist monitor manufacturing processes. Constructive Z-scores may point out deviations from goal specs, probably requiring changes to keep up high quality requirements.
4. Healthcare: Z-scores are employed in varied medical purposes, resembling assessing the expansion of infants or monitoring important indicators. Constructive Z-scores may point out a deviation from the norm, requiring additional investigation.
5. Sports activities Analytics: In sports activities, Z-scores can be utilized to match the efficiency of athletes. A constructive Z-score for a specific statistic suggests superior efficiency relative to the common.
6. Environmental Science: Z-scores are employed in analyzing environmental information, resembling air pollution ranges or local weather change indicators. Constructive Z-scores may spotlight areas of concern requiring environmental intervention.
7. Social Sciences: Researchers make the most of Z-scores in analyzing social information, resembling earnings ranges or academic attainment. Constructive Z-scores can assist determine subgroups with increased ranges of sure traits.
Decoding Constructive Z-Scores in Context
It is essential to keep in mind that the interpretation of a constructive Z-score is at all times context-dependent. A Z-score of 1 is perhaps thought-about important in a single software however insignificant in one other. The sensible significance of a Z-score is determined by the particular context, the variability of the information, and the objectives of the evaluation.
For instance, a Z-score of 1 is perhaps thought-about extremely important if it represents the efficiency of a crucial part in an plane engine, whereas the identical Z-score is perhaps much less important if it represents a minor fluctuation in every day gross sales figures.
Limitations of Z-Scores
Whereas Z-scores are a robust software, they do have limitations:
- Assumption of Normality: Z-scores depend on the idea that the information is generally distributed. If the information considerably deviates from normality, the interpretation of Z-scores is perhaps deceptive.
- Sensitivity to Outliers: Outliers can disproportionately affect the imply and commonplace deviation, thus affecting the calculation and interpretation of Z-scores.
- Concentrate on Relative Efficiency: Z-scores primarily mirror relative efficiency inside a selected dataset. They do not present details about absolute efficiency or the underlying causes for the noticed variations.
Conclusion
Constructive Z-scores are a beneficial software for understanding and deciphering information inside a usually distributed dataset. They supply a standardized approach to quantify how far a knowledge level lies above the imply, permitting for comparisons throughout totally different datasets and contexts. Nevertheless, it is important to grasp the underlying assumptions, limitations, and the significance of deciphering Z-scores inside their particular context to keep away from misinterpretations and draw significant conclusions. By fastidiously contemplating these elements, researchers and analysts can successfully leverage constructive Z-scores to realize beneficial insights throughout a variety of disciplines. The Z-chart, due to this fact, serves as a basic software in statistical evaluation, providing a transparent and concise methodology for understanding likelihood and making knowledgeable choices primarily based on information.

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Decoding the Z-Chart: A Deep Dive into Constructive Z-Scores and Their Functions. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!