Diabetic Medicines: A Complete Drug Chart and Information
Associated Articles: Diabetic Medicines: A Complete Drug Chart and Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing matter associated to Diabetic Medicines: A Complete Drug Chart and Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Diabetic Medicines: A Complete Drug Chart and Information
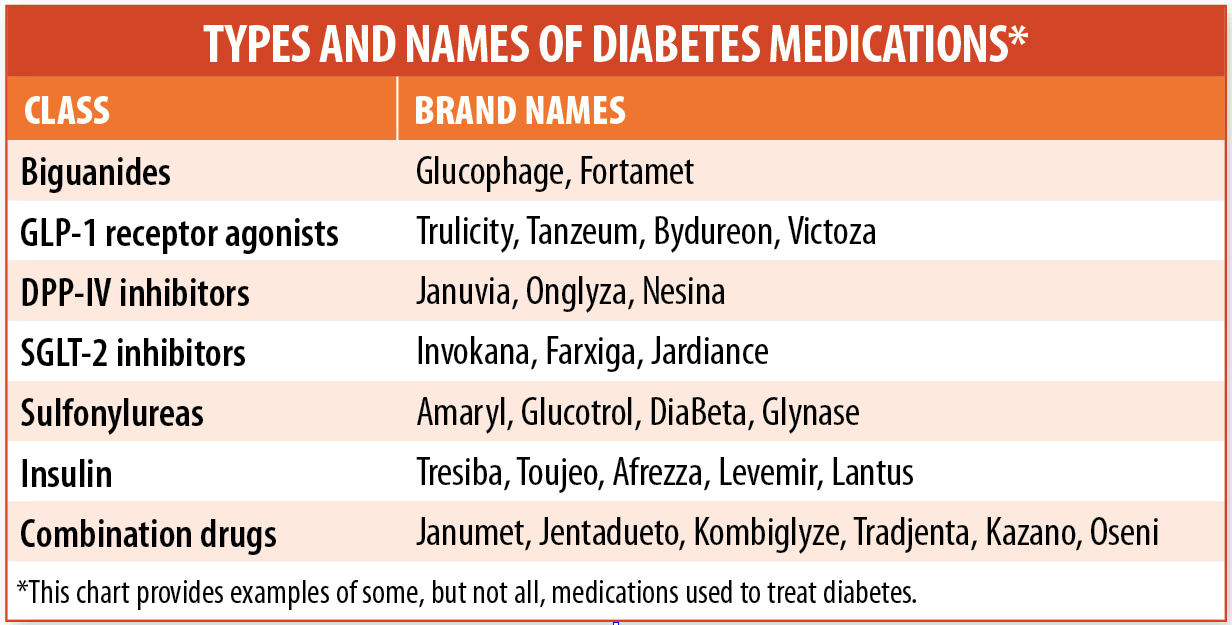
Diabetes mellitus, a power metabolic dysfunction characterised by hyperglycemia, impacts thousands and thousands worldwide. Efficient administration depends closely on treatment, chosen based mostly on the kind of diabetes (sort 1, sort 2, or gestational), particular person affected person components, and therapy objectives. This text offers a complete overview of diabetic drugs, introduced in a drug chart format, adopted by detailed explanations of every drug class and concerns for his or her use.
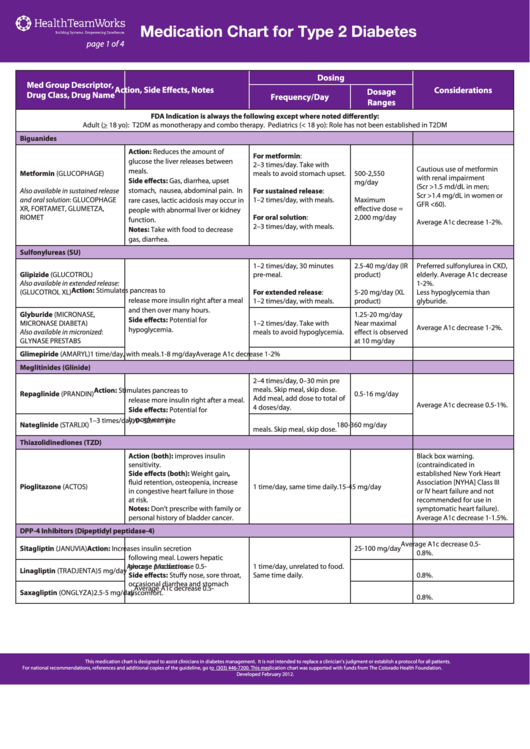
Diabetic Treatment Drug Chart:
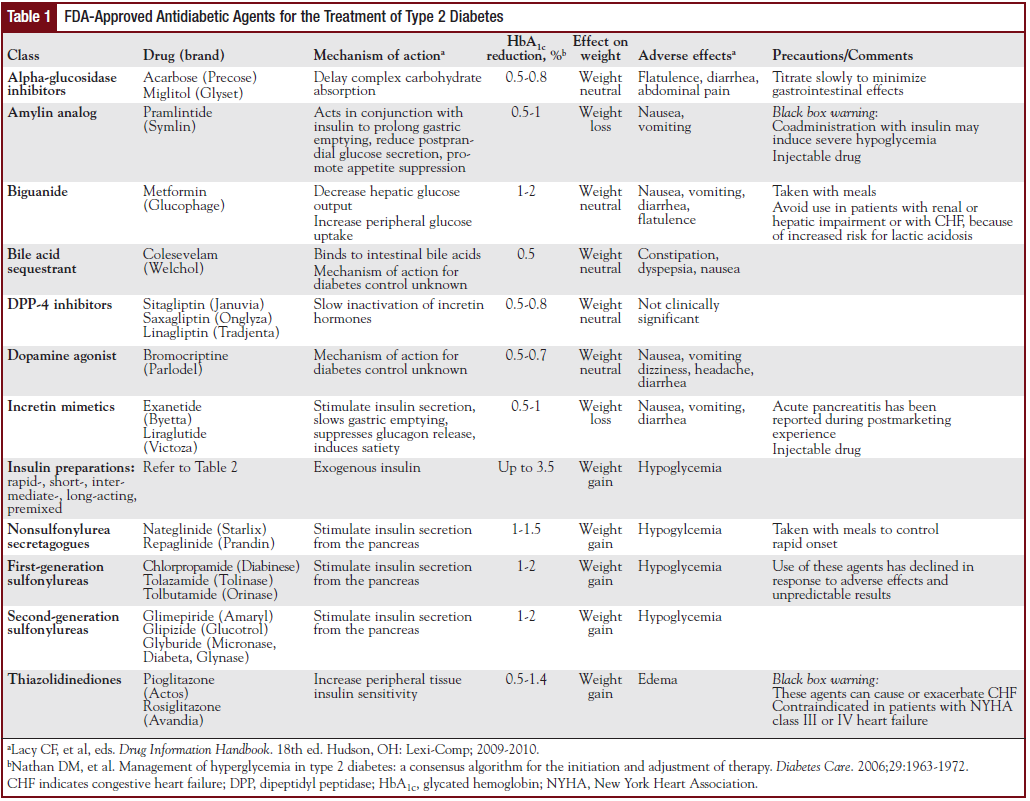
| Drug Class | Drug Identify(s) | Mechanism of Motion | Onset of Motion | Peak Impact | Period of Motion | Frequent Facet Results | Contraindications/Precautions | Monitoring Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Insulin Aspart (NovoLog), Insulin Lispro (Humalog), Insulin Glulisine (Apidra) (Fast-acting) Insulin Common (Humulin R, Novolin R) (Quick-acting) Insulin NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N) (Intermediate-acting) Insulin Glargine (Lantus), Insulin Detemir (Levemir), Insulin Degludec (Tresiba) (Lengthy-acting) |
Mimics endogenous insulin, facilitating glucose uptake into cells. Totally different formulations have various onset and period. | Minutes-1 hour | 1-3 hours | 3-8 hours (speedy/brief), 10-18 hours (intermediate), 24+ hours (lengthy) | Hypoglycemia, weight achieve, lipohypertrophy, injection website reactions | Allergy to insulin, hypersensitivity. Cautious titration required. | Blood glucose ranges, weight, HbA1c |
| Sulfonylureas | Glyburide (DiaBeta, Micronase), Glipizide (Glucotrol), Glimepiride (Amaryl) | Stimulate insulin launch from pancreatic beta cells. | 30-60 minutes | 2-4 hours | 12-24 hours | Hypoglycemia, weight achieve, nausea, allergic reactions | Renal or hepatic impairment, historical past of sulfonamide allergy. Not for sort 1 diabetes. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, liver operate exams |
| Meglitinides | Repaglinide (Prandin), Nateglinide (Starlix) | Stimulate insulin launch from pancreatic beta cells, just like sulfonylureas however with shorter period. | half-hour | 1-2 hours | 3-6 hours | Hypoglycemia, weight achieve, nausea, allergic reactions | Renal or hepatic impairment. Not for sort 1 diabetes. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c |
| Biguanides | Metformin (Glucophage, Fortamet) | Decreases hepatic glucose manufacturing, will increase insulin sensitivity, and improves glucose uptake. | 1-2 hours | 2-4 hours | 12-24 hours | Gastrointestinal upset (diarrhea, nausea), lactic acidosis (uncommon however critical) | Renal impairment, hepatic illness, alcohol abuse, coronary heart failure. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, renal operate exams |
| Thiazolidinediones | Pioglitazone (Actos), Rosiglitazone (Avandia) (Usually much less most well-liked as a result of cardiovascular dangers) | Enhance insulin sensitivity by performing on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ). | A number of days | Variable | Variable | Fluid retention, weight achieve, coronary heart failure, bone fractures | Hepatic impairment, coronary heart failure, bladder most cancers danger (pioglitazone). | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, liver operate exams, echocardiogram |
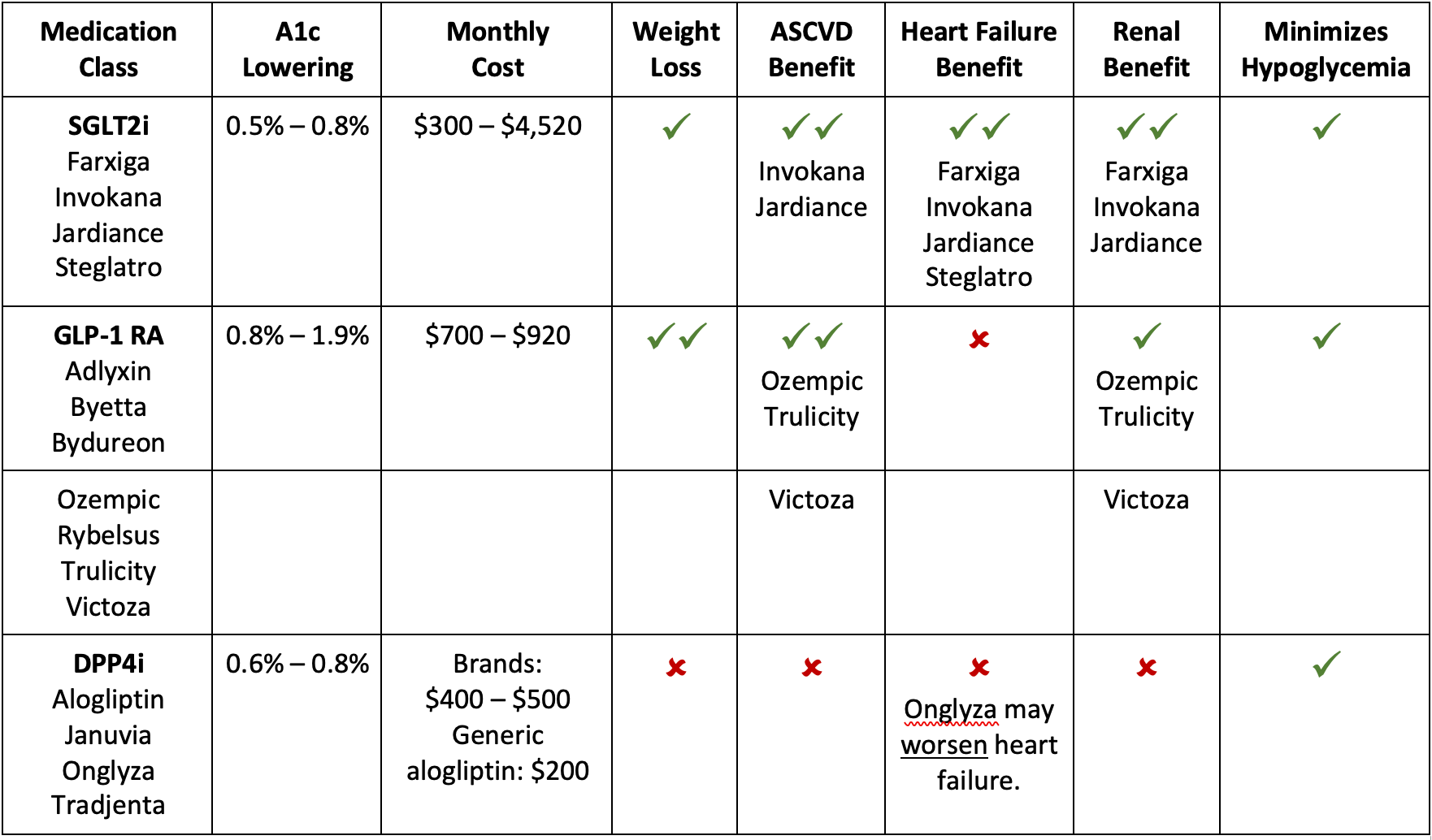
| DPP-4 Inhibitors | Sitagliptin (Januvia), Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Linagliptin (Tradjenta), Alogliptin (Nesina) | Enhance incretin hormones, resulting in enhanced insulin secretion and decreased glucagon secretion. | 1-2 hours | 2-4 hours | 24 hours | Higher respiratory infections, headache, nausea | Renal impairment, pancreatitis historical past. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, renal operate exams |
| SGLT2 Inhibitors | Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance) | Inhibit sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) within the kidneys, rising glucose excretion in urine. | 1-2 hours | 2-4 hours | 24 hours | Genitourinary infections, dehydration, elevated danger of fractures | Renal impairment, extreme dehydration, hypersensitivity. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, renal operate exams, electrolytes |
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy), Liraglutide (Victoza), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon) | Mimic incretin hormones, selling insulin launch, suppressing glucagon, and slowing gastric emptying. | Variable | Variable | Variable | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, pancreatitis (uncommon) | Historical past of pancreatitis, gastroparesis. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, weight, gastrointestinal signs |
| Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors | Acarbose (Precose), Miglitol (Glyset) | Inhibit alpha-glucosidase enzymes within the gut, delaying carbohydrate digestion and absorption. | 30-60 minutes | Variable | Variable | Gastrointestinal upset (diarrhea, flatulence) | Inflammatory bowel illness, hepatic impairment. | Blood glucose ranges, HbA1c |
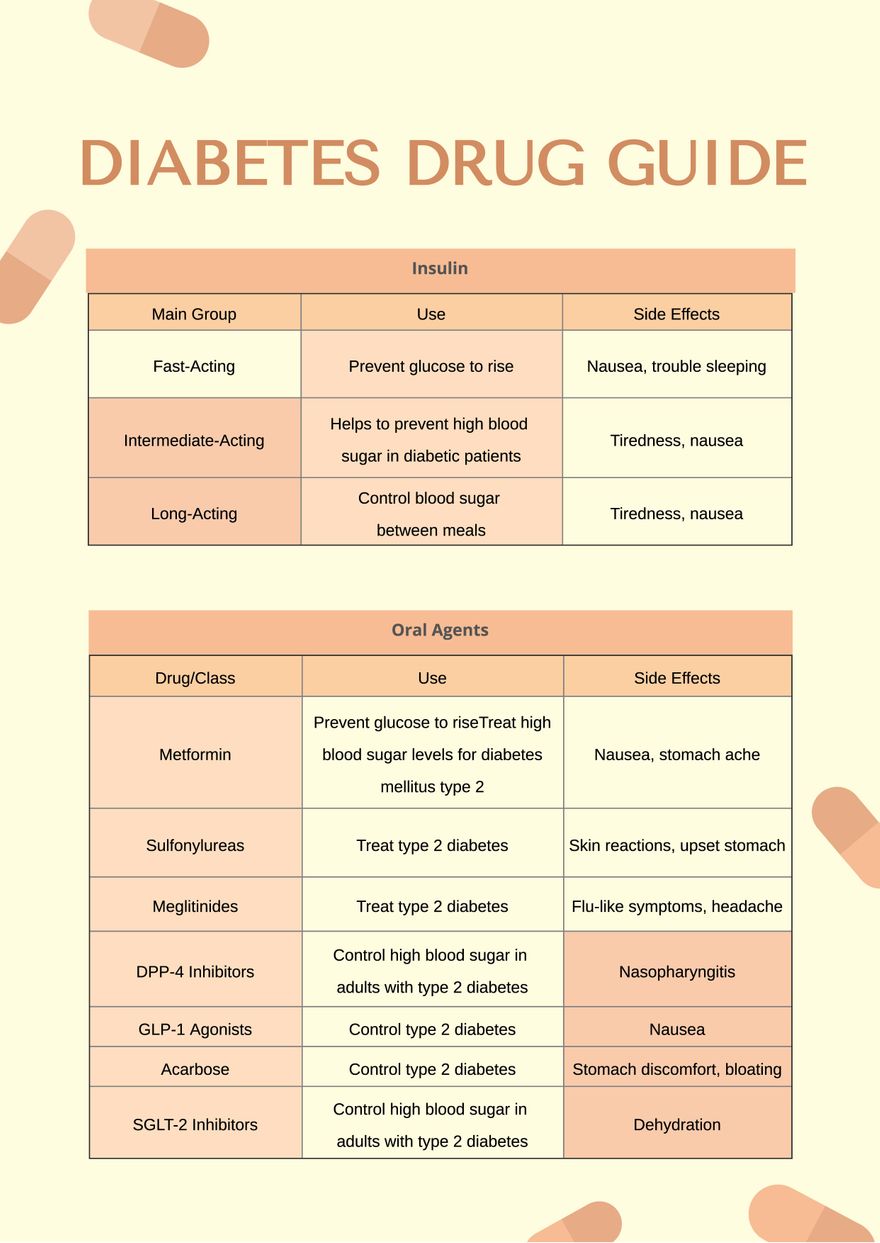
Detailed Clarification of Drug Lessons:
1. Insulin: The cornerstone of sort 1 diabetes administration and infrequently utilized in sort 2 diabetes when different drugs are inadequate. Totally different insulin formulations present flexibility in managing blood glucose ranges all through the day. Fast-acting insulins are used earlier than meals, short-acting can be utilized for mealtime or basal protection, intermediate-acting present longer-lasting protection, and long-acting insulins present a basal degree of insulin all through the day.
2. Sulfonylureas: These older brokers stimulate insulin launch from the pancreas. They’re efficient in people with some residual beta-cell operate however may cause important hypoglycemia, particularly in aged sufferers or these with impaired renal operate.
3. Meglitinides: Just like sulfonylureas, however with a shorter period of motion, making them higher suited to sufferers whose hyperglycemia is primarily postprandial (after meals).
4. Biguanides (Metformin): The primary-line treatment for many sufferers with sort 2 diabetes. Metformin’s mechanism of motion is multifactorial, enhancing insulin sensitivity and lowering hepatic glucose manufacturing. It is typically well-tolerated however may cause gastrointestinal unwanted side effects. Lactic acidosis, a uncommon however critical complication, is a significant concern, notably in sufferers with renal impairment.
5. Thiazolidinediones: These brokers enhance insulin sensitivity by performing on PPAR-γ receptors. Nevertheless, their use has decreased considerably as a result of considerations about cardiovascular dangers, fluid retention, and weight achieve.
6. DPP-4 Inhibitors: These drugs improve ranges of incretin hormones, enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon launch. They’re typically well-tolerated and have a low danger of hypoglycemia.
7. SGLT2 Inhibitors: These medication work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose within the kidneys, resulting in elevated glucose excretion within the urine. They’ve proven important advantages in lowering cardiovascular occasions and are efficient in reducing blood glucose ranges. Nevertheless, they’ll improve the danger of urinary tract infections and dehydration.
8. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These drugs mimic the results of incretin hormones, resulting in improved glucose management, weight reduction, and cardiovascular advantages. They’re usually utilized in sufferers with sort 2 diabetes who haven’t achieved enough glycemic management with different drugs. Nausea and gastrointestinal unwanted side effects are frequent.
9. Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: These brokers delay carbohydrate absorption within the gut, lowering postprandial hyperglycemia. They’re usually utilized in mixture with different drugs. Gastrointestinal unwanted side effects are frequent.
Concerns for Treatment Choice:
The selection of diabetic treatment relies on a number of components, together with:
- Sort of diabetes: Sort 1 diabetes requires insulin remedy, whereas sort 2 diabetes administration might contain life-style modifications, oral drugs, or insulin.
- Glycemic management: The severity of hyperglycemia and the affected person’s HbA1c ranges will affect the selection of treatment.
- Affected person-specific components: Age, renal and hepatic operate, different medical situations (e.g., coronary heart failure, heart problems), and particular person preferences all play a task.
- Value and availability: The associated fee and accessibility of medicines can affect therapy choices.
- Potential unwanted side effects: The chance-benefit profile of every treatment must be fastidiously thought-about.
Conclusion:
Efficient administration of diabetes requires a personalised method. This text offers a complete overview of generally used diabetic drugs, however it’s essential to seek the advice of with a healthcare skilled to find out essentially the most applicable therapy plan for particular person wants. Common monitoring of blood glucose ranges, HbA1c, and different related parameters is important for optimizing glycemic management and minimizing the danger of long-term issues. This data is for academic functions solely and shouldn’t be thought-about medical recommendation. At all times seek the advice of your physician or different certified healthcare skilled earlier than beginning or altering any treatment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Diabetic Medicines: A Complete Drug Chart and Information. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!