distinction between a bar chart and histogram
Associated Articles: distinction between a bar chart and histogram
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to distinction between a bar chart and histogram. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Charts vs. Histograms: Unveiling the Variations in Information Visualization
![What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? [SOLVED]](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/screenshot-2021-03-01-at-9-17-06-am-1614570481.png)
Bar charts and histograms are each highly effective instruments for visualizing knowledge, significantly when coping with categorical or numerical knowledge, respectively. Nevertheless, regardless of their superficial similarities – each make the most of rectangular bars to symbolize knowledge – there are essential variations of their software, building, and the kind of info they convey. Understanding these variations is significant for selecting the suitable chart to successfully talk your findings and keep away from misinterpretations.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Categorical vs. Numerical Information
Earlier than diving into the specifics of bar charts and histograms, it’s important to make clear the excellence between categorical and numerical knowledge. This elementary distinction dictates which chart sort is acceptable.
-
Categorical Information: Any such knowledge represents qualities or traits that may be divided into distinct classes or teams. These classes are usually non-numerical and will be qualitative (e.g., colours, forms of fruits, nations) or nominal (e.g., gender, marital standing). The order of the classes is usually arbitrary, although generally a logical order exists (e.g., ranges of schooling).
-
Numerical Information: This knowledge sort consists of numbers representing portions or measurements. Numerical knowledge will be additional labeled as:
- Discrete Information: Information that may solely tackle particular, separate values (e.g., the variety of automobiles in a parking zone, the variety of college students in a category). There are gaps between attainable values.
- Steady Information: Information that may tackle any worth inside a given vary (e.g., top, weight, temperature). There aren’t any gaps between attainable values.
Bar Charts: Visualizing Categorical Information
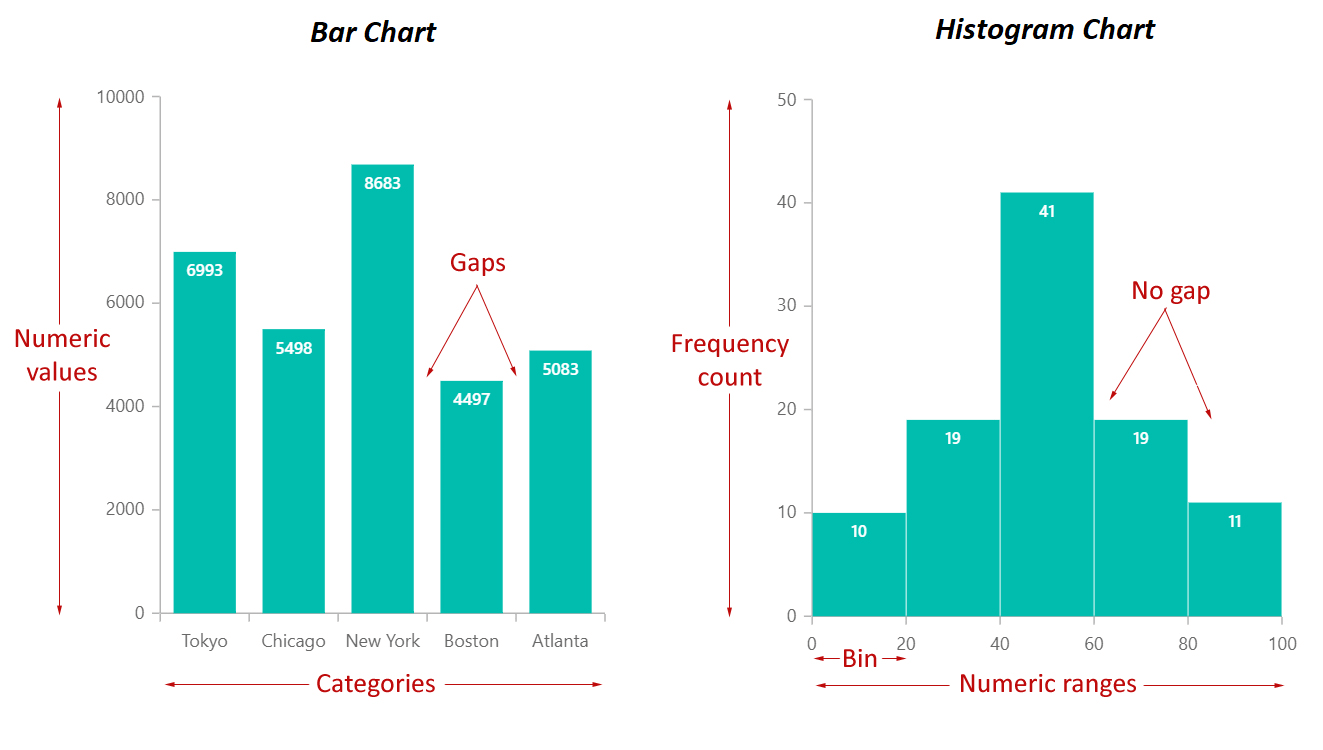
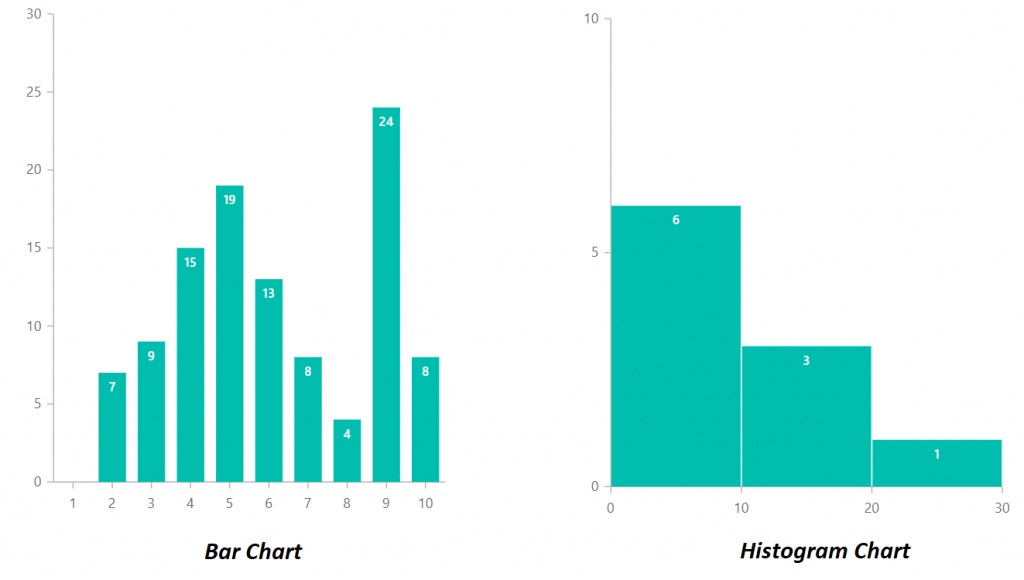
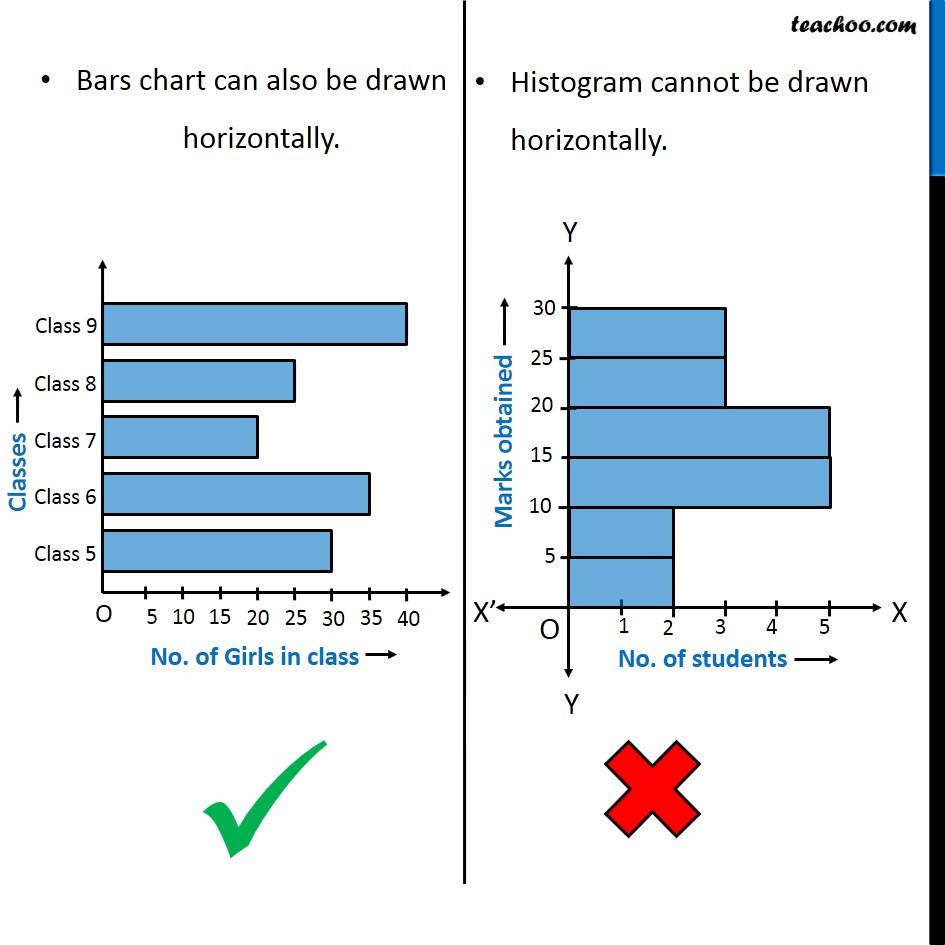
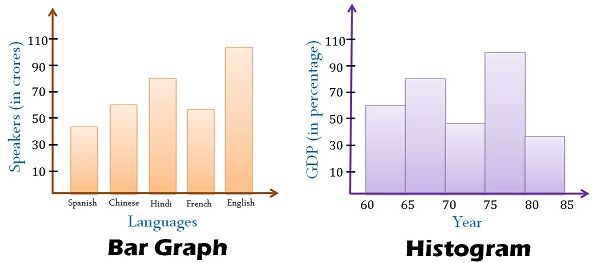
Bar charts are primarily used to match the frequencies or proportions of various classes inside a dataset. Every bar represents a single class, and its top (or size, relying on the chart’s orientation) corresponds to the worth related to that class. The classes are usually displayed alongside the horizontal axis (x-axis), whereas the frequencies or proportions are proven on the vertical axis (y-axis).
Key Traits of Bar Charts:
- Discrete Classes: Bar charts are designed for categorical knowledge, the place every bar represents a definite, separate class.
- Gaps Between Bars: A vital function distinguishing bar charts from histograms is the presence of gaps between the bars. These gaps emphasize the distinct nature of the classes and visually separate them.
- Order of Classes: Whereas the order of classes is usually arbitrary, it may be strategically chosen to focus on tendencies or patterns. For instance, arranging classes from highest to lowest frequency can enhance readability.
- A number of Variables: Bar charts can successfully show knowledge for a number of variables utilizing grouped or stacked bar charts. Grouped bar charts show a number of bars for every class, evaluating totally different points throughout the identical class. Stacked bar charts present the composition of every class, with segments representing totally different sub-categories.
- Appropriate for Comparisons: Bar charts excel at facilitating comparisons between totally different classes, making it simple to determine the biggest or smallest values, and spot vital variations.
Examples of Bar Chart Purposes:
- Evaluating gross sales figures throughout totally different product strains.
- Exhibiting the distribution of respondents throughout varied age teams in a survey.
- Illustrating the market share of various corporations in an trade.
- Visualizing the variety of college students enrolled in numerous educational departments.
Histograms: Visualizing Numerical Information Distributions
Histograms, not like bar charts, are designed to show the distribution of numerical knowledge. They present how regularly knowledge factors fall inside particular ranges or intervals (known as bins or lessons). Every bar in a histogram represents a bin, and its top corresponds to the variety of knowledge factors that fall inside that bin’s vary.
Key Traits of Histograms:
- Numerical Information: Histograms are particularly designed for numerical knowledge, whether or not discrete or steady.
- No Gaps Between Bars: In contrast to bar charts, histograms don’t have any gaps between the bars. The bars contact one another to symbolize the continual nature of the information, even when the information itself is discrete.
- Bins or Intervals: The information is split into bins, and the variety of bins considerably influences the looks of the histogram. Selecting the suitable variety of bins is essential for successfully representing the information’s distribution. Too few bins could obscure necessary particulars, whereas too many bins could result in a jagged and uninformative graph.
- Frequency Distribution: Histograms visually symbolize the frequency distribution of the information, displaying the place the information is concentrated and the form of the distribution (e.g., regular, skewed, bimodal).
- Information Density: The peak of every bar displays the density of knowledge factors inside that bin. Taller bars point out a better focus of knowledge factors in that vary.
Examples of Histogram Purposes:
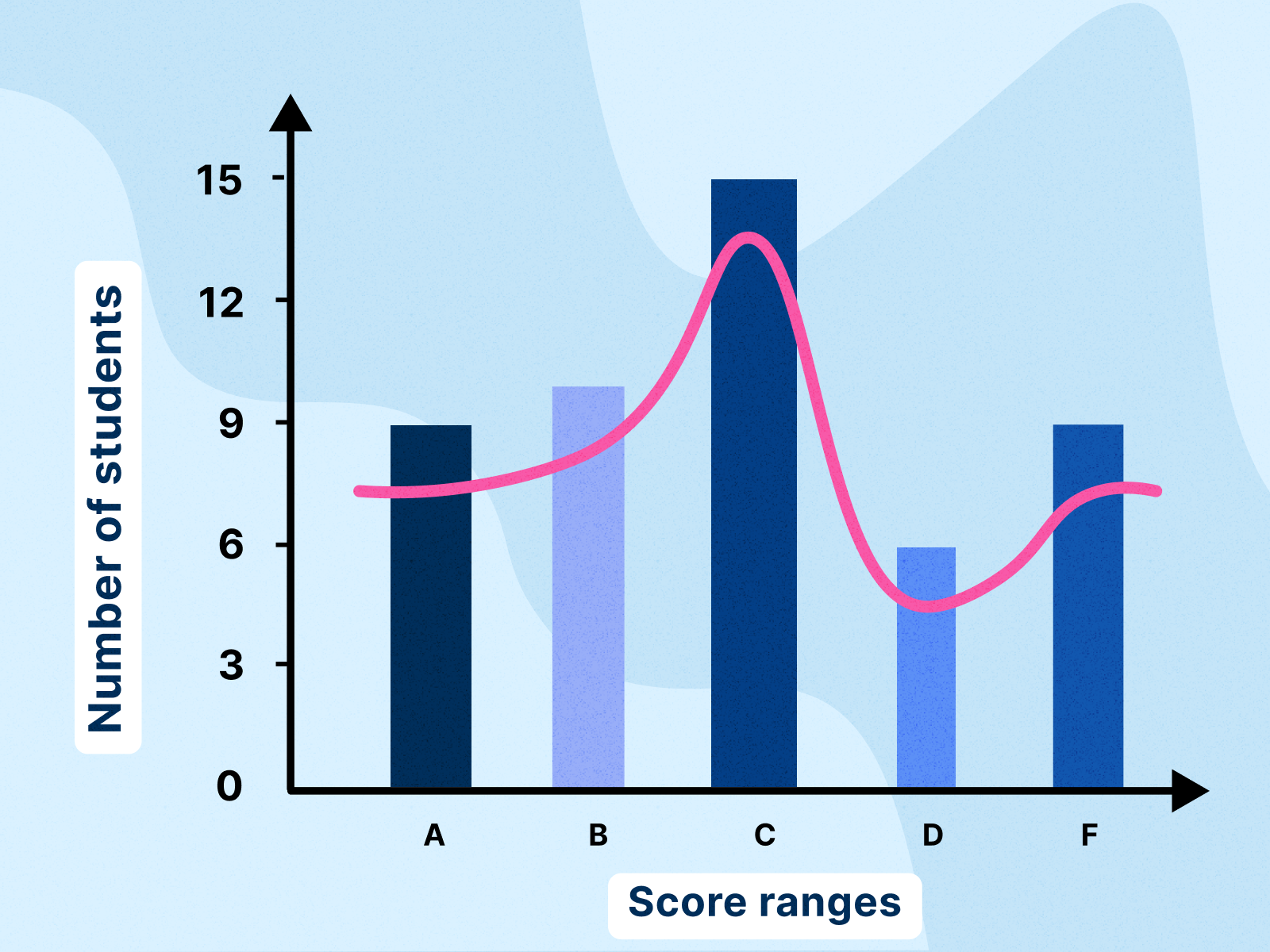
- Exhibiting the distribution of examination scores in a category.
- Visualizing the distribution of heights of people in a inhabitants.
- Illustrating the distribution of revenue ranges in a metropolis.
- Analyzing the distribution of ready instances at a customer support heart.
Key Variations Summarized:
| Function | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Information Kind | Categorical | Numerical (discrete or steady) |
| X-axis | Classes | Numerical intervals (bins) |
| Y-axis | Frequency or Proportion | Frequency or Density |
| Gaps between bars | Current | Absent |
| Goal | Evaluate classes, present proportions | Present knowledge distribution, reveal patterns |
Selecting Between Bar Charts and Histograms:
The selection between a bar chart and a histogram relies upon solely on the character of your knowledge. In case your knowledge is categorical, a bar chart is the suitable selection. In case your knowledge is numerical, a histogram is the higher choice for visualizing the information’s distribution. Utilizing the incorrect chart sort can result in misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions. As an example, utilizing a histogram for categorical knowledge could be inappropriate as it might indicate a steady relationship between classes that does not exist.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Issues
Each bar charts and histograms will be enhanced with varied options to enhance their readability and effectiveness. These embody:



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into distinction between a bar chart and histogram. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!