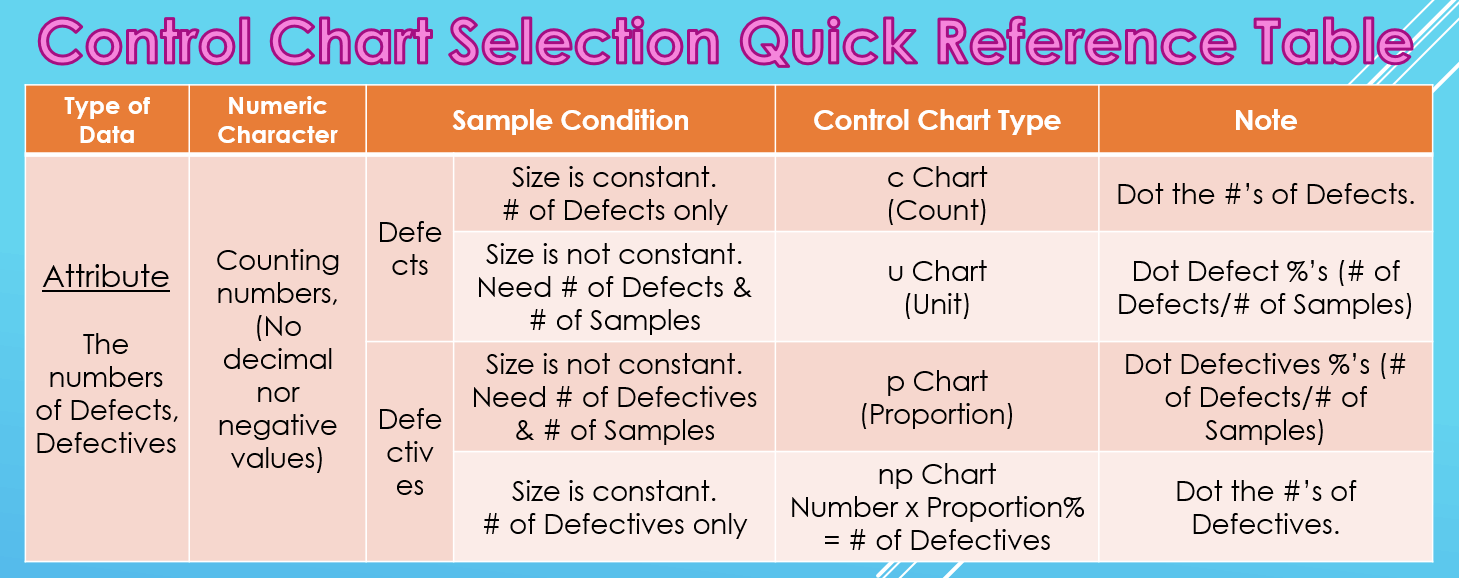
distinction between p chart and np chart
Associated Articles: distinction between p chart and np chart
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to distinction between p chart and np chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
P-Chart vs. NP-Chart: A Complete Comparability for Statistical Course of Management

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is an important instrument for monitoring and enhancing the standard of processes. Two generally used management charts for analyzing attribute knowledge – knowledge that represents the presence or absence of a attribute – are the p-chart and the np-chart. Whereas each goal to trace the proportion of nonconforming items, they differ considerably of their building and utility, resulting in distinct benefits and drawbacks in varied situations. This text offers a complete comparability of p-charts and np-charts, clarifying their variations, functions, and limitations.
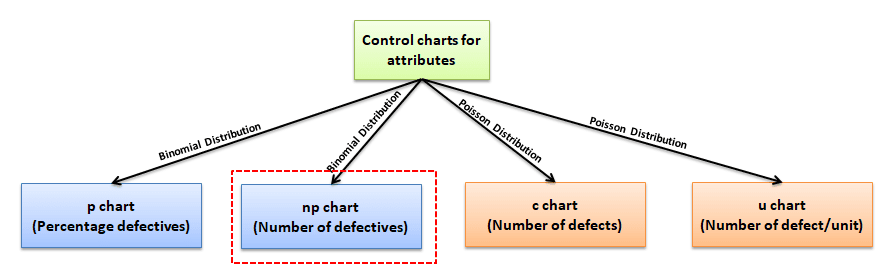
Understanding Attribute Information and Management Charts
Earlier than diving into the specifics of p-charts and np-charts, it is essential to know the context of attribute knowledge. In contrast to variable knowledge, which measures steady portions (e.g., weight, size, temperature), attribute knowledge classifies objects as conforming or nonconforming to a particular high quality attribute. As an illustration, a manufactured half could be categorized as "faulty" or "non-defective," a buyer survey response as "glad" or "dissatisfied," or a transaction as "fraudulent" or "respectable."
Management charts visually symbolize the variation in a course of over time. They assist establish factors the place the method deviates considerably from its anticipated conduct, indicating potential issues that require investigation and correction. The p-chart and np-chart are each designed for attribute knowledge, however they strategy the issue from barely totally different angles.
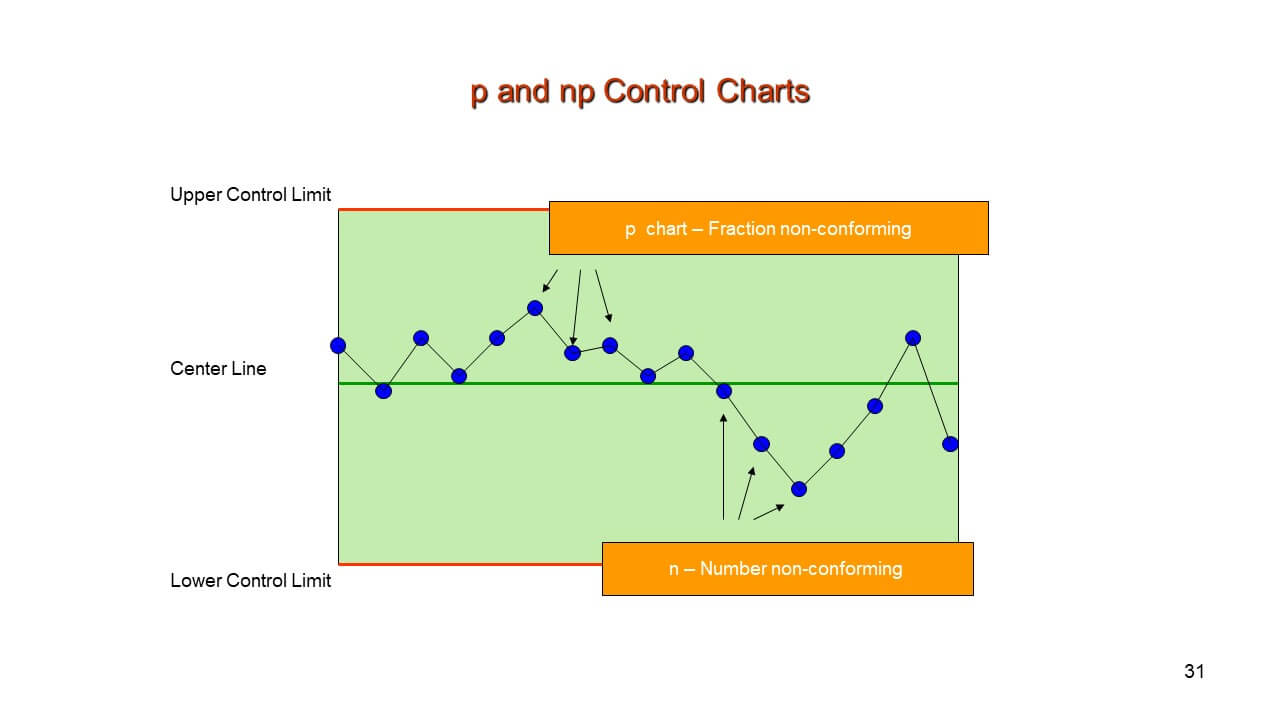
The P-Chart: Proportion of Nonconforming Items
The p-chart tracks the proportion of nonconforming items in a pattern. It is ideally suited when the pattern measurement varies from subgroup to subgroup. Think about a high quality management inspector checking batches of manufactured objects; some batches would possibly include 100 objects, whereas others would possibly include 500. The p-chart successfully handles this variability by specializing in the proportion of defects, no matter the pattern measurement.
Development of a P-Chart:
-
Information Assortment: Gather knowledge on the variety of nonconforming items (defectives) in every subgroup (pattern). File the pattern measurement (n) for every subgroup.
-
Calculate the Proportion of Nonconforming Items (p): For every subgroup, calculate p = (variety of defectives) / (pattern measurement).
-
Calculate the General Proportion of Nonconforming Items (p̄): That is the common of all the person p values calculated in step 2. This represents the central tendency of the method.
-
Calculate the Commonplace Deviation of the Proportion (σp): This measures the variability of the proportion of defectives. The formulation is: σp = √[p̄(1-p̄)/n̄], the place n̄ is the common pattern measurement throughout all subgroups.
-
Set up Management Limits: The management limits are sometimes set at three customary deviations from the central line (p̄). The higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) are calculated as follows:
- UCL = p̄ + 3σp
- LCL = p̄ – 3σp
Observe: If the LCL falls beneath zero, it is sometimes set to zero, as a proportion can’t be adverse.
-
Plot the Information: Plot the person p values for every subgroup on the chart, together with the central line (p̄) and the management limits (UCL and LCL).
The NP-Chart: Variety of Nonconforming Items
The np-chart tracks the quantity of nonconforming items in a pattern. It is best when the pattern measurement stays fixed throughout all subgroups. Take into account a scenario the place an organization constantly inspects batches of 100 widgets. The np-chart immediately shows the variety of faulty widgets in every batch.
Development of an NP-Chart:
-
Information Assortment: Gather knowledge on the variety of nonconforming items (defectives) in every subgroup (pattern). The pattern measurement (n) should be fixed for all subgroups.
-
Calculate the Common Variety of Nonconforming Items (np̄): That is the common variety of defectives throughout all subgroups. It is calculated as np̄ = n * p̄, the place p̄ is the general proportion of nonconforming items (calculated as within the p-chart).
-
Calculate the Commonplace Deviation of the Variety of Nonconforming Items (σnp): This measures the variability within the variety of defectives. The formulation is: σnp = √[n p̄ (1 – p̄)].
-
Set up Management Limits: The management limits are sometimes set at three customary deviations from the central line (np̄).
- UCL = np̄ + 3σnp
- LCL = np̄ – 3σnp
Just like the p-chart, if the LCL falls beneath zero, it is set to zero.
-
Plot the Information: Plot the variety of defectives (np) for every subgroup on the chart, together with the central line (np̄) and the management limits (UCL and LCL).
Key Variations Summarized:
| Characteristic | P-Chart | NP-Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Y-axis | Proportion of nonconforming items (p) | Variety of nonconforming items (np) |
| Pattern Dimension (n) | Variable | Fixed |
| Central Line | Common proportion (p̄) | Common variety of nonconforming items (np̄) |
| Management Limits | Based mostly on proportion and common pattern measurement | Based mostly on variety of nonconforming items |
| Software | Variable pattern sizes | Fixed pattern sizes |
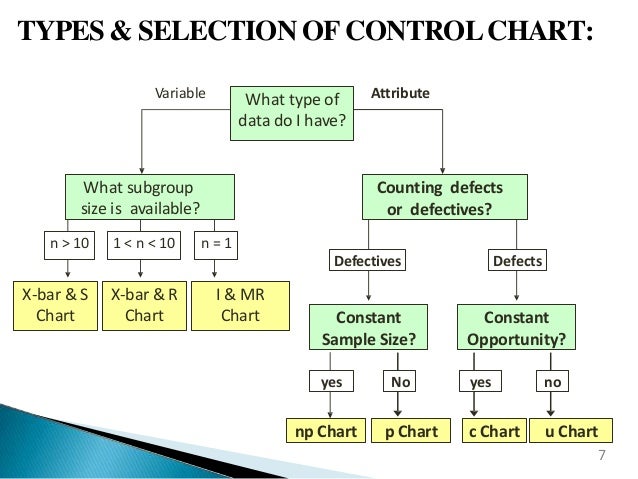
Selecting Between P-Chart and NP-Chart:
The selection between a p-chart and an np-chart relies upon totally on the consistency of the pattern measurement.
-
Use a p-chart when: Pattern sizes range considerably from subgroup to subgroup. That is frequent in conditions the place sampling is predicated on availability or comfort.
-
Use an np-chart when: Pattern sizes are fixed throughout all subgroups. This offers a extra simple interpretation of the variety of defects. It is typically most popular in conditions with standardized manufacturing processes.
Benefits and Disadvantages:
P-Chart:
Benefits:
- Handles variable pattern sizes successfully.
- Straight exhibits the proportion of defects, making interpretation simpler in some contexts.
Disadvantages:
- Barely extra complicated calculations in comparison with the np-chart.
- Management limits could be influenced by the variability in pattern sizes.
NP-Chart:
Benefits:
- Easier calculations and simpler interpretation.
- Extra delicate to adjustments within the variety of defects when pattern measurement is fixed.
Disadvantages:
- Not appropriate for conditions with variable pattern sizes.
- Won’t be as intuitive for evaluating processes with totally different pattern sizes.
Past the Fundamentals: Concerns for Sensible Software
Each p-charts and np-chart depend on a number of assumptions for correct interpretation. These embrace:
- Independence of observations: The standard of 1 merchandise mustn’t affect the standard of one other.
- Fixed course of parameters: The underlying course of needs to be secure (in management) apart from assignable causes of variation.
- Random sampling: Samples needs to be consultant of your entire course of.
- Enough pattern measurement: Smaller pattern sizes can result in much less exact management limits. A common guideline is to have a minimum of 25 subgroups for dependable management restrict estimation.
Failure to satisfy these assumptions can result in deceptive outcomes and inaccurate conclusions. Moreover, cautious consideration of the precise context and the character of the attribute knowledge is essential for choosing and deciphering the suitable management chart. Subtle statistical software program packages can assist within the building and evaluation of those charts, offering instruments for detecting patterns and particular causes of variation.
Conclusion:
The p-chart and np-chart are useful instruments for monitoring and enhancing the standard of processes that generate attribute knowledge. The selection between these two charts relies on whether or not the pattern measurement is fixed or variable. Understanding their variations, benefits, and limitations is essential for efficient utility in varied high quality management situations. By rigorously choosing and deciphering these charts, organizations can achieve useful insights into their processes and implement efficient methods for steady enchancment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into distinction between p chart and np chart. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!