Mastering Katakana: A Complete Information with Chart and Pronunciation
Associated Articles: Mastering Katakana: A Complete Information with Chart and Pronunciation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Mastering Katakana: A Complete Information with Chart and Pronunciation. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering Katakana: A Complete Information with Chart and Pronunciation

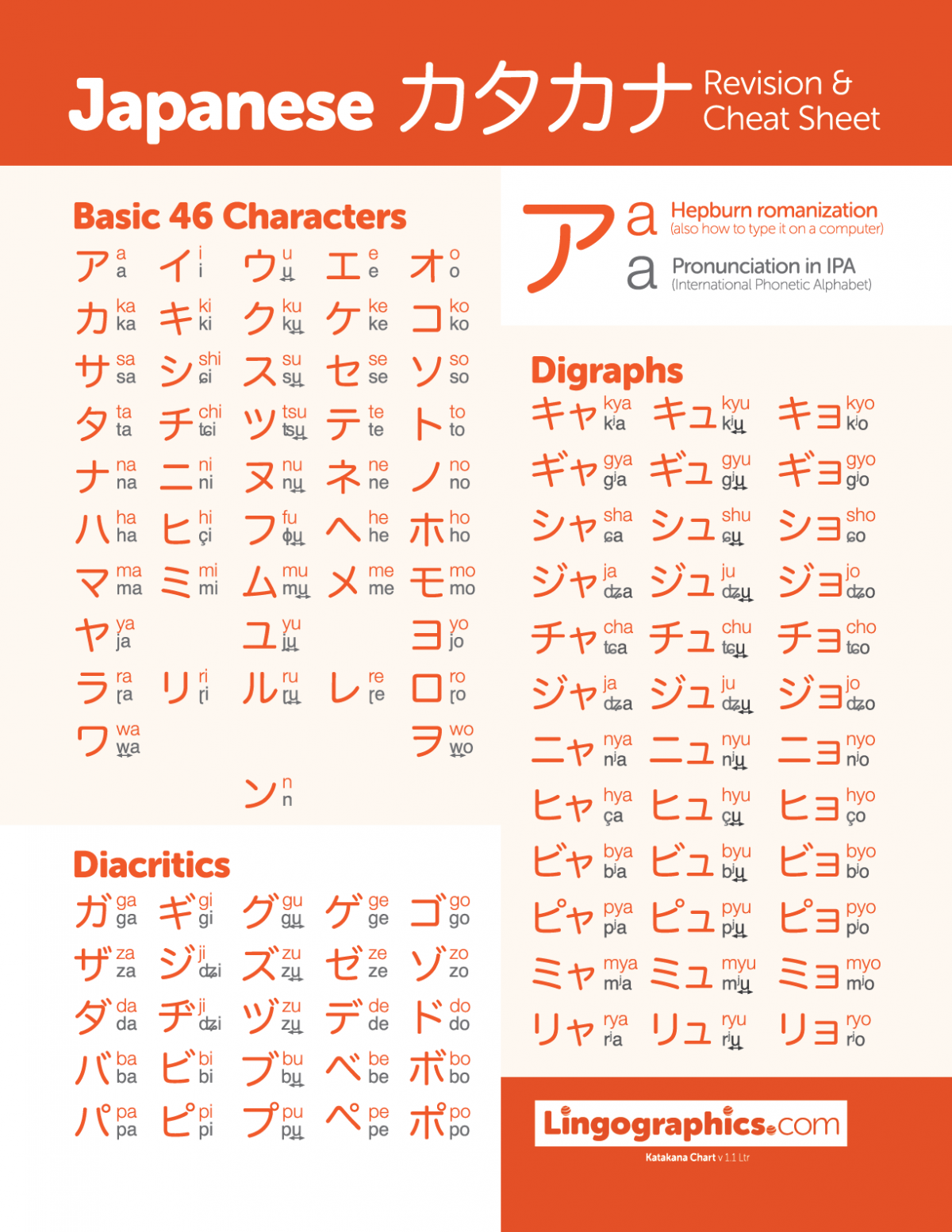
Katakana (カタカナ) is without doubt one of the three writing methods utilized in trendy Japanese, alongside hiragana and kanji. Not like hiragana, which is primarily used for native Japanese phrases, katakana is predominantly used for international loanwords, onomatopoeia, emphasis, and generally for scientific terminology. Understanding katakana is essential for anybody severe about studying Japanese, because it unlocks an unlimited vocabulary derived from different languages and permits for a deeper appreciation of the nuances of the Japanese language. This text gives a complete information to katakana, together with an in depth chart, pronunciation ideas, and examples to assist in your studying journey.
The Katakana Chart: A Basis for Studying
The next chart presents all the essential katakana characters, categorized for simpler memorization. Every character is accompanied by its romanization (utilizing Hepburn romanization, essentially the most extensively accepted system), and instance phrases as an example its utilization. Keep in mind that pronunciation could be barely nuanced relying on context and surrounding sounds.
| Character | Romanization | Instance Phrase (Romaji) | Instance Phrase (English Translation) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ア | a | アヒル (ahiru) | duck | |
| イ | i | イチゴ (ichigo) | strawberry | |
| ウ | u | ウサギ (usagi) | rabbit | |
| エ | e | エビ (ebi) | shrimp | |
| オ | o | オレンジ (orenji) | orange | |
| カ | ka | カバン ( kaban) | bag | |
| キ | ki | キリン (kirin) | giraffe | |
| ク | ku | クマ (kuma) | bear | |
| ケ | ke | ケーキ (keeki) | cake | |
| コ | ko | コアラ (koala) | koala | |
| サ | sa | サカナ (sakana) | fish | |
| シ | shi | シャツ (shatsu) | shirt | |
| ス | su | スプーン (supūn) | spoon | |
| セ | se | センス (sensu) | sense | |
| ソ | so | ソファ (couch) | couch | |
| タ | ta | タクシー (takushī) | taxi | |
| チ | chi | チケット (chiketto) | ticket | |
| ツ | tsu | ツール (tsūru) | software | Usually pronounced as "tsu" however can sound like "tu" relying on the context. |
| テ | te | テレホン (Terehon) | phone | |
| ト | to | トマト (tomato) | tomato | |
| ナ | na | ナンバー (nanbā) | quantity | |
| ニ | ni | ニンジン (ninjin) | carrot | |
| ヌ | nu | ニュース (nyūsu) | information | |
| ネ | ne | ネクタイ (nektai) | necktie | |
| ノ | no | ノート (nōto) | word | |
| ハ | ha | ハンバーガー (hanbāgā) | hamburger | |
| ヒ | hello | ヒト (hito) | particular person | |
| フ | fu | フルーツ (furūtsu) | fruit | |
| ヘ | he | ヘルメット (herumetto) | helmet | |
| ホ | ho | ホテル (hoteru) | lodge | |
| マ | ma | マシン (mashin) | machine | |
| ミ | mi | ミカン (mikan) | mandarin orange | |
| ム | mu | ミュージック (myūjikku) | music | |
| メ | me | メガネ (megane) | glasses | |
| モ | mo | モデル (moderu) | mannequin | |
| ヤ | ya | ヤクルト (yakuruto) | Yakult (a probiotic drink) | |
| ユ | yu | ユニット (yunitto) | unit | |
| ヨ | yo | ヨーグルト (yoguruto) | yogurt | |
| ラ | ra | ラジオ (rajio) | radio | |
| リ | ri | リモコン (rimokon) | distant management | |
| ル | ru | ルール (rūru) | rule | |
| レ | re | レコード (rekōdo) | document | |
| ロ | ro | ロケット (roketto) | rocket | |
| ワ | wa | ワシントン (Washinton) | Washington | |
| ヲ | wo | ヲタク (otaku) | otaku (obsessive fan) | Not often utilized in trendy Japanese. |
| ン | n | シンガー (singā) | singer | Represents the "n" sound. At all times follows a vowel. |
Pronunciation Nuances and Issues:
Whereas the romanization gives a basic information, mastering katakana pronunciation requires consideration to element. A number of factors warrant additional clarification:
-
Vowel Sounds: Japanese vowel sounds are usually pure and distinct, not like some English vowels which may have a number of pronunciations. Apply announcing every vowel individually to develop a transparent understanding.
-
Consonant Sounds: Many consonant sounds are just like English, however some delicate variations exist. As an example, the "r" sound in Japanese is extra of a flap of the tongue, not like the English "r." Equally, the "s" and "sh" sounds can differ barely.
-
Small "tsu" (っ): This character does not symbolize a sound by itself. It is a "sokuon" (促音), indicating a gemination (doubling) of the next consonant. For instance, "バッテン" (batten) has a doubled "t" sound.
-
"n" Sound (ん): The sound represented by "n" varies relying on the next sound. Earlier than a vowel, it is a easy "n" sound. Earlier than a consonant, it is a nasal sound just like the "n" in "sink." Earlier than a pause, it could possibly sound like an "m" or "ng."
-
Lengthy Vowels: In some phrases, vowels are lengthened to point a particular which means or emphasis. That is normally indicated by a macron (¯) over the vowel in romanization (e.g., "ō," "ē"). Listening to native audio system is essential to greedy the nuances of lengthy vowels.
-
Pitch Accent: Japanese makes use of pitch accent, which means the pitch of the voice adjustments inside a phrase. This isn’t mirrored in romanization and requires listening follow to grasp.
Past the Fundamentals: Combining Characters and Superior Utilization
Whereas the essential chart covers the elemental characters, understanding how they mix is important for studying extra advanced phrases. Katakana characters are mixed to symbolize international phrases and sounds that do not have direct equivalents in Japanese.
As an example, the phrase "pc" is written as コンピューター (konpyūtā). Discover how the katakana characters are used to approximate the English sounds. This skill to symbolize international sounds is a key attribute of katakana.
Moreover, katakana is usually used for emphasis or to create a stylistic impact. For instance, utilizing katakana for a phrase in a sentence can draw consideration to it, just like utilizing italics in English. This stylistic use provides one other layer of complexity and nuance to the language.
Studying Methods for Mastering Katakana:
Efficient studying includes a multi-faceted method:
-
Flashcards: Create flashcards with the katakana character on one aspect and its romanization and an instance phrase on the opposite. Common overview is essential.
-
Writing Apply: Repeatedly writing the characters helps to strengthen muscle reminiscence and enhance recognition.
-
Listening Apply: Hearken to Japanese audio and attempt to determine the katakana phrases used. Deal with pronunciation and intonation.
-
Immersion: Encompass your self with Japanese media, similar to anime, manga, or music, to come across katakana in context.
-
Make the most of On-line Assets: Quite a few web sites and apps provide interactive katakana studying instruments and quizzes.
-
Deal with Phrase Households: Group similar-looking characters collectively to assist memorization. For instance, characters with related radicals (components of the character) usually share associated sounds.
Conclusion:
Mastering katakana is an important step in your Japanese language journey. This text gives a strong basis, however constant follow and immersion are important for fluency. By understanding the characters, their pronunciation nuances, and their numerous purposes, you’ll unlock a good portion of the Japanese lexicon and improve your total comprehension of the language. Bear in mind to make the most of the assets obtainable and stay persistent in your efforts. With dedication and follow, you’ll confidently navigate the world of katakana and additional your Japanese language expertise.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Mastering Katakana: A Complete Information with Chart and Pronunciation. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!