Mastering the P Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes
Associated Articles: Mastering the P Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Mastering the P Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the P Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes
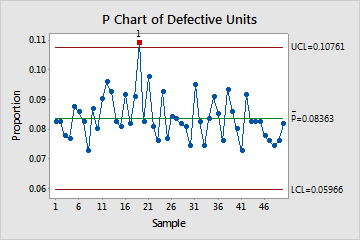
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is an important device for monitoring and enhancing manufacturing and repair processes. Whereas many SPC charts give attention to steady knowledge (like weight or temperature), a good portion of high quality management includes attributes – traits which can be both current or absent, conforming or non-conforming. The p-chart, a strong device inside Minitab Statistical Software program, is particularly designed for controlling the proportion of non-conforming models in a pattern. This text supplies a complete information to understanding, creating, deciphering, and troubleshooting p-charts inside Minitab, equipping you with the information to successfully make the most of this important high quality management instrument.
Understanding the Fundamentals of the P-Chart
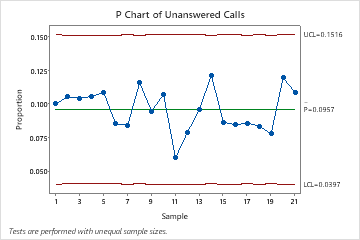
The p-chart, often known as a proportion chart, tracks the proportion (or proportion) of faulty objects in a pattern over time. In contrast to charts for steady knowledge like X-bar and R charts, the p-chart focuses on the fraction of defects, not the variety of defects itself. That is essential as a result of pattern sizes typically range in real-world functions. A p-chart successfully accounts for these variations, permitting for constant monitoring no matter pattern measurement fluctuations.
The important thing components of a p-chart embrace:
- Pattern Dimension (n): The variety of models inspected in every pattern. This may be fixed or variable throughout samples.
- Variety of Nonconforming Items (x): The depend of faulty or non-conforming models inside every pattern.
- Pattern Proportion (p): The proportion of nonconforming models in every pattern, calculated as x/n.
- Middle Line (p-bar): The common proportion of nonconforming models throughout all samples. This serves because the central tendency of the method.
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): The higher boundary past which the method is taken into account statistically uncontrolled. Factors exceeding the UCL point out potential issues.
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): The decrease boundary beneath which the method is taken into account statistically uncontrolled. Factors beneath the LCL may sign enhancements or point out uncommon circumstances.
Making a P-Chart in Minitab
Minitab simplifies the creation and evaluation of p-charts. The method includes these steps:
-
Knowledge Entry: Enter your knowledge into Minitab. You want at the least two columns: one for the pattern quantity (or subgroup identifier) and one other for the variety of nonconforming models in every pattern. A 3rd column specifying the pattern measurement for every subgroup can also be required if the pattern measurement varies.
-
Choosing the P-Chart Perform: Navigate to "Stat" > "Management Charts" > "Attributes Charts" > "P".
-
Knowledge Enter: Specify the columns containing the pattern quantity and the variety of nonconforming models. In case your pattern sizes range, it’s essential to additionally specify the column containing the pattern sizes.
-
Choices: Minitab supplies a number of choices to customise your p-chart, together with:
- Technique for estimating p-bar: You’ll be able to select to make use of the general common proportion of nonconforming models or a selected goal worth if identified.
- Management Limits: Minitab lets you select between customary deviation limits (based mostly on the binomial distribution) and different strategies.
- Subgroup sizes: Minitab lets you specify if the subgroup sizes are fixed or variable.
- Checks for particular causes: Minitab presents a number of checks to detect patterns indicating out-of-control conditions, equivalent to runs, traits, and unusually excessive or low factors. These checks assist establish assignable causes of variation.
-
Chart Technology: Click on "OK" to generate the p-chart. Minitab will show the chart, together with the middle line, management limits, and knowledge factors representing the pattern proportions.
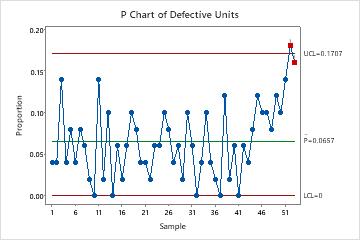
Decoding the P-Chart
Decoding a p-chart includes inspecting the plotted factors in relation to the management limits and heart line.
-
Factors inside the management limits: If all factors fall inside the UCL and LCL, the method is taken into account statistically in management. This means the method is steady and predictable.
-
Factors exterior the management limits: Factors exceeding the UCL or falling beneath the LCL point out a statistically vital deviation from the method common. This means the method is uncontrolled, and an investigation is required to establish and proper the assignable causes of variation.
-
Patterns inside the management limits: Even when all factors are inside the management limits, patterns like traits, cycles, or uncommon clustering can point out potential issues. These patterns may not be statistically vital sufficient to set off an out-of-control sign however nonetheless warrant investigation. Minitab’s checks for particular causes spotlight such patterns.
Troubleshooting and Superior Concerns
A number of components can affect the effectiveness and interpretation of a p-chart:
-
Pattern Dimension: A bigger pattern measurement typically results in extra exact estimates of the method proportion and narrower management limits. Nonetheless, extraordinarily massive pattern sizes can masks small shifts within the course of.
-
Course of Stability: The p-chart assumes the method is steady when calculating the management limits. If the method is considerably unstable, the management limits could also be unreliable. It is essential to make sure course of stability earlier than producing a p-chart.
-
Non-Normality: The p-chart depends on the binomial distribution, which assumes a continuing chance of nonconformity. If this assumption is violated, the chart’s interpretation could also be much less dependable.
-
Knowledge Transformation: In conditions with extremely skewed knowledge or vital variation in pattern sizes, knowledge transformations is likely to be essential to enhance the chart’s efficiency and interpretation.
-
Utilizing a Goal Worth: If a goal proportion of nonconforming models exists, you should use this worth to calculate the middle line, enhancing the chart’s interpretability.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Functions and Extensions
The p-chart types the inspiration for a number of superior functions inside Minitab and the broader discipline of SPC:
-
C-Chart: When the pattern measurement is fixed, a c-chart, which tracks the variety of nonconformities moderately than the proportion, can be utilized. Minitab readily permits for the creation and evaluation of c-charts.
-
U-Chart: For conditions with various pattern sizes and a give attention to the variety of nonconformities per unit, a u-chart is suitable. This chart normalizes for the variable pattern sizes, offering a constant measure of nonconformity charge.
-
Multivariate Management Charts: For processes with a number of attributes, multivariate management charts can be utilized to concurrently monitor a number of traits.
-
Time Collection Evaluation: Combining p-charts with time sequence evaluation may help establish the foundation causes of course of variation and predict future efficiency.
-
Functionality Evaluation: After establishing course of management, functionality evaluation can assess the method’s capacity to fulfill predefined high quality specs.
Conclusion
The p-chart is a strong device inside Minitab for monitoring and enhancing processes involving attributes. By understanding its rules, successfully using Minitab’s capabilities, and deciphering the outcomes rigorously, high quality professionals can considerably improve course of management, scale back defects, and enhance total services or products high quality. This text has offered a complete overview of p-chart creation, interpretation, and troubleshooting, equipping readers with the information to leverage this important SPC approach for efficient high quality administration. Keep in mind that correct knowledge assortment and understanding of the underlying course of are essential for profitable software and interpretation of any statistical course of management chart, together with the p-chart. Constant monitoring and proactive investigation of out-of-control indicators are key to attaining steady enchancment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Mastering the P Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!