Mastering X-bar and R Charts in Excel: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Associated Articles: Mastering X-bar and R Charts in Excel: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Mastering X-bar and R Charts in Excel: A Complete Information to Course of Management. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering X-bar and R Charts in Excel: A Complete Information to Course of Management

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is an important instrument for monitoring and enhancing manufacturing and enterprise processes. Among the many most generally used SPC charts are the X-bar and R charts, which observe the typical (X-bar) and vary (R) of a course of over time. These charts successfully spotlight variations in a course of, enabling well timed intervention to stop defects and preserve constant high quality. Whereas specialised statistical software program exists, Excel, with its available knowledge evaluation instruments and add-ins, gives a robust and accessible platform for creating and deciphering X-bar and R charts. This text will information you thru the method of making and understanding X-bar and R charts in Excel, overlaying knowledge preparation, chart building, interpretation, and potential limitations.
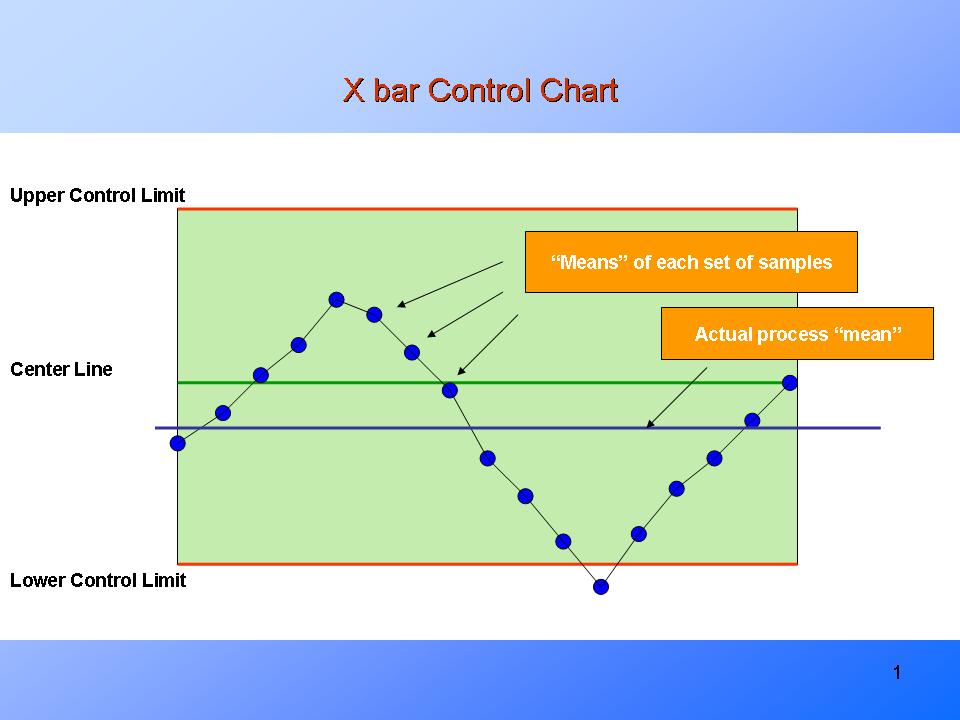
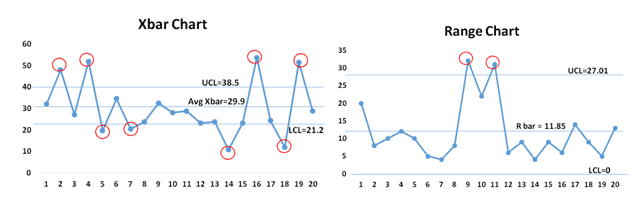
1. Understanding X-bar and R Charts
The X-bar chart displays the central tendency of a course of, representing the typical of subgroups of information collected at common intervals. The R chart, then again, tracks the variability inside every subgroup, particularly the vary (the distinction between the most important and smallest values). By analyzing each charts concurrently, we acquire a complete understanding of course of stability.
-
X-bar Chart: This chart visually represents the typical of every subgroup. Traits, shifts, or uncommon patterns within the X-bar chart point out potential issues with the method imply. Management limits are calculated to outline the appropriate vary for the typical. Factors outdoors these limits counsel a course of that’s uncontrolled.
-
R Chart: This chart shows the vary of every subgroup, illustrating the variability inside every pattern. A steady course of will exhibit constant variability throughout the management limits. Factors outdoors the management limits counsel extreme variability, indicating a possible drawback with the method dispersion.
Utilizing each charts collectively gives a extra full image than both chart alone. A course of could be thought-about statistically steady (in management) provided that each the X-bar and R charts present no factors outdoors the management limits and no discernible patterns throughout the management limits.
2. Knowledge Preparation: The Basis of Efficient SPC
Earlier than developing the charts, meticulous knowledge preparation is important. The information needs to be collected systematically, guaranteeing:
-
Subgroup Dimension: Subgroups needs to be of constant dimension (usually 4-5 knowledge factors). Bigger subgroups scale back the sensitivity to small variations, whereas smaller subgroups could also be extra inclined to random fluctuations. The optimum subgroup dimension relies on the precise course of and knowledge traits.
-
Rational Subgrouping: Knowledge needs to be collected in a approach that displays the pure variation throughout the course of. Subgroups ought to symbolize samples taken underneath comparable situations (e.g., identical machine, operator, time of day).
-
Knowledge Integrity: Guarantee accuracy and completeness of the information. Errors in knowledge entry can considerably distort the outcomes and result in misinterpretations. Often test for outliers and potential knowledge entry errors.
-
Enough Knowledge: A enough variety of subgroups is essential for dependable outcomes. Typically, a minimum of 20-25 subgroups are beneficial for a sturdy evaluation. Fewer subgroups might result in inaccurate management limits and unreliable conclusions.
3. Establishing X-bar and R Charts in Excel
Excel gives a number of strategies for creating X-bar and R charts. Whereas the built-in charting instruments are restricted, utilizing the Knowledge Evaluation ToolPak gives a extra sturdy resolution.
-
Putting in the Knowledge Evaluation ToolPak: If not already put in, go to File > Choices > Add-Ins > Handle: Excel Add-ins > Go. Test the "Evaluation ToolPak" field and click on OK.
-
Coming into Knowledge: Set up your knowledge in columns, with every column representing a subgroup and every row representing an information level inside a subgroup.
-
Utilizing the Knowledge Evaluation ToolPak: Go to Knowledge > Knowledge Evaluation > Descriptive Statistics. Choose your knowledge vary, selecting the "Abstract statistics" choice. It will present fundamental descriptive statistics for every subgroup. Whereas this does not immediately create the charts, it gives the required abstract knowledge for handbook chart building or use with different instruments.
-
Guide Chart Development: Utilizing the abstract statistics, you may manually create the charts. Calculate the X-bar (common) and R (vary) for every subgroup. Then, create separate charts for X-bar and R, plotting the values towards the subgroup quantity. Management limits will have to be calculated utilizing statistical formulation (defined within the subsequent part).
-
Utilizing Add-ins (e.g., XLSTAT): A number of Excel add-ins supply superior statistical capabilities, together with computerized X-bar and R chart technology. These add-ins usually present extra refined options like computerized management restrict calculation, functionality evaluation, and extra detailed interpretations.
4. Calculating Management Limits
Management limits are essential for deciphering the charts. They outline the appropriate vary of variation for the method. Factors outdoors these limits point out potential issues. Management limits are usually calculated utilizing the next formulation:
-
X-bar Chart Management Limits:
- Central Line (CL): Common of all subgroup averages (X-double bar)
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
R Chart Management Limits:
- Central Line (CL): Common of all subgroup ranges (R-bar)
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): D4 * R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): D3 * R-bar
The place A2, D3, and D4 are constants that depend upon the subgroup dimension (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or could be calculated utilizing statistical software program.
5. Deciphering X-bar and R Charts
As soon as the charts are constructed, interpretation entails figuring out patterns and deviations that counsel course of instability. Key indicators of out-of-control processes embrace:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: That is the obvious signal of course of instability. Examine the causes of those outliers.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward development suggests a gradual shift within the course of imply or variability.
-
Cycles or patterns: Recurring patterns point out the presence of predictable variations, usually associated to time-related elements.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors round particular values suggests the presence of subgroups with totally different traits.
-
Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or beneath the central line can point out a shift within the course of.
6. Limitations of X-bar and R Charts
Whereas X-bar and R charts are highly effective instruments, they’ve limitations:
-
Assumption of normality: The management limits are primarily based on the idea of usually distributed knowledge. If the information is considerably non-normal, the management limits could also be inaccurate.
-
Sensitivity to subgroup dimension: The selection of subgroup dimension impacts the sensitivity of the charts. Incorrect subgroup dimension can result in misinterpretations.
-
Restricted skill to determine particular causes: Whereas the charts spotlight issues, they don’t determine the basis causes. Additional investigation is critical to pinpoint the supply of variations.
-
Not appropriate for all processes: X-bar and R charts are only for steady knowledge. They aren’t appropriate for attributes knowledge (e.g., variety of defects).
7. Conclusion
X-bar and R charts are important instruments for monitoring and enhancing course of stability. Excel, with its available instruments and add-ins, gives a robust platform for developing and deciphering these charts. Nevertheless, correct knowledge preparation, correct management restrict calculation, and cautious interpretation are essential for acquiring significant outcomes. Understanding the restrictions of those charts and supplementing them with different statistical methods, as needed, is important for complete course of enchancment. Do not forget that efficient SPC isn’t just about creating charts; it’s about utilizing the data they supply to make data-driven choices and repeatedly enhance processes. By mastering the usage of X-bar and R charts in Excel, you may considerably improve your skill to observe and enhance high quality in numerous functions.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Mastering X-bar and R Charts in Excel: A Complete Information to Course of Management. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!