The Chart of Accounts: Spine of Monetary Administration
Associated Articles: The Chart of Accounts: Spine of Monetary Administration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to The Chart of Accounts: Spine of Monetary Administration. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Chart of Accounts: Spine of Monetary Administration
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-accounts.asp_final-438b76f8e6e444dd8f4cd8736b0baa6a.png)
The chart of accounts (COA) is the bedrock of any group’s monetary reporting system. It is a structured checklist of all of the accounts utilized by a enterprise to document its monetary transactions. Consider it as an in depth, categorized index of each monetary exercise – from receiving funds to paying suppliers, recording property, and monitoring liabilities. A well-designed chart of accounts is essential for correct monetary reporting, environment friendly monetary administration, and knowledgeable decision-making. This text will delve into the intricacies of a chart of accounts, exploring its construction, design issues, and the impression it has on a corporation’s monetary well being.
Understanding the Construction: A Hierarchical System
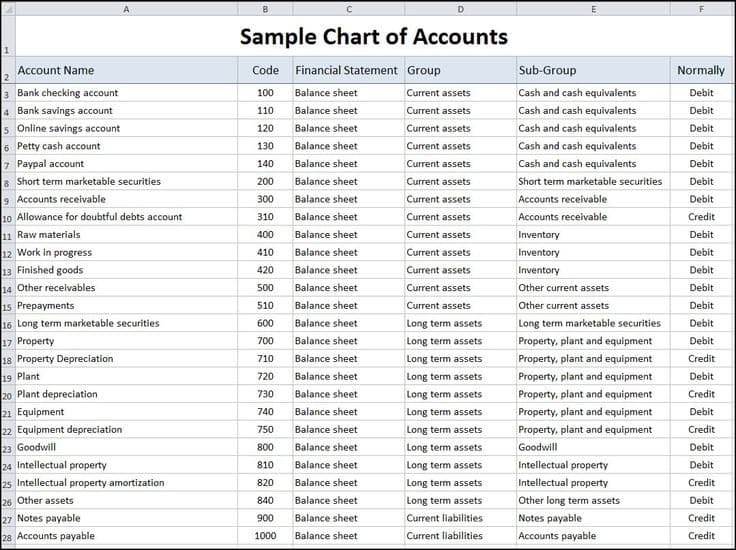
A chart of accounts is a hierarchical system, sometimes organized utilizing a numbering system that enables for detailed categorization and sub-categorization of accounts. This construction facilitates straightforward navigation and reporting. The most typical construction follows a basic ledger format, dividing accounts into main classes, then sub-categories, and eventually, particular person accounts. These classes typically align with the basic accounting equation: Belongings = Liabilities + Fairness.
Main Account Classes:
-
Belongings: These characterize what an organization owns. They’re additional categorized into:
- Present Belongings: Belongings anticipated to be transformed into money or used inside one yr (e.g., money, accounts receivable, stock, pay as you go bills).
- Non-Present Belongings (Lengthy-term Belongings): Belongings with a lifespan exceeding one yr (e.g., property, plant, and gear (PP&E), intangible property like patents and copyrights, long-term investments).
-
Liabilities: These characterize what an organization owes to others. They’re additionally categorized into:
- Present Liabilities: Obligations due inside one yr (e.g., accounts payable, salaries payable, short-term loans).
- Non-Present Liabilities (Lengthy-term Liabilities): Obligations due in a couple of yr (e.g., long-term loans, bonds payable).
-
Fairness: This represents the house owners’ stake within the firm. For sole proprietorships and partnerships, this is likely to be a easy proprietor’s fairness account. For companies, it is extra complicated, together with:
- Frequent Inventory: Represents the possession shares issued to traders.
- Retained Earnings: Collected earnings that haven’t been distributed as dividends.
- Treasury Inventory: Firm’s personal shares repurchased from the market.
Income and Expense Accounts: These accounts are essential for measuring profitability. They’re sometimes included throughout the fairness part, as web revenue will increase retained earnings.
- Income Accounts: Report revenue generated from the core enterprise operations (e.g., gross sales income, service income, curiosity income).
- Expense Accounts: Report the prices incurred in producing income (e.g., value of products bought (COGS), salaries expense, hire expense, advertising expense).
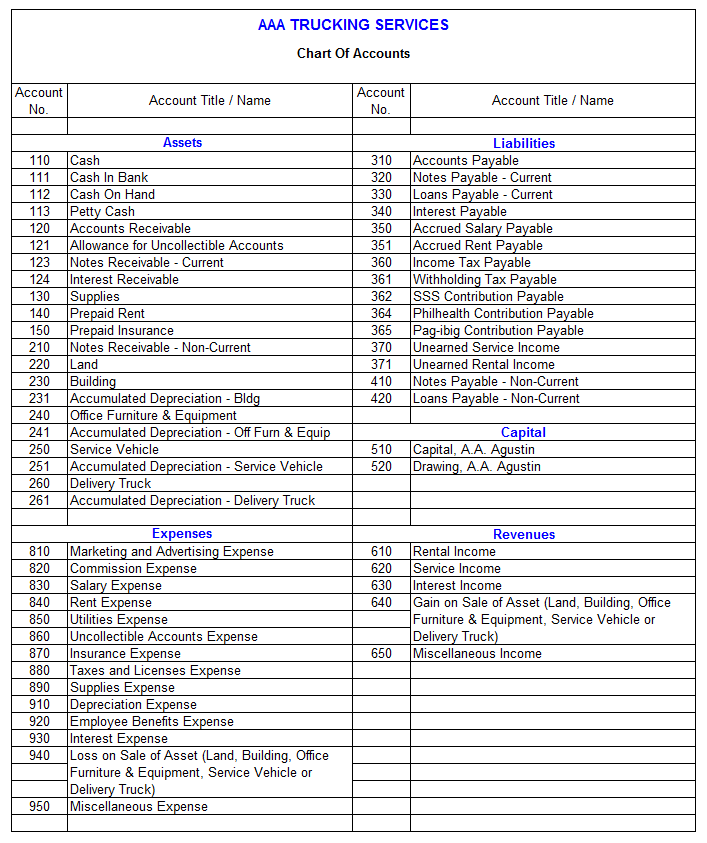
Numbering System:
The numbering system inside a chart of accounts is important for group and reporting. A typical method is to make use of a hierarchical numbering system, typically with a set variety of digits for every degree. For instance:
- 1000-1999: Belongings
- 2000-2999: Liabilities
- 3000-3999: Fairness
- 4000-4999: Income
- 5000-5999: Bills
Inside every class, additional sub-accounts could be added. For instance, throughout the 1000-1999 Asset class:
- 1100: Money
- 1200: Accounts Receivable
- 1300: Stock
- 1400: Pay as you go Bills
This detailed numbering system ensures that each transaction is precisely categorized and could be simply positioned for reporting functions.
Designing a Chart of Accounts: Key Issues
Creating an efficient chart of accounts requires cautious planning and consideration of the group’s particular wants. Listed here are some key elements to contemplate:
- Trade Specifics: The chart of accounts ought to mirror the distinctive facets of the trade. A producing firm may have totally different account wants than a service-based enterprise.
- Firm Measurement and Complexity: A small enterprise may want an easier COA than a big multinational company.
- Future Development: The COA must be versatile sufficient to accommodate future development and growth.
- Reporting Necessities: The COA have to be designed to generate the studies required by administration, traders, and regulatory our bodies.
- Accounting Software program Compatibility: The COA must be appropriate with the group’s accounting software program. Most accounting software program packages enable for personalisation of the COA.
Sustaining and Updating the Chart of Accounts:
A chart of accounts will not be a static doc. Because the enterprise grows and evolves, the COA must be up to date to mirror these adjustments. This may contain including new accounts, modifying present accounts, or deleting out of date accounts. Common critiques and updates make sure the COA stays related and correct.
Influence on Monetary Reporting and Choice Making:
A well-designed and maintained chart of accounts is instrumental in producing correct and dependable monetary statements. This, in flip, permits for knowledgeable decision-making. Correct monetary knowledge gives insights into profitability, liquidity, solvency, and total monetary well being. This info is essential for:
- Efficiency Analysis: Assessing the efficiency of various departments or product traces.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Growing correct budgets and monetary forecasts.
- Funding Selections: Making knowledgeable choices about investments and capital expenditures.
- Compliance: Assembly regulatory reporting necessities.
Conclusion:
The chart of accounts is excess of only a checklist of accounts; it is a basic instrument for managing and understanding a enterprise’s funds. A well-structured, complete, and frequently up to date chart of accounts is important for correct monetary reporting, environment friendly monetary administration, and knowledgeable decision-making. Investing the effort and time to create and preserve a strong chart of accounts is an funding within the long-term monetary well being and success of any group. Understanding its construction, design issues, and its impression on monetary reporting is essential for anybody concerned within the monetary administration of a enterprise, from small entrepreneurs to giant company finance groups. Ignoring the significance of a well-designed COA can result in inaccurate monetary reporting, hindering efficient decision-making and doubtlessly jeopardizing the monetary stability of the group.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into The Chart of Accounts: Spine of Monetary Administration. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!