The Japanese Inventory Market Crash of 1990: A Chart-Pushed Evaluation and Lasting Legacy
Associated Articles: The Japanese Inventory Market Crash of 1990: A Chart-Pushed Evaluation and Lasting Legacy
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The Japanese Inventory Market Crash of 1990: A Chart-Pushed Evaluation and Lasting Legacy. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Japanese Inventory Market Crash of 1990: A Chart-Pushed Evaluation and Lasting Legacy

The Japanese inventory market, as soon as an emblem of financial dynamism and seemingly unstoppable progress, skilled a devastating crash starting in 1990, a interval also known as the "Misplaced Decade" (and even "Misplaced Two A long time"). This text will delve into the intricacies of this crash, using chart evaluation to know its development, determine key turning factors, and discover the lingering penalties that proceed to form Japan’s financial panorama at this time.
The Bubble Economic system and its Inevitable Burst:
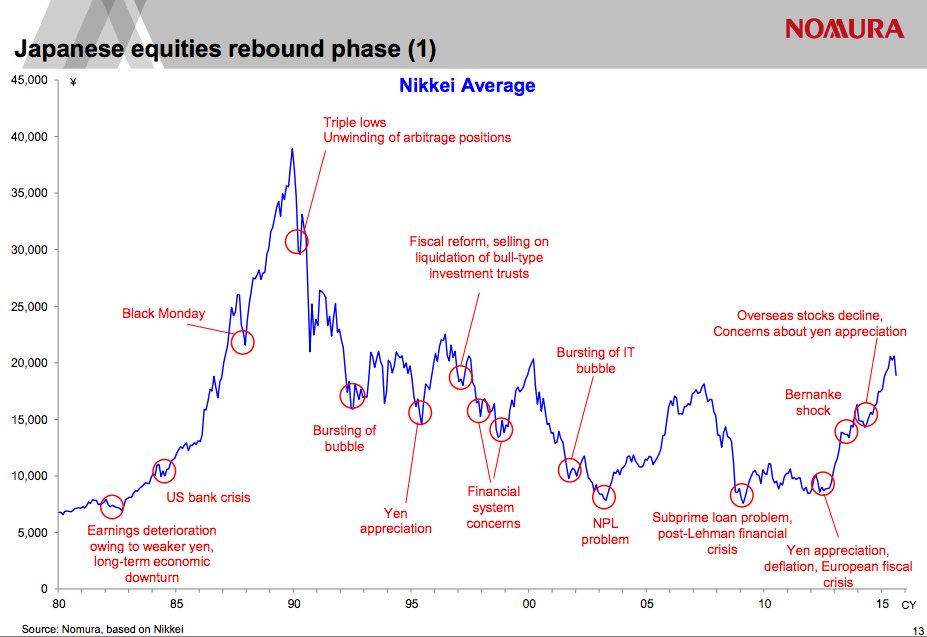
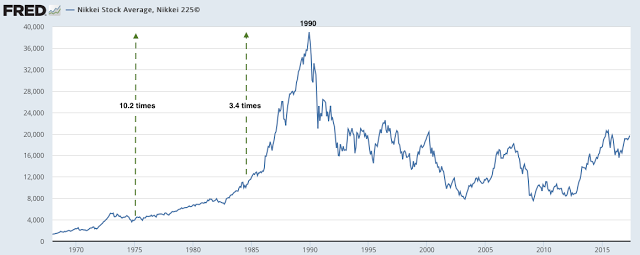
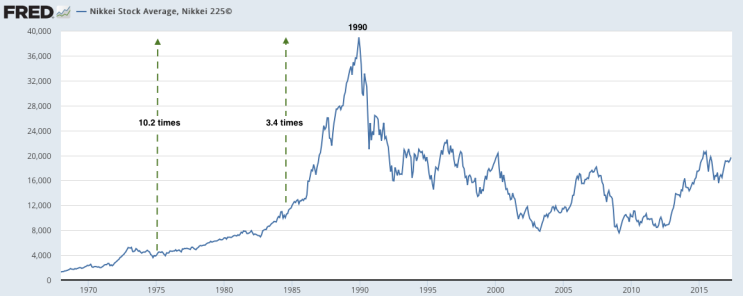
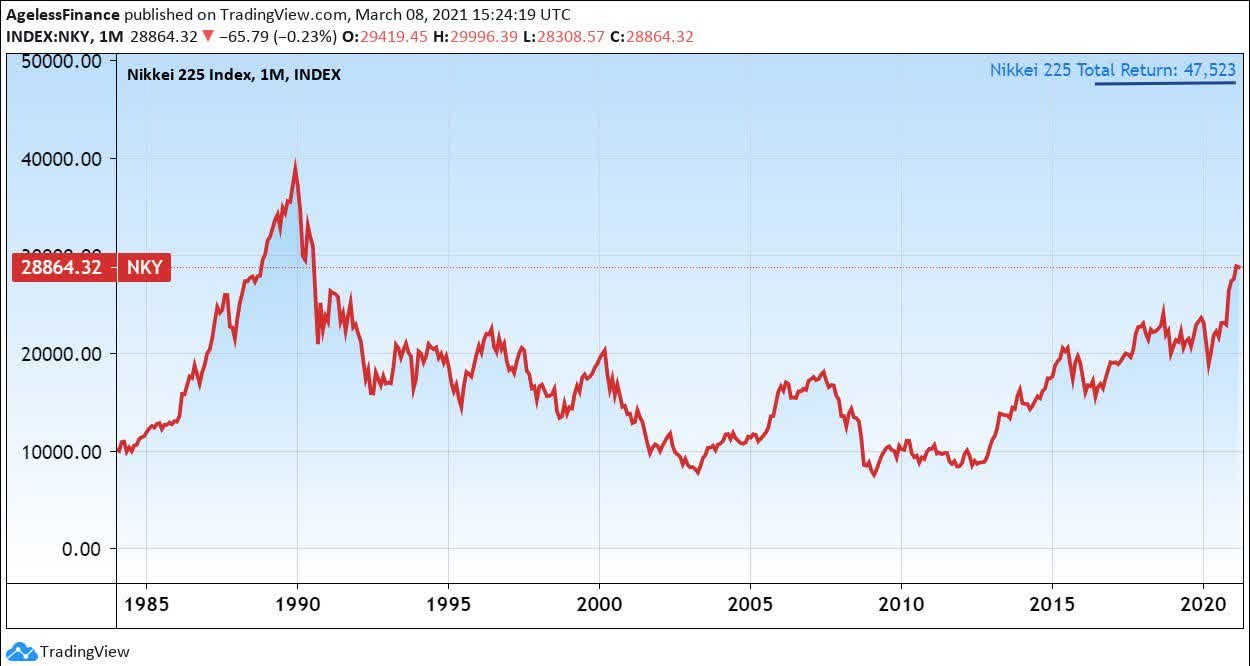
The previous years witnessed the formation of an enormous asset bubble, fueled by unfastened financial coverage, aggressive lending practices by banks, and a speculative frenzy. The Nikkei 225 index, Japan’s benchmark inventory market index, soared to unprecedented heights, peaking at 38,957.44 on December 29, 1989. (Insert chart right here: Nikkei 225 index from 1980-2000, highlighting the height in late 1989 and the following decline) This chart vividly illustrates the fast ascent, adopted by the equally dramatic collapse.
A number of elements contributed to this bubble:
- Simple Financial Coverage: The Financial institution of Japan’s low rates of interest inspired extreme borrowing and funding, fueling speculative actions in actual property and shares.
- Speculative Investments: A tradition of hypothesis and herd mentality drove buyers to chase returns with out enough due diligence, making a self-reinforcing cycle of value will increase.
- Actual Property Growth: Concurrently, an enormous actual property bubble inflated property values to unsustainable ranges, additional exacerbating the general asset bubble. (Insert chart right here: Japanese land costs from 1980-2000, displaying the height and subsequent decline, probably overlaid with the Nikkei 225 for comparability) This chart would display the sturdy correlation between the inventory market and actual property booms and busts.
- Overvalued Property: The elemental worth of many corporations and properties was far beneath their market costs, making the market inherently susceptible to a correction.
The Crash and its Phases:
The crash wasn’t a single occasion however reasonably a protracted decline characterised by a number of phases:
- Preliminary Plunge (1990-1992): The preliminary part witnessed a fast and important drop within the Nikkei 225, as buyers started to comprehend the unsustainable nature of the bubble. The bursting of the true property bubble performed an important function, triggering a wave of bankruptcies and defaults. (Insert chart element right here: Specializing in the interval 1990-1992, highlighting key drops and volatility) This zoomed-in chart would emphasize the sharp preliminary decline.
- Consolidation and Volatility (1992-1998): This era was characterised by important volatility and a chronic interval of sideways buying and selling, with the market struggling to discover a steady footing. Repeated makes an attempt at restoration have been thwarted by underlying financial weaknesses and the lingering results of the debt disaster. (Insert chart element right here: Specializing in the interval 1992-1998, showcasing the sideways motion and occasional sharp drops) This part would visually display the extended interval of uncertainty.
- Lingering Stagnation (1998-2000): The market continued to languish, failing to regain its pre-crash ranges. The extended interval of low progress and deflation solidified the "Misplaced Decade" label. (Insert chart element right here: Specializing in the interval 1998-2000, illustrating the gradual, gradual decline and the failure to get better) This is able to spotlight the persistent weak point and the failure to realize a significant rebound.
Key Chart Indicators in the course of the Crash:
Analyzing the charts reveals a number of key indicators that characterised the crash:
- Quantity: Excessive buying and selling volumes in the course of the preliminary plunge indicated panic promoting and a insecurity available in the market. (Illustrate this with a quantity indicator on the value chart) Decrease volumes in the course of the later phases recommend decreased participation and an absence of investor enthusiasm.
- Shifting Averages: The breakdown of key shifting averages (e.g., 200-day, 50-day) supplied sturdy affirmation of the bearish pattern. (Present examples of shifting averages on the chart) These would present the numerous pattern modifications and the failure of makes an attempt to regain assist ranges.
- Assist and Resistance Ranges: The repeated failure of the market to interrupt by key assist ranges indicated the depth of the bearish sentiment. (Spotlight these ranges on the chart) This is able to illustrate the constant downward strain and the dearth of shopping for curiosity.
Lengthy-Time period Penalties:
The Japanese inventory market crash had profound and lasting penalties:
- Deflation: The crash contributed to a chronic interval of deflation, which hampered financial progress and discouraged funding.
- Banking Disaster: The collapse of asset values led to a banking disaster, with quite a few monetary establishments battling unhealthy loans and non-performing property.
- Misplaced Decade(s): The extended financial stagnation led to a big decline in residing requirements and a lack of confidence within the Japanese financial mannequin.
- Demographic Challenges: The financial downturn exacerbated current demographic challenges, reminiscent of an ageing inhabitants and declining delivery charges.
Classes Discovered:
The Japanese inventory market crash serves as a cautionary story concerning the risks of asset bubbles, unfastened financial coverage, and speculative funding. It highlights the significance of sound financial fundamentals, prudent regulation, and a balanced strategy to financial progress. The expertise additionally underscores the numerous long-term penalties of financial crises, even a long time after the preliminary occasion. The restoration, whereas gradual and uneven, demonstrates the resilience of the Japanese economic system, but additionally the lasting scars of the "Misplaced Decade(s)."
(Conclusion):
The charts present a robust visible illustration of the dramatic occasions surrounding the Japanese inventory market crash of 1990. By analyzing the patterns and indicators, we acquire a deeper understanding of the elements that contributed to the disaster and its lasting influence on the Japanese economic system. Whereas the Nikkei has seen durations of restoration since then, the crash stays a pivotal second in Japanese financial historical past, a reminder of the fragility of monetary markets and the significance of sustainable financial insurance policies. Additional analysis into particular firm performances and governmental responses would offer even richer insights into this complicated historic occasion. (Embody a ultimate chart displaying the Nikkei 225 from 2000 to the current, illustrating the eventual restoration and volatility.) This ultimate chart would offer a way of closure and present the long-term perspective available on the market’s efficiency after the crash.



/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/46696946/GettyImages-110050440.0.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into The Japanese Inventory Market Crash of 1990: A Chart-Pushed Evaluation and Lasting Legacy. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!