The pH Chart and Nutrient Availability: A Complete Information for Plant Well being
Associated Articles: The pH Chart and Nutrient Availability: A Complete Information for Plant Well being
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to The pH Chart and Nutrient Availability: A Complete Information for Plant Well being. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The pH Chart and Nutrient Availability: A Complete Information for Plant Well being

The pH of your soil or rising medium is a vital issue influencing the provision of important vitamins to your crops. Understanding the connection between pH and nutrient uptake is key to profitable gardening, farming, and hydroponics. This text delves into the intricacies of the pH chart, explaining how completely different pH ranges have an effect on nutrient solubility and uptake, and providing sensible methods for managing soil pH to optimize plant well being and yield.
Understanding the pH Scale:
The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of an answer, starting from 0 to 14. A pH of seven is taken into account impartial. Values beneath 7 point out acidity, whereas values above 7 point out alkalinity. Every entire quantity change on the size represents a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity. For instance, a pH of 6 is ten instances extra acidic than a pH of seven, and a pH of 5 is ten instances extra acidic than a pH of 6. This logarithmic scale highlights the numerous impression even small pH fluctuations can have on plant nutrient availability.
The Impression of pH on Nutrient Availability:
Completely different vitamins exhibit various solubility and availability throughout the pH vary. Whereas the perfect pH vary varies barely relying on the plant species, most crops thrive inside a comparatively slim vary, usually between 6.0 and seven.0. Outdoors this optimum vary, the provision of a number of important vitamins might be severely compromised, resulting in nutrient deficiencies and stunted development.
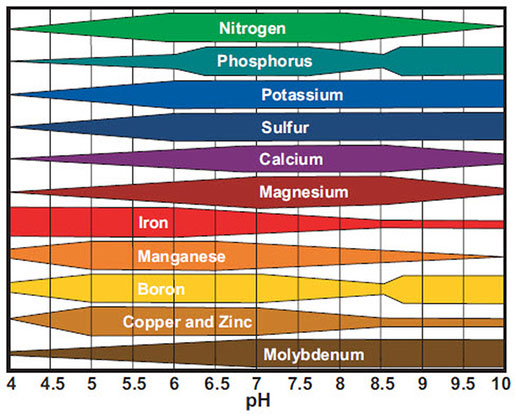
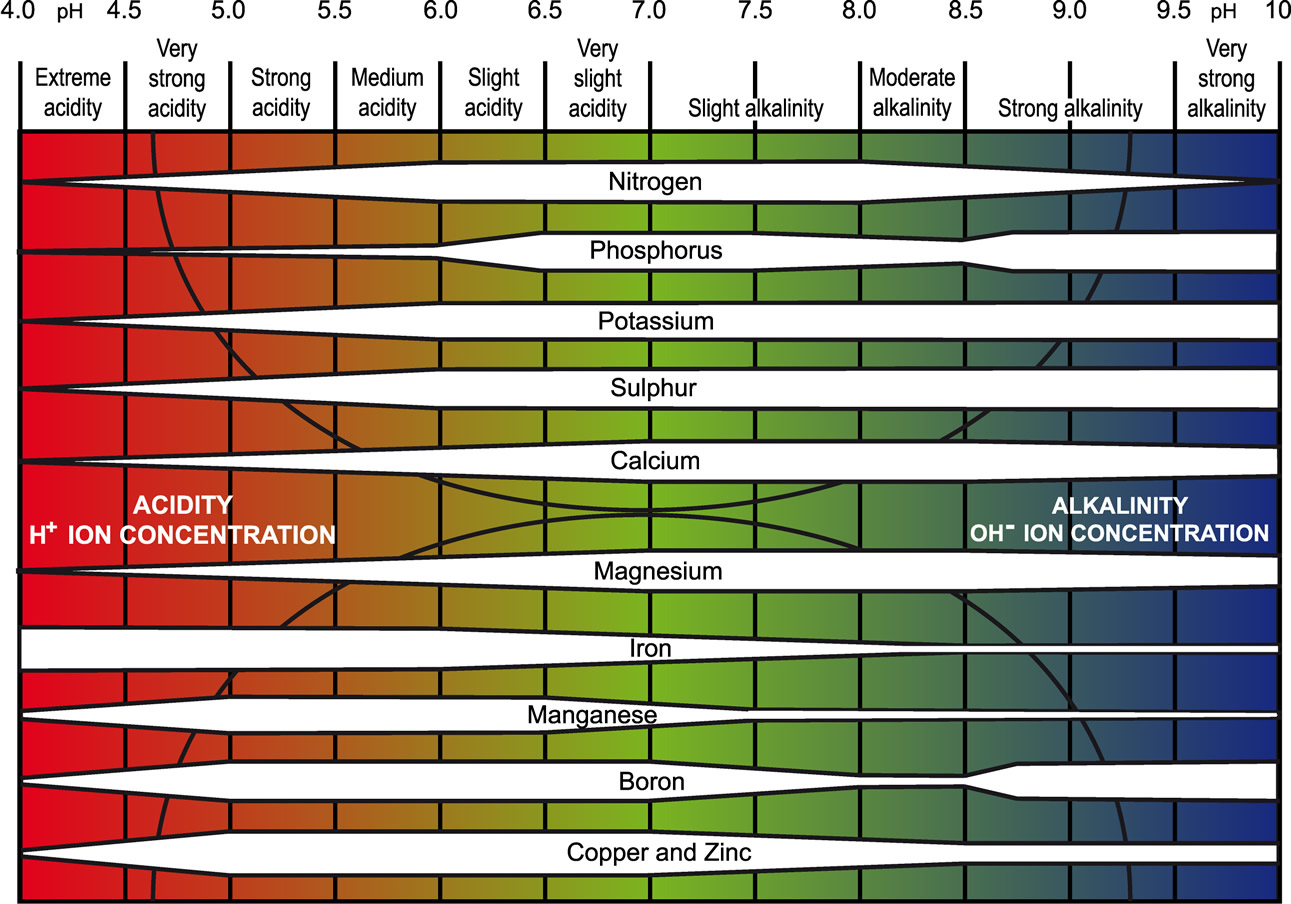
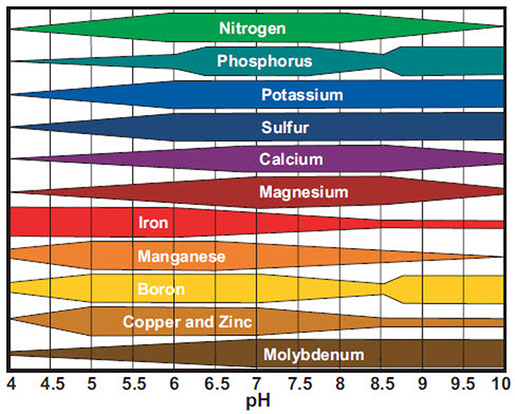
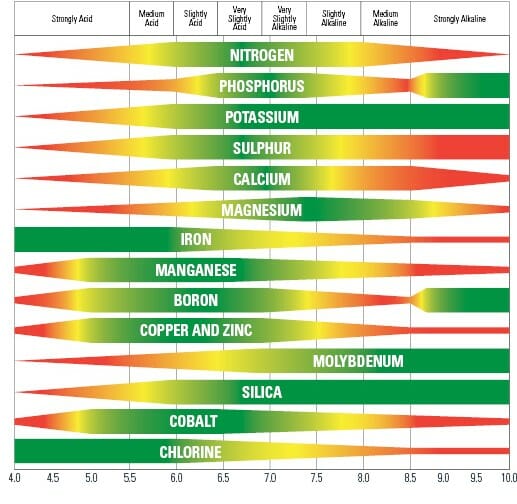
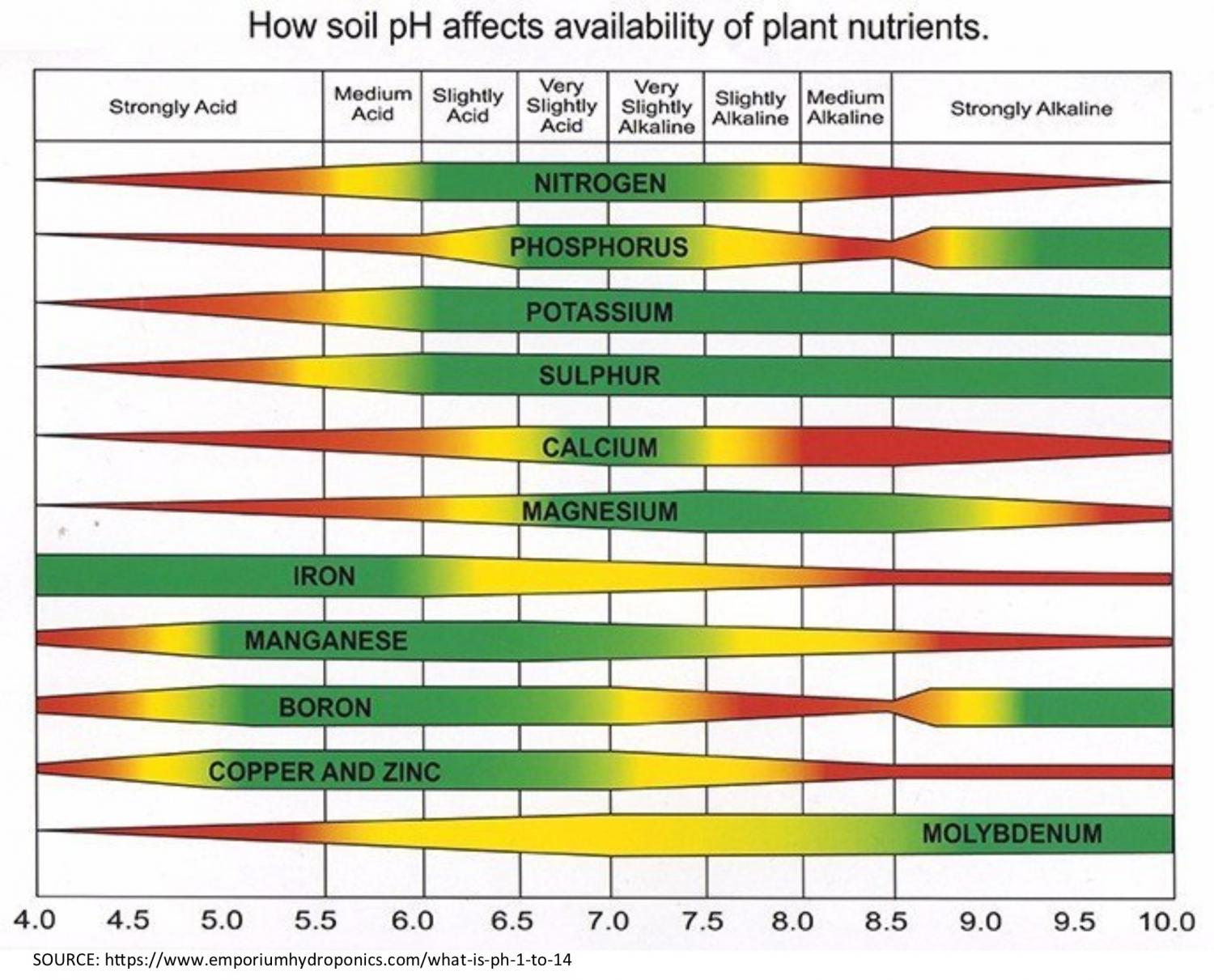
The pH Chart and Nutrient Solubility:
A visible illustration of nutrient availability throughout the pH spectrum, typically referred to as a "pH chart," is a useful instrument for gardeners and growers. Whereas the precise numbers could fluctuate barely relying on the supply and soil composition, a normal illustration reveals the next tendencies:
-
Acidic Situations (pH beneath 6.0): In extremely acidic soils, the provision of phosphorus (P), molybdenum (Mo), and calcium (Ca) is considerably lowered. These vitamins turn into much less soluble and are much less readily absorbed by plant roots. Conversely, micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and boron (B) turn into extra soluble and doubtlessly attain poisonous ranges. This may result in nutrient imbalances and toxicity signs.
-
Optimum Vary (pH 6.0-7.0): This vary typically offers the optimum stability for many important vitamins. Most macronutrients (nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (Okay), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca)) and micronutrients are available for plant uptake inside this vary. Because of this sustaining a soil pH inside this vary is essential for wholesome plant development.
-
Alkaline Situations (pH above 7.0): Because the pH rises above 7.0, the provision of iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), and molybdenum (Mo) decreases dramatically. These micronutrients turn into much less soluble and are much less readily absorbed by plant roots. Conversely, phosphorus (P) availability additionally diminishes in extremely alkaline circumstances. This may result in deficiencies in important micronutrients and have an effect on plant development and improvement.
Particular Nutrient Concerns:
Let’s look at the impression of pH on particular nutrient availability in additional element:
-
Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus availability is extremely delicate to pH modifications. It’s most out there in barely acidic to impartial circumstances (pH 6.0-7.0). In extremely acidic or alkaline soils, phosphorus turns into sure to different parts, making it unavailable to crops.
-
Iron (Fe): Iron availability is inversely associated to pH. It’s extremely soluble and out there in acidic circumstances however turns into more and more insoluble because the pH rises above 7.0, resulting in iron chlorosis (yellowing of leaves as a result of iron deficiency).
-
Manganese (Mn): Much like iron, manganese availability is larger in acidic circumstances and reduces because the pH will increase. Manganese toxicity can happen in acidic soils, whereas deficiency is frequent in alkaline soils.
-
Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum availability is usually larger in alkaline circumstances. Nonetheless, extreme molybdenum can turn into poisonous to crops at excessive pH ranges.
-
Nitrogen (N): Whereas not as instantly affected by pH as another vitamins, nitrogen availability might be not directly influenced. Modifications in pH can have an effect on the exercise of soil microorganisms accountable for nitrogen biking, impacting its availability to crops.
-
Potassium (Okay): Potassium availability is comparatively much less affected by pH in comparison with different vitamins. Nonetheless, excessive pH ranges (each extremely acidic and extremely alkaline) can nonetheless negatively impression its uptake.
Sensible Methods for Managing Soil pH:
Sustaining the optimum pH vary on your crops requires cautious monitoring and adjustment. A number of strategies can be utilized to regulate soil pH:
-
Soil Testing: Common soil testing is essential to find out the present pH and nutrient ranges. Soil testing kits are available from backyard facilities and on-line retailers.
-
Liming: To boost the pH of acidic soils (enhance alkalinity), agricultural lime (calcium carbonate) is often used. The quantity of lime wanted is dependent upon the present pH and the specified pH vary.
-
Elemental Sulfur: To decrease the pH of alkaline soils (enhance acidity), elemental sulfur is commonly utilized. Sulfur oxidizes within the soil, producing sulfuric acid, which lowers the pH.
-
Natural Matter: Incorporating natural matter, equivalent to compost and well-rotted manure, may also help buffer soil pH and enhance nutrient availability. Natural matter improves soil construction, water retention, and microbial exercise, all of which contribute to higher nutrient administration.
-
Acidifying Fertilizers: Sure fertilizers, equivalent to ammonium sulfate, can contribute to decreasing soil pH. Nonetheless, these must be used cautiously and in accordance with soil check suggestions.
-
Hydroponics: Hydroponic methods enable for exact management over nutrient options and pH ranges, eliminating the challenges related to soil pH administration.
Conclusion:
The pH chart and its implications for nutrient availability are elementary to profitable plant cultivation. By understanding the connection between pH and nutrient solubility, growers can successfully handle soil pH to optimize nutrient uptake, forestall deficiencies, and maximize plant well being and yield. Common soil testing, applicable pH changes, and the incorporation of natural matter are essential steps in making a thriving rising setting on your crops. Bear in mind to all the time seek the advice of dependable assets and observe really helpful utility charges when adjusting soil pH to keep away from potential injury to crops or the setting.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into The pH Chart and Nutrient Availability: A Complete Information for Plant Well being. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!