Understanding Acid-Base Steadiness: A Complete Information with Charts and Interpretations
Associated Articles: Understanding Acid-Base Steadiness: A Complete Information with Charts and Interpretations
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding Acid-Base Steadiness: A Complete Information with Charts and Interpretations. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding Acid-Base Steadiness: A Complete Information with Charts and Interpretations
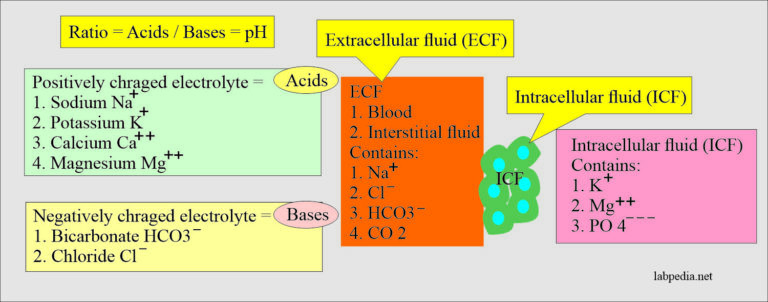
Sustaining a exact steadiness between acids and bases within the physique is essential for survival. This delicate equilibrium, generally known as acid-base steadiness or homeostasis, instantly impacts quite a few physiological processes, from enzyme exercise and mobile perform to oxygen transport and neurological signaling. Disruptions to this steadiness, leading to acidosis (extra acid) or alkalosis (extra base), can have extreme and even life-threatening penalties. This text will discover the mechanisms concerned in acid-base regulation, present an in depth understanding of related charts utilized in scientific settings, and supply interpretations of widespread acid-base imbalances.
The Physique’s Acid-Base Chemistry:
The physique generates acids constantly as byproducts of metabolism. These embrace risky acids like carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), which could be eradicated via the lungs as carbon dioxide (CO₂), and non-volatile acids like lactic acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid, that are eradicated primarily by the kidneys. The physique employs a number of refined mechanisms to buffer these acids and preserve a comparatively fixed pH inside a slim vary of seven.35 to 7.45. Deviation outdoors this vary can rapidly result in important physiological dysfunction.
Buffer Techniques:
The primary line of protection in opposition to adjustments in pH is the physique’s buffer techniques. These techniques act as chemical sponges, absorbing extra H+ ions (acids) or OH- ions (bases) to reduce fluctuations in pH. The main buffer techniques embrace:
- Bicarbonate Buffer System: That is a very powerful buffer system within the physique, involving the bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻) and carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). It is essential for buffering each risky and non-volatile acids.
- Phosphate Buffer System: This technique performs a big function in intracellular fluid and renal tubular fluid buffering. It entails dihydrogen phosphate (H₂PO₄⁻) and monohydrogen phosphate (HPO₄²⁻) ions.
- Protein Buffer System: Proteins, with their quite a few ionizable amino acid aspect chains, contribute considerably to buffering capability, each intracellularly and in plasma. Hemoglobin in pink blood cells is a very essential protein buffer.
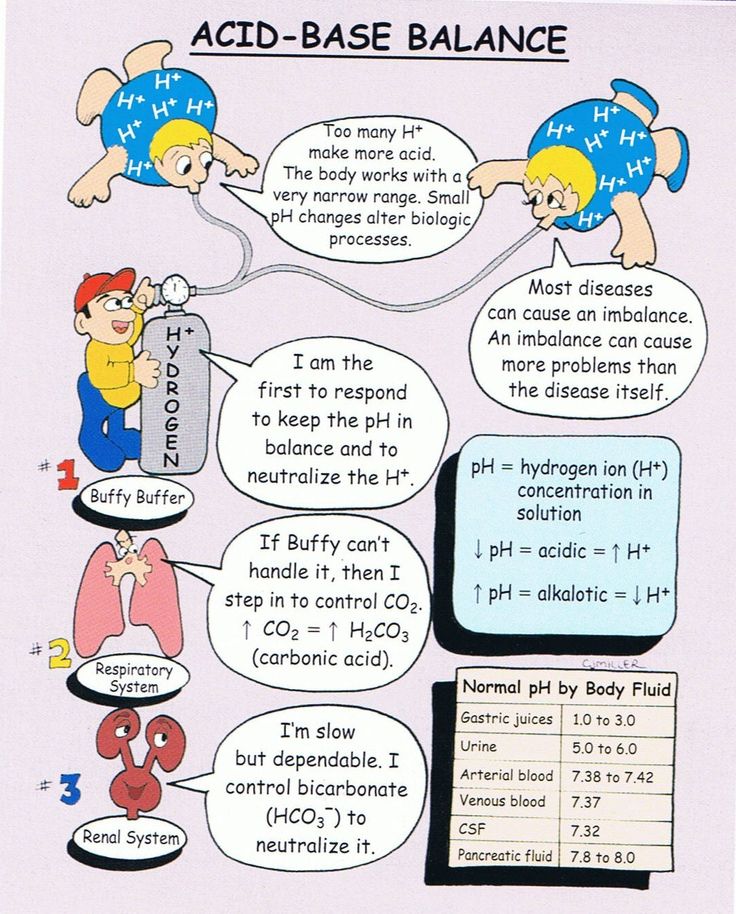
Respiratory Compensation:
The respiratory system performs a vital function in regulating acid-base steadiness by controlling the elimination of carbon dioxide (CO₂). Elevated CO₂ ranges result in elevated carbonic acid formation, decreasing blood pH (respiratory acidosis). Conversely, decreased CO₂ ranges elevate blood pH (respiratory alkalosis). The respiratory system responds quickly to adjustments in pH, adjusting air flow price to compensate for acid-base imbalances. Elevated air flow (hyperventilation) reduces CO₂ ranges, whereas decreased air flow (hypoventilation) will increase CO₂ ranges.
Renal Compensation:
The kidneys present probably the most highly effective and long-term mechanism for acid-base regulation. They obtain this via a number of processes:
- Reabsorption of Bicarbonate: The kidneys reabsorb virtually all filtered bicarbonate, stopping its loss within the urine.
- Excretion of H+ Ions: The kidneys excrete H+ ions via the urine, both instantly or certain to buffers like phosphate and ammonia.
- Technology of New Bicarbonate: The kidneys generate new bicarbonate ions to replenish these consumed in buffering acids.
Acid-Base Charts and Interpretation:
Clinically, arterial blood fuel (ABG) evaluation is crucial for assessing acid-base standing. The outcomes are sometimes offered in a chart displaying key parameters:
- pH: This instantly signifies the acidity or alkalinity of the blood (7.35-7.45).
- Partial Stress of Carbon Dioxide (PaCO₂): This displays the respiratory part of acid-base steadiness (regular vary: 35-45 mmHg).
- Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻): This displays the metabolic part of acid-base steadiness (regular vary: 22-26 mEq/L).
- Oxygen Saturation (SaO₂): This means the share of hemoglobin saturated with oxygen (regular vary: 95-100%).
- Base Extra (BE): This represents the quantity of base wanted to titrate the blood to a pH of seven.4 at 37°C and a PaCO₂ of 40 mmHg. It gives an total evaluation of the metabolic part.
Deciphering Acid-Base Imbalances utilizing the Anion Hole:
The anion hole is the distinction between the measured cations (sodium and potassium) and the measured anions (chloride and bicarbonate) in plasma. It helps differentiate between metabolic acidosis causes. A traditional anion hole suggests a lack of bicarbonate (e.g., diarrhea), whereas an elevated anion hole suggests an accumulation of unmeasured anions (e.g., lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis).
Charts and Examples:
(Observe: Precise charts could be visible representations of knowledge. The next describes the data offered in such charts.)
Instance 1: Respiratory Acidosis
A chart may present:
- pH: 7.25 (low)
- PaCO₂: 55 mmHg (excessive)
- HCO₃⁻: 28 mEq/L (barely elevated – renal compensation)
- BE: +2 mEq/L (gentle)
This means respiratory acidosis on account of hypoventilation (e.g., COPD, pneumonia). The elevated bicarbonate displays the kidneys’ try and compensate.
Instance 2: Metabolic Alkalosis
A chart may present:
- pH: 7.50 (excessive)
- PaCO₂: 50 mmHg (barely elevated – respiratory compensation)
- HCO₃⁻: 35 mEq/L (excessive)
- BE: +8 mEq/L (important)
This means metabolic alkalosis, presumably on account of vomiting or diuretic use. The marginally elevated PaCO₂ displays respiratory compensation via hypoventilation.
Instance 3: Metabolic Acidosis (Regular Anion Hole)
A chart may present:
- pH: 7.20 (low)
- PaCO₂: 30 mmHg (low – respiratory compensation)
- HCO₃⁻: 15 mEq/L (low)
- BE: -8 mEq/L (important)
- Anion Hole: Regular
This implies metabolic acidosis on account of bicarbonate loss (e.g., diarrhea). The low PaCO₂ displays respiratory compensation via hyperventilation.
Instance 4: Metabolic Acidosis (Elevated Anion Hole)
A chart may present:
- pH: 7.28 (low)
- PaCO₂: 28 mmHg (low – respiratory compensation)
- HCO₃⁻: 18 mEq/L (low)
- BE: -6 mEq/L (important)
- Anion Hole: Elevated
This implies metabolic acidosis on account of accumulation of unmeasured anions (e.g., lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis). The low PaCO₂ displays respiratory compensation.
Conclusion:
Understanding acid-base steadiness is essential for decoding scientific information and managing sufferers with acid-base problems. Cautious evaluation of arterial blood fuel outcomes, contemplating the pH, PaCO₂, HCO₃⁻, BE, and anion hole, permits clinicians to establish the kind and severity of the imbalance, decide the underlying trigger, and implement applicable therapy methods. This text gives a basis for decoding acid-base charts and understanding the advanced interaction between respiratory and renal techniques in sustaining this important physiological equilibrium. Additional in-depth research of particular acid-base problems and their administration is really helpful for healthcare professionals.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Understanding Acid-Base Steadiness: A Complete Information with Charts and Interpretations. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!