Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
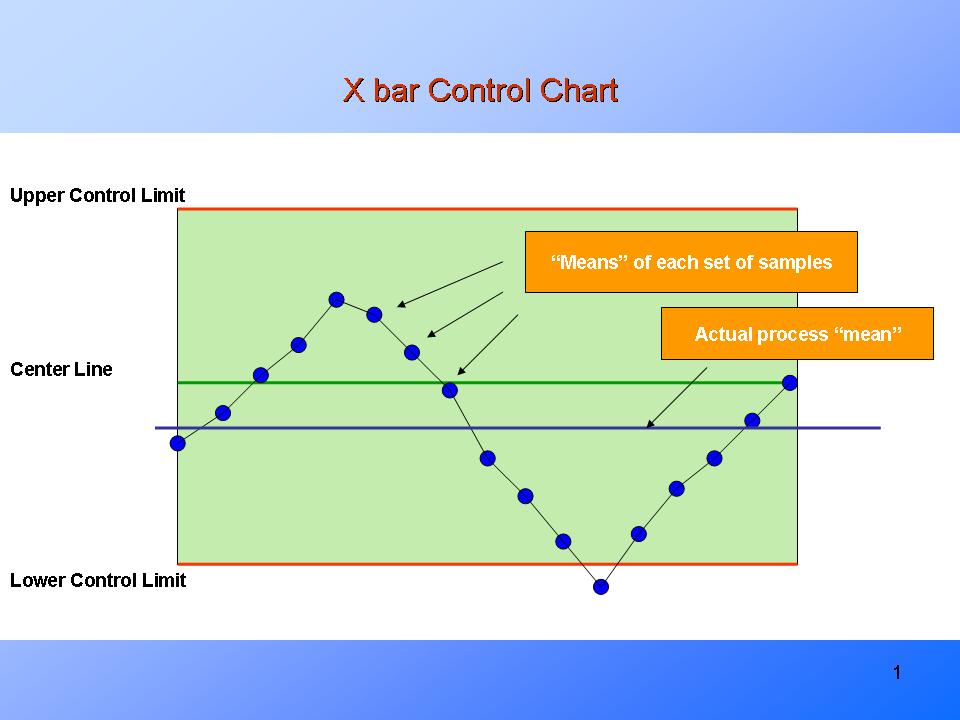
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is an important methodology for monitoring and enhancing the standard of producing and different processes. On the coronary heart of SPC lie management charts, graphical instruments that show knowledge over time, permitting for the identification of traits and patterns indicating course of instability. Among the many most generally used management charts are the X-bar (common) and R (vary) charts, a robust pair designed for monitoring the central tendency and variability of a course of. This text will delve into the idea, software, and interpretation of X-bar and R charts, offering a complete understanding of their function in high quality administration.
The Essence of X-bar and R Charts
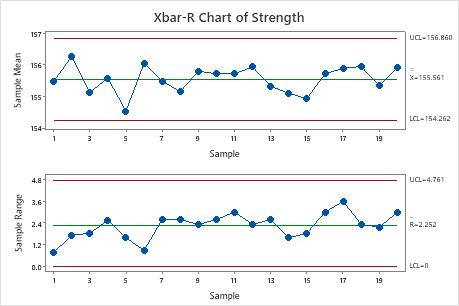
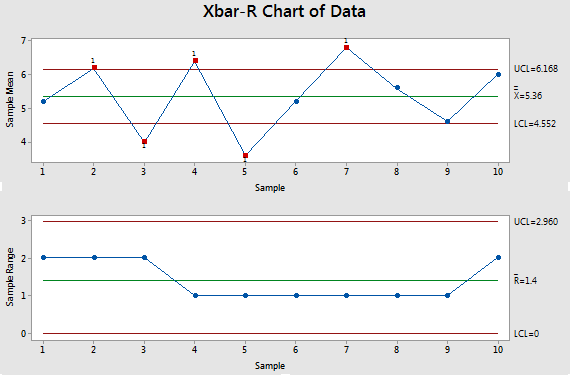
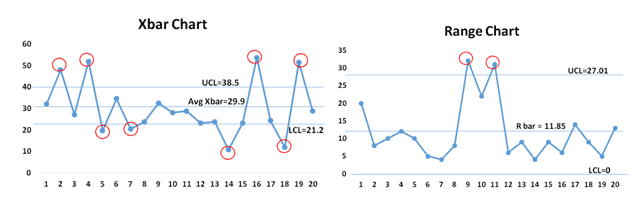
X-bar and R charts are variable management charts, that means they’re used for steady knowledge (knowledge that may tackle any worth inside a spread). They work in tandem: the X-bar chart tracks the typical (imply) of subgroups of knowledge, whereas the R chart displays the vary (the distinction between the best and lowest values) inside those self same subgroups. By concurrently monitoring each the central tendency and the variability, these charts present a holistic view of course of efficiency.
-
X-bar Chart: This chart plots the typical of every subgroup of knowledge in opposition to time. The central line represents the general common of all subgroups, whereas the higher and decrease management limits (UCL and LCL) outline the suitable vary of variation across the common. Factors falling outdoors these limits recommend a possible shift within the course of imply, indicating a trigger for investigation.
-
R Chart: This chart plots the vary of every subgroup in opposition to time. Much like the X-bar chart, it incorporates a central line representing the typical vary of all subgroups and higher and decrease management limits. Factors outdoors these limits recommend elevated variability throughout the course of, once more signaling a possible downside.
Why Use X-bar and R Charts Collectively?
Utilizing X-bar and R charts concurrently is significant for a whole course of evaluation. Whereas the X-bar chart alerts shifts within the course of common, the R chart detects modifications in course of variability. A course of could be unstable even when its common stays fixed if the variability will increase considerably. Conversely, a secure common with excessive variability can nonetheless result in unacceptable ranges of defects. Due to this fact, each charts are vital to offer an entire image of course of stability and functionality.
Setting up X-bar and R Charts: A Step-by-Step Information
The development of X-bar and R charts includes a number of key steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Collect knowledge from the method being monitored. It is essential to gather knowledge constantly and systematically, guaranteeing correct illustration. Knowledge must be collected in subgroups of a constant dimension (usually 4-5 samples per subgroup). The subgroup dimension must be chosen based mostly on elements resembling the method cycle time and the assets out there for knowledge assortment. Bigger subgroups present extra exact estimates of the method imply and variability however might not detect small shifts as rapidly as smaller subgroups.
-
Calculating Subgroup Statistics: For every subgroup, calculate the typical (X-bar) and the vary (R). The common is solely the sum of the information factors within the subgroup divided by the variety of knowledge factors. The vary is the distinction between the biggest and smallest knowledge factors within the subgroup.
-
Calculating Total Statistics: Calculate the general common of the subgroup averages (X-double bar) and the typical of the subgroup ranges (R-bar). These values will function the central traces for the X-bar and R charts, respectively.
-
Figuring out Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (A2, D3, D4) that rely on the subgroup dimension. These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The formulation for the management limits are:
-
X-bar Chart:
- UCL = X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- LCL = X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
R Chart:
- UCL = D4 * R-bar
- LCL = D3 * R-bar (Observe: D3 is 0 for subgroup sizes lower than 7)
-
-
Chart Development: Plot the subgroup averages (X-bar) on the X-bar chart and the subgroup ranges (R) on the R chart. Draw the central traces and management limits on each charts.
Decoding X-bar and R Charts
As soon as the charts are constructed, deciphering them is essential for efficient course of management. A number of patterns can point out course of instability:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level falling outdoors the UCL or LCL on both chart signifies a possible particular explanation for variation. This requires fast investigation to establish and eradicate the foundation trigger.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward development suggests a scientific shift within the course of imply or variability. Even when factors stay throughout the management limits, a development signifies a possible downside that wants consideration earlier than it results in factors outdoors the bounds.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or under the central line signifies potential stratification or subgroups with totally different traits.
-
Cycles: Repeating patterns or cycles recommend the presence of periodic influences on the method.
-
Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or under the central line, even when throughout the management limits, can point out a shift within the course of. The variety of consecutive factors required to represent a run is dependent upon the specified stage of significance.
Benefits and Limitations of X-bar and R Charts
Benefits:
- Simplicity and ease of use: X-bar and R charts are comparatively simple to assemble and interpret, making them accessible to a variety of customers.
- Actual-time monitoring: They permit for steady monitoring of the method, enabling well timed detection of issues.
- Price-effective: They’re comparatively cheap to implement and keep.
- Efficient in detecting shifts in each the imply and variability: The mixed use supplies a complete evaluation of course of stability.
Limitations:
- Assumption of normality: The calculation of management limits assumes that the information are usually distributed. If the information are considerably non-normal, different management charts could also be extra acceptable.
- Sensitivity to outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the calculation of management limits, doubtlessly masking different necessary patterns.
- Subgroup dimension limitations: The effectiveness of the charts is dependent upon the suitable choice of subgroup dimension.
- Requires constant knowledge assortment: Correct and constant knowledge assortment is essential for the reliability of the charts.
Software program and Instruments for X-bar and R Chart Creation
Quite a few software program packages and instruments can be found for creating and analyzing X-bar and R charts. These embrace statistical software program resembling Minitab, JMP, and R, in addition to spreadsheet packages like Microsoft Excel, which supply built-in features or add-ons for management chart creation.
Conclusion
X-bar and R charts are invaluable instruments for monitoring and enhancing course of efficiency. Their simplicity, effectiveness, and widespread applicability make them a cornerstone of Statistical Course of Management. By rigorously amassing knowledge, establishing the charts appropriately, and deciphering the outcomes diligently, organizations can leverage these charts to reinforce high quality, cut back waste, and enhance total effectivity. Nonetheless, it is essential to recollect the restrictions of those charts and to contemplate different strategies if the underlying assumptions aren’t met. The profitable implementation of X-bar and R charts requires a dedication to data-driven decision-making and a steady enchancment mindset.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!