Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Instance
Associated Articles: Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Instance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Instance. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Instance
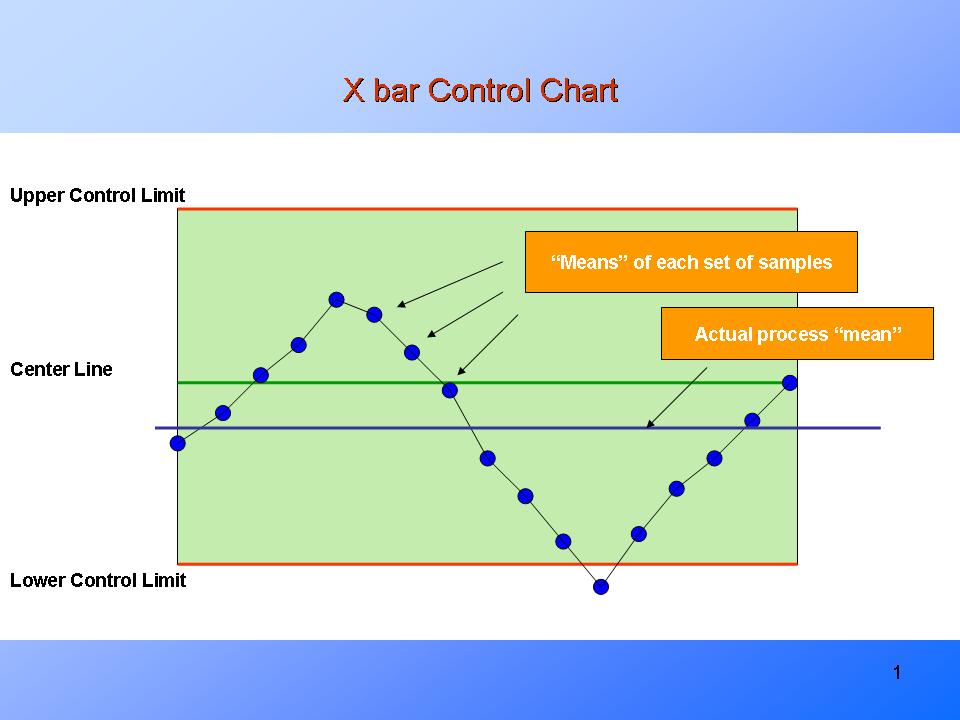
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a robust methodology used to watch and enhance the standard of processes. One of the crucial broadly used instruments in SPC is the X-bar and R chart, a robust duo designed to trace the central tendency and variability of a course of over time. This text will delve into the intricacies of X-bar and R charts, offering a complete instance to solidify understanding and show their sensible utility.
What are X-bar and R Charts?
X-bar and R charts are management charts utilized in pairs. They’re designed for variables information, that means information that may be measured on a steady scale (e.g., weight, size, temperature). The X-bar chart screens the common (imply) of a course of, whereas the R chart tracks the vary of the information inside every subgroup. By analyzing these two charts concurrently, we will acquire worthwhile insights into the steadiness and functionality of a course of.
-
X-bar Chart: This chart shows the common of a subgroup of measurements taken at common intervals. It helps determine shifts within the course of imply over time. A steady course of will present X-bar values constantly throughout the management limits.
-
R Chart: This chart shows the vary of every subgroup, representing the variability inside every subgroup. It helps detect modifications within the course of variability. A steady course of will exhibit R values constantly throughout the management limits.
Why Use X-bar and R Charts?
Utilizing X-bar and R charts affords a number of key benefits:
- Early Detection of Issues: These charts permit for the early detection of shifts within the course of imply or variability, stopping the manufacturing of faulty services or products.
- Course of Enchancment: By figuring out sources of variation and shifts within the imply, X-bar and R charts present worthwhile info for course of enchancment initiatives.
- Decreased Waste: Early detection of issues minimizes waste related to faulty merchandise, rework, and scrap.
- Improved Effectivity: By sustaining a steady course of, X-bar and R charts contribute to improved effectivity and productiveness.
- Information-Pushed Choice Making: The charts present goal information to assist decision-making associated to course of management and enchancment.
Developing X-bar and R Charts: A Step-by-Step Instance
Let’s think about a producing course of producing metal rods. The size of every rod is measured, and we gather information in subgroups of 5 rods. We gather information for 25 subgroups (125 rods in whole). The next desk reveals the information collected:
| Subgroup | Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | Measurement 4 | Measurement 5 | X-bar (Common) | Vary (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 9.9 | 10.04 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 10.14 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 10.04 | 0.3 |
| 5 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 10.06 | 0.3 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 25 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 10.04 | 0.3 |
(Be aware: The "…" represents the information for subgroups 6 by way of 24. For brevity, the complete dataset is just not included right here, however a whole dataset could be crucial for a real-world utility.)
1. Calculate the X-bar and R for every subgroup:
For every subgroup, calculate the common (X-bar) and the vary (R). The vary is solely the distinction between the most important and smallest measurement within the subgroup. These calculations are proven within the desk above.
2. Calculate the general common X-double bar (X̄) and common vary R-bar (R̄):
Sum all of the X-bar values and divide by the variety of subgroups (25). Equally, sum all of the R values and divide by the variety of subgroups (25). Let’s assume, for this instance, that after calculating these values from the entire dataset, we receive:
X̄ = 10.08
R̄ = 0.32
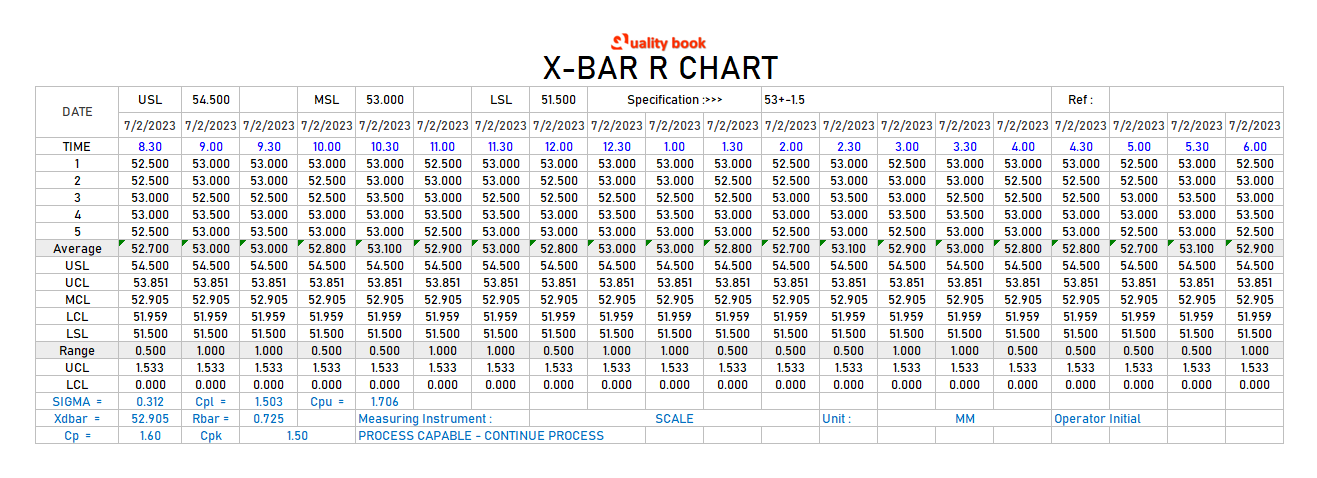
3. Decide the Management Limits:
We use management chart constants to find out the management limits. These constants depend upon the subgroup dimension (n=5 in our instance). For n=5, we will use normal management chart constants tables to seek out the next values:
- A2 (for X-bar chart): 0.577
- D3 (for R chart): 0
- D4 (for R chart): 2.115
Now, we will calculate the management limits:
-
X-bar Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCLx) = X̄ + A2 R̄ = 10.08 + 0.577 0.32 = 10.27
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCLx) = X̄ – A2 R̄ = 10.08 – 0.577 0.32 = 9.89
-
R Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCLr) = D4 R̄ = 2.115 0.32 = 0.68
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCLr) = D3 R̄ = 0 0.32 = 0
4. Plot the Information:
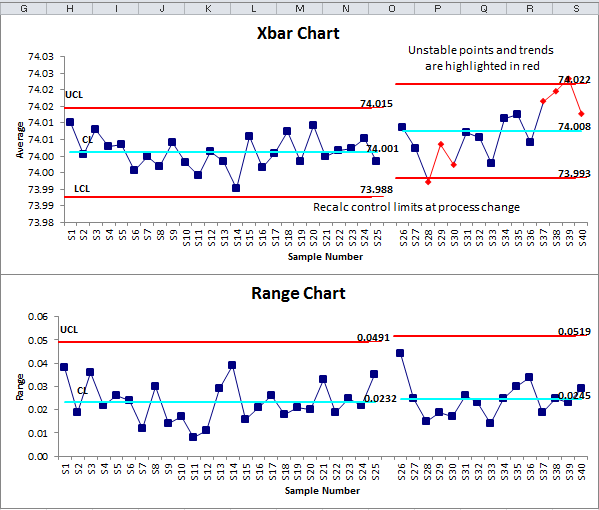
Plot the X-bar values and R values on their respective charts. The X-axis represents the subgroup quantity, and the Y-axis represents the X-bar and R values. Draw the middle line (CL) at X̄ and R̄, and the UCL and LCL for every chart.
5. Analyze the Charts:
Study the charts for any factors exterior the management limits or any patterns that recommend the method is just not steady. Factors exterior the management limits point out a possible drawback with the method. Patterns corresponding to traits, cycles, or stratification additionally point out instability.
Deciphering the Outcomes and Taking Motion
If all factors fall throughout the management limits and there aren’t any apparent patterns, the method is taken into account statistically steady. Nevertheless, if factors fall exterior the management limits or patterns are noticed, it signifies that the method is unstable and desires investigation. The investigation ought to concentrate on figuring out the foundation causes of the instability and implementing corrective actions.
For instance, if a degree on the X-bar chart falls above the UCL, it means that the common size of the metal rods has elevated considerably. This is likely to be on account of a change within the machine settings, a change within the uncooked materials, or another issue. Equally, a degree on the R chart falling above the UCL suggests elevated variability within the size of the rods. This is likely to be on account of inconsistencies within the manufacturing course of or operator error.
Additional Issues:
- Subgroup Dimension: The selection of subgroup dimension is essential. Bigger subgroups present extra details about variability however might require extra time and sources to gather.
- Information Assortment: Correct and constant information assortment is crucial for the effectiveness of X-bar and R charts.
- Software program: Statistical software program packages can automate the calculations and plotting of X-bar and R charts, simplifying the method.
Conclusion:
X-bar and R charts are invaluable instruments for monitoring and enhancing course of high quality. By offering a visible illustration of course of efficiency, these charts allow early detection of issues, facilitating well timed corrective actions and course of enchancment initiatives. The instance offered illustrates the step-by-step means of establishing and decoding X-bar and R charts, demonstrating their sensible utility in enhancing course of stability and decreasing variability. Bear in mind, the important thing to profitable implementation lies in correct information assortment, cautious evaluation, and a dedication to steady enchancment. By understanding and making use of this highly effective methodology, organizations can considerably improve their merchandise, companies, and general effectivity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Instance. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!