Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a robust instrument used to watch and enhance the standard of processes. A vital aspect of SPC is using management charts, which graphically show knowledge over time, permitting for the identification of developments and patterns that point out course of instability. Among the many most generally used management charts are the X-bar and R charts, a robust mixture designed to watch the central tendency and variability of a course of. This text offers a complete overview of X-bar and R charts, overlaying their building, interpretation, and sensible functions.
What are X-bar and R Charts?
The X-bar and R chart is a paired management chart used to watch the common (X-bar) and vary (R) of a course of. They’re significantly helpful for variables knowledge, which means knowledge that may be measured on a steady scale (e.g., weight, size, temperature). The X-bar chart tracks the central tendency of the method, indicating whether or not the common is shifting over time. The R chart screens the method variability, revealing whether or not the unfold of the info is rising or reducing. By monitoring each the common and variability, these charts present an entire image of course of stability.
When to Use X-bar and R Charts?
X-bar and R charts are perfect for conditions the place:
- Variables knowledge is collected: The info being monitored should be steady and measurable.
- Subgroups are available: Information ought to be collected in rational subgroups, that are samples taken at common intervals or from a constant supply. Subgroup dimension (n) is often between 4 and 10, though bigger subgroups are typically used. The selection of subgroup dimension impacts the sensitivity of the charts.
- Course of stability is desired: The charts are designed to detect shifts within the course of imply and variability, indicating a necessity for corrective motion.
- Steady monitoring is important: Common knowledge assortment and charting permit for immediate detection of issues and stop defects from reaching the client.
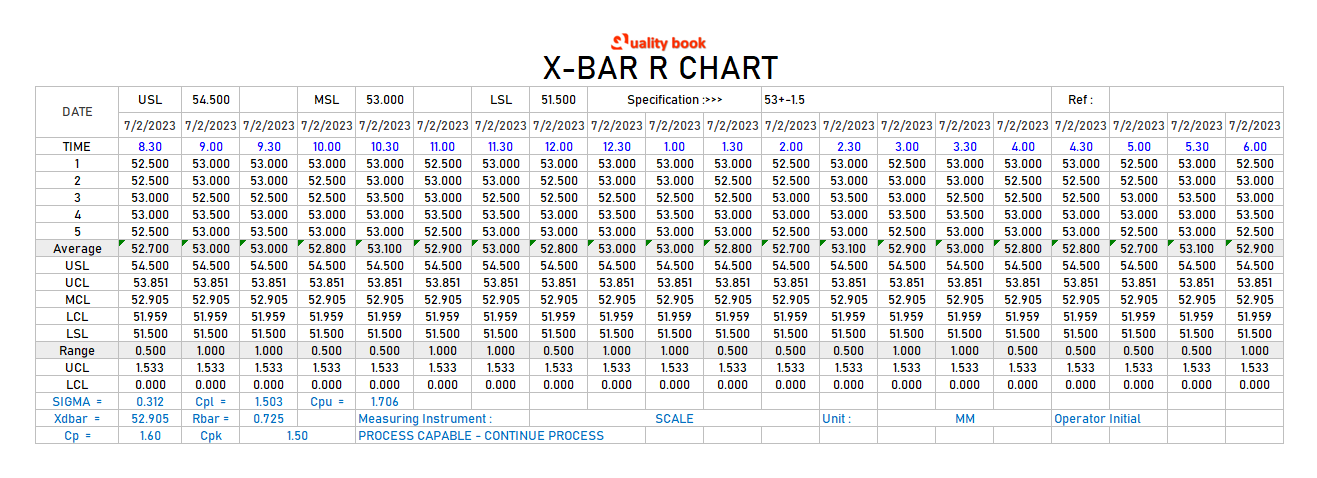
Developing X-bar and R Charts: A Step-by-Step Information
Developing X-bar and R charts entails a number of steps:
-
Information Assortment: Acquire knowledge in rational subgroups. Every subgroup ought to include ‘n’ samples taken below related situations. A minimal of 20-25 subgroups is mostly really useful for correct chart building.
-
Calculate Subgroup Statistics: For every subgroup, calculate the common (X-bar) and the vary (R). The common is the sum of the info factors divided by the variety of knowledge factors within the subgroup. The vary is the distinction between the most important and smallest values within the subgroup.
-
Calculate General Statistics: Calculate the general common of the subgroup averages (X-double bar) and the common of the subgroup ranges (R-bar). These are calculated as follows:
- X-double bar (X̄): Sum of all X-bar values / Variety of subgroups
- R-bar (R̄): Sum of all R values / Variety of subgroups
-
Decide Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (A2, D3, D4) which rely on the subgroup dimension (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The management limits for the X-bar and R charts are calculated as follows:
-
X-bar Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- Heart Line (CL): X-double bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
R Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): D4 * R-bar
- Heart Line (CL): R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): D3 * R-bar (Word: D3 is 0 for n ≤ 6 in some tables)
-
-
Assemble the Charts: Plot the X-bar and R values for every subgroup on their respective charts. Draw the middle line and higher and decrease management limits on every chart.
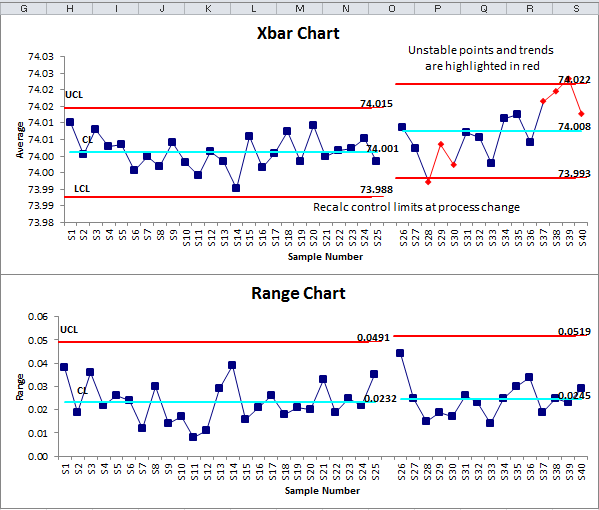
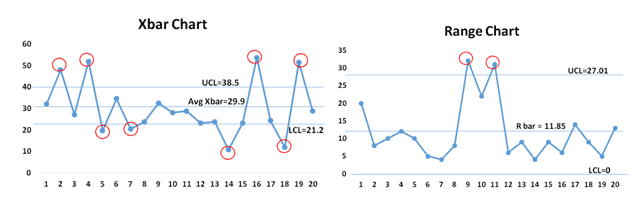
Decoding X-bar and R Charts
As soon as the charts are constructed, decoding them entails in search of patterns that point out course of instability. The next are widespread indicators of out-of-control processes:
- Factors exterior the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or under the LCL signifies a major deviation from the method common or variability.
- Traits: A constant upward or downward development suggests a gradual shift within the course of imply or variability.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low values point out cyclical variations within the course of.
- Stratification: Clustering of factors round a selected worth suggests the presence of assignable causes.
- Runs: A collection of consecutive factors above or under the middle line, even when throughout the management limits, would possibly point out a shift within the course of. Westgard guidelines present a proper framework for figuring out runs.
Addressing Out-of-Management Situations
When an out-of-control situation is recognized, it is essential to analyze the underlying trigger. This usually entails:
- Figuring out assignable causes: This entails analyzing the method and figuring out any elements that may have contributed to the deviation (e.g., machine malfunction, modifications in uncooked supplies, operator error).
- Implementing corrective actions: As soon as the assignable trigger is recognized, corrective actions ought to be taken to eradicate the issue and restore course of stability.
- Re-establishing management: After corrective actions are applied, new knowledge ought to be collected and new charts constructed to confirm that the method is again below management.
Benefits of Utilizing X-bar and R Charts
- Early detection of issues: The charts permit for the early detection of shifts within the course of imply and variability, stopping the manufacturing of faulty merchandise.
- Improved course of understanding: The charts present precious insights into the method habits, serving to to determine areas for enchancment.
- Decreased variability: By monitoring and controlling variability, the charts contribute to decreasing defects and bettering product high quality.
- Goal evaluation of course of functionality: The charts can be utilized to evaluate the potential of the method to satisfy specs.
- Information-driven decision-making: The charts present goal knowledge that can be utilized to make knowledgeable choices about course of enchancment.
Limitations of X-bar and R Charts
- Assumption of normality: The charts are simplest when the info is generally distributed. If the info is considerably non-normal, various management charts could also be extra acceptable.
- Subgroup dimension limitations: The selection of subgroup dimension can have an effect on the sensitivity of the charts. Too small a subgroup dimension can result in elevated variability, whereas too giant a subgroup dimension can masks small shifts within the course of.
- Sensitivity to outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the management limits and obscure different patterns. Sturdy strategies could also be essential to deal with outliers.
- Requires constant knowledge assortment: Correct and constant knowledge assortment is important for the efficient use of the charts.
Software program and Instruments
Quite a few software program packages and instruments can be found for setting up and decoding X-bar and R charts, together with:
- Statistical software program packages: Similar to Minitab, JMP, and R, provide superior options for knowledge evaluation and management chart building.
- Spreadsheet software program: Applications like Microsoft Excel can be utilized to create fundamental X-bar and R charts, though their capabilities are extra restricted.
- Devoted SPC software program: Specialised SPC software program packages provide complete instruments for course of monitoring and management.
In conclusion, X-bar and R charts are important instruments for monitoring and bettering the standard of processes. Their easy building and interpretation, coupled with their means to detect shifts in each the imply and variability, make them a precious asset in any high quality administration system. By understanding the ideas behind these charts and diligently making use of them, organizations can considerably enhance their operational effectivity and produce high-quality merchandise persistently. Nevertheless, it is essential to recollect the restrictions and assumptions related to these charts and to think about various strategies when essential. Correct coaching and understanding are important for efficient implementation and interpretation of X-bar and R charts.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Understanding and Implementing X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!