Understanding Debits and Credit: A Complete Information to T-Charts in Accounting
Associated Articles: Understanding Debits and Credit: A Complete Information to T-Charts in Accounting
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding Debits and Credit: A Complete Information to T-Charts in Accounting. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding Debits and Credit: A Complete Information to T-Charts in Accounting
The inspiration of double-entry bookkeeping, the bedrock of recent accounting, rests upon the ideas of debits and credit. Whereas the phrases might sound intimidating at first, understanding debits and credit is essential for anybody concerned in monetary record-keeping, from small enterprise homeowners to seasoned accountants. This text supplies a complete exploration of debits and credit, using the ever-present T-chart as a visible assist to solidify understanding.
The Elementary Equation: The Coronary heart of Double-Entry Bookkeeping
Double-entry bookkeeping ensures that the accounting equation all the time stays balanced. This basic equation is:
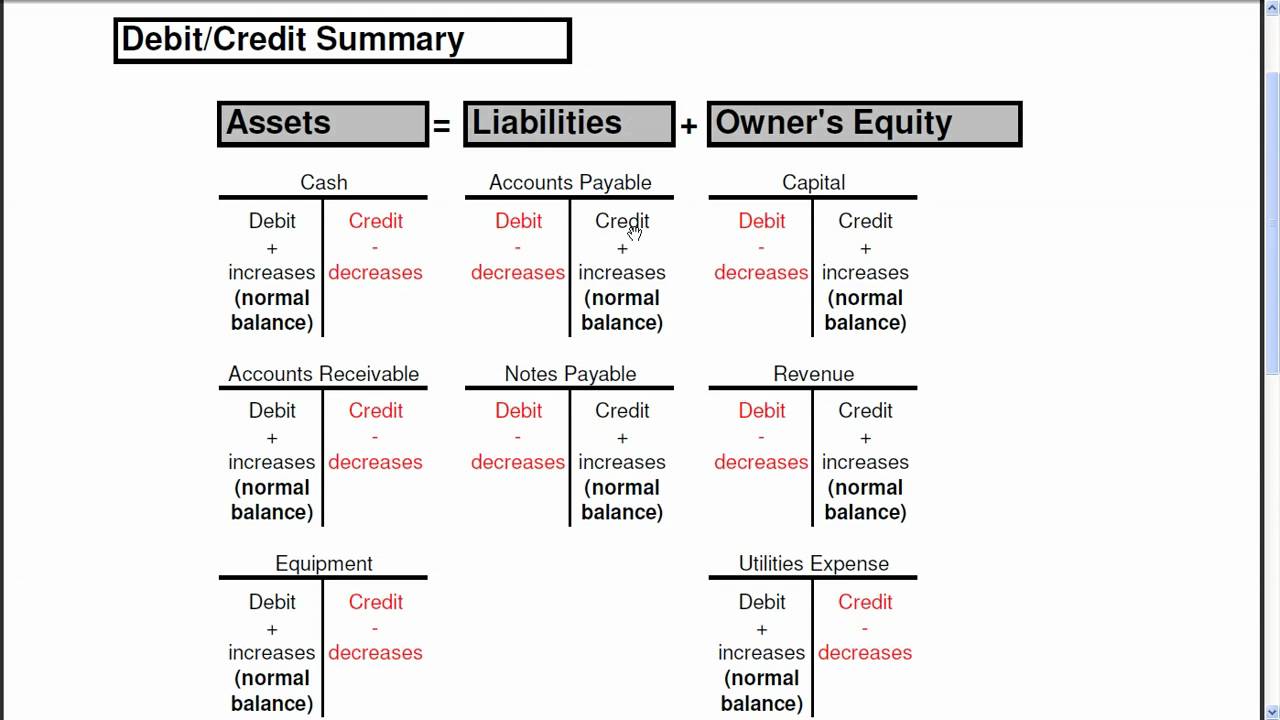
Belongings = Liabilities + Fairness
Each monetary transaction impacts at the least two accounts, sustaining this equality. A debit will increase the left aspect (Belongings) and a credit score will increase the suitable aspect (Liabilities and Fairness). Conversely, a credit score decreases the left aspect (Belongings) and a debit decreases the suitable aspect (Liabilities and Fairness). This seemingly easy idea is the important thing to correct monetary reporting.
The T-Chart: A Visible Illustration of Debits and Credit
The T-chart is a straightforward but highly effective software for visualizing debits and credit. It is named for its resemblance to the letter "T," with the left aspect representing debits (Dr.) and the suitable aspect representing credit (Cr.).
Account Title
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| | |
---------------------------------Every transaction is recorded on the suitable aspect of the T-chart, making certain the stability stays constant. The great thing about the T-chart lies in its simplicity – it permits for a transparent and concise document of every transaction’s impression on an account’s stability.
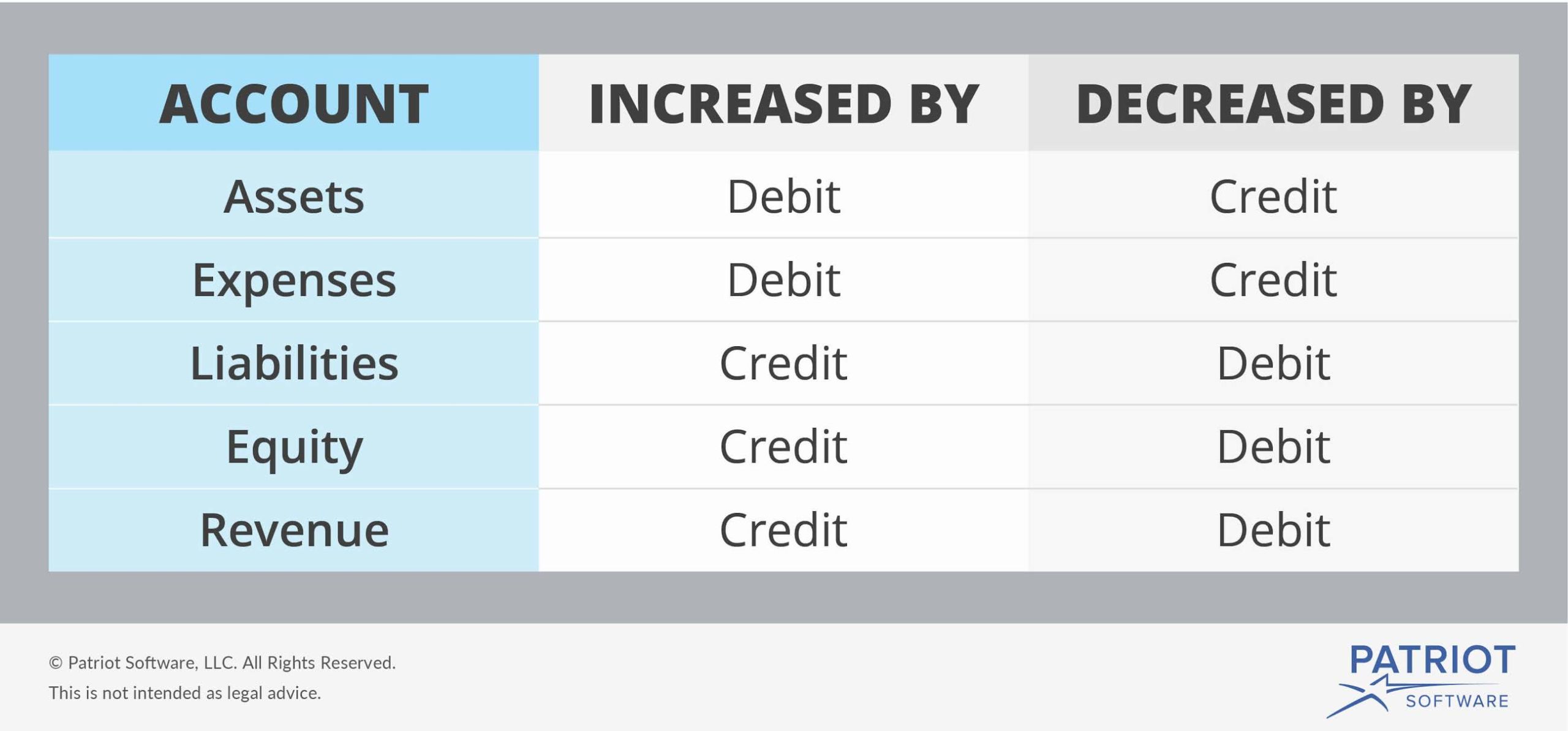
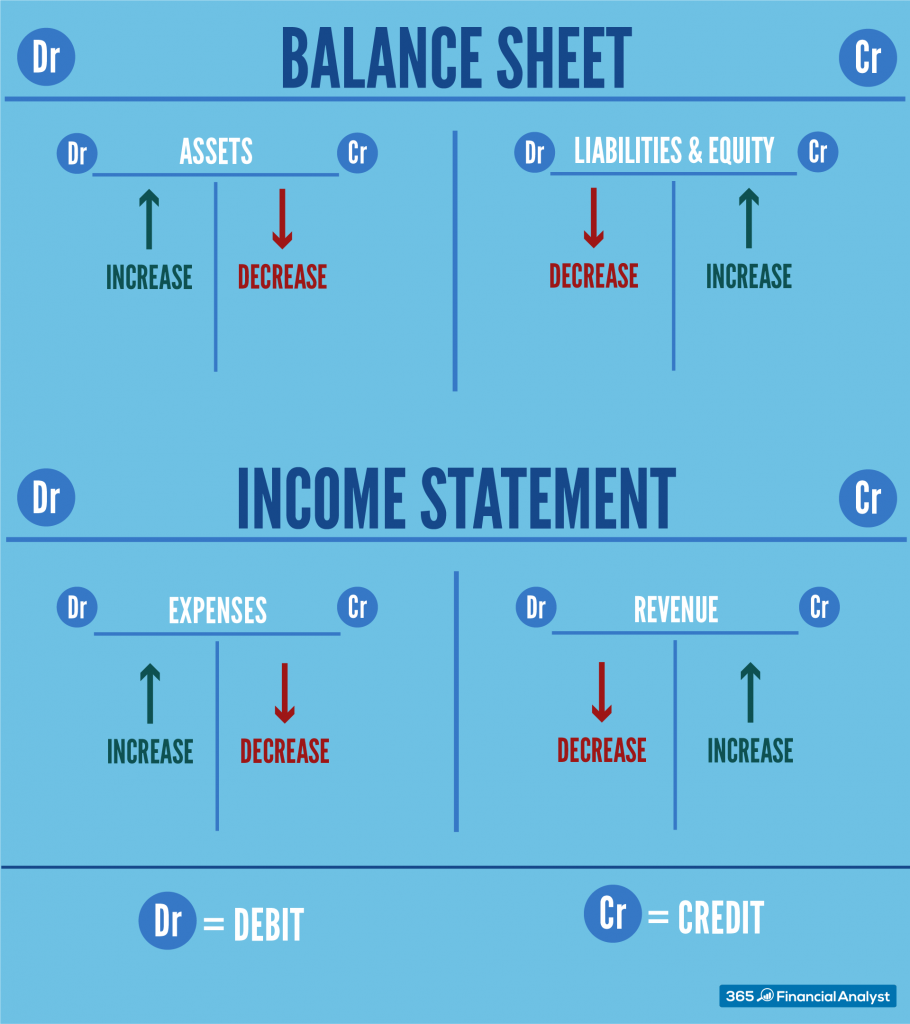
The Guidelines of Debits and Credit: A Detailed Breakdown
The impression of debits and credit varies relying on the kind of account. Accounts are broadly categorized into 5 classes:
-
Belongings: These are sources owned by an organization, reminiscent of money, accounts receivable, stock, and tools. The rule for belongings is:
- Debit will increase, Credit score decreases
For instance, if an organization receives money from a buyer, the Money account (an asset) is debited to extend its stability. If the corporate sells tools, the Tools account is credited to lower its stability.
-
Liabilities: These are obligations owed by an organization to others, reminiscent of accounts payable, loans payable, and salaries payable. The rule for liabilities is:
- Debit decreases, Credit score will increase
If an organization pays off a portion of a mortgage, the Loans Payable account (a legal responsibility) is debited to lower its stability. If the corporate incurs a brand new debt, the related legal responsibility account is credited to extend its stability.
-
Fairness: This represents the homeowners’ stake within the firm. It contains retained earnings, widespread inventory, and contributed capital. The rule for fairness accounts is:
- Debit decreases, Credit score will increase
If the corporate distributes dividends to shareholders, the Retained Earnings account (an fairness account) is debited to lower its stability. If the corporate points new shares of inventory, the Frequent Inventory account is credited to extend its stability.
-
Income: These are will increase in fairness ensuing from the sale of products or companies. The rule for income accounts is:
- Debit decreases, Credit score will increase
When an organization makes a sale, the Income account is credited to extend its stability. Adjusting entries may debit income to appropriate overstatements.
-
Bills: These are decreases in fairness ensuing from the price of doing enterprise. The rule for expense accounts is:
- Debit will increase, Credit score decreases
When an organization incurs an expense (e.g., hire, salaries), the related Expense account is debited to extend its stability. Adjusting entries may credit score bills to appropriate overstatements.
Illustrative Examples: Placing all of it Collectively
Let’s illustrate these ideas with some examples utilizing T-charts:
Instance 1: Money Obtained from Buyer
An organization receives $1,000 money from a buyer for companies rendered.
Money
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| $1,000 | |
---------------------------------
Accounts Receivable
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| | $1,000 |
---------------------------------
Service Income
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| | $1,000 |
---------------------------------Money (asset) is debited to extend, Accounts Receivable (asset) is credited to lower because the receivable is collected, and Service Income (income) is credited to extend.
Instance 2: Buy of Tools on Credit score
An organization purchases tools for $5,000 on credit score.
Tools
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| $5,000 | |
---------------------------------
Accounts Payable
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| | $5,000 |
---------------------------------Tools (asset) is debited to extend, and Accounts Payable (legal responsibility) is credited to extend as a result of the acquisition was made on credit score.
Instance 3: Cost of Salaries
An organization pays its workers $2,000 in salaries.
Salaries Expense
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| $2,000 | |
---------------------------------
Money
---------------------------------
| Debit (Dr.) | Credit score (Cr.) |
---------------------------------
| | $2,000 |
---------------------------------Salaries Expense (expense) is debited to extend, and Money (asset) is credited to lower as money is paid out.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Functions of Debits and Credit
The ideas of debits and credit prolong past easy transactions. They’re essential for understanding extra advanced accounting ideas reminiscent of:
- Adjusting Entries: These entries are made on the finish of an accounting interval to replace accounts and guarantee accuracy. They usually contain adjusting expense and income accounts.
- Closing Entries: These entries are made on the finish of an accounting interval to switch the balances of non permanent accounts (income, expense, and dividend accounts) to retained earnings.
- Monetary Assertion Preparation: The data recorded utilizing debits and credit within the common ledger is the premise for getting ready the stability sheet, earnings assertion, and assertion of money flows.
Mastering Debits and Credit: A Steady Studying Course of
Understanding debits and credit is a basic talent for anybody working with monetary info. Whereas the principles might sound advanced initially, constant observe and utility will solidify your understanding. Utilizing T-charts as a visible assist can considerably enhance your means to trace transactions and keep correct monetary information. Bear in mind, the secret’s to know the impression of every transaction on the accounting equation and apply the suitable debit or credit score to keep up stability. Continued studying and observe will make mastering debits and credit a rewarding and important a part of your monetary literacy. By constant utility and observe with real-world eventualities, you may confidently navigate the world of accounting and monetary record-keeping. The T-chart will grow to be your trusted companion on this journey.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Understanding Debits and Credit: A Complete Information to T-Charts in Accounting. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!