Understanding P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Complete Information
Statistical evaluation kinds the bedrock of contemporary scientific inquiry, enabling researchers to attract significant conclusions from information. Two essential ideas underpin a lot of this evaluation: the p-value and levels of freedom. Whereas usually used collectively, they signify distinct however interconnected facets of statistical inference. This text will delve right into a complete clarification of each, highlighting their particular person roles and their synergistic relationship, significantly throughout the context of speculation testing. We can even discover how these ideas are visually represented and interpreted.
1. The P-value: A Measure of Proof In opposition to the Null Speculation
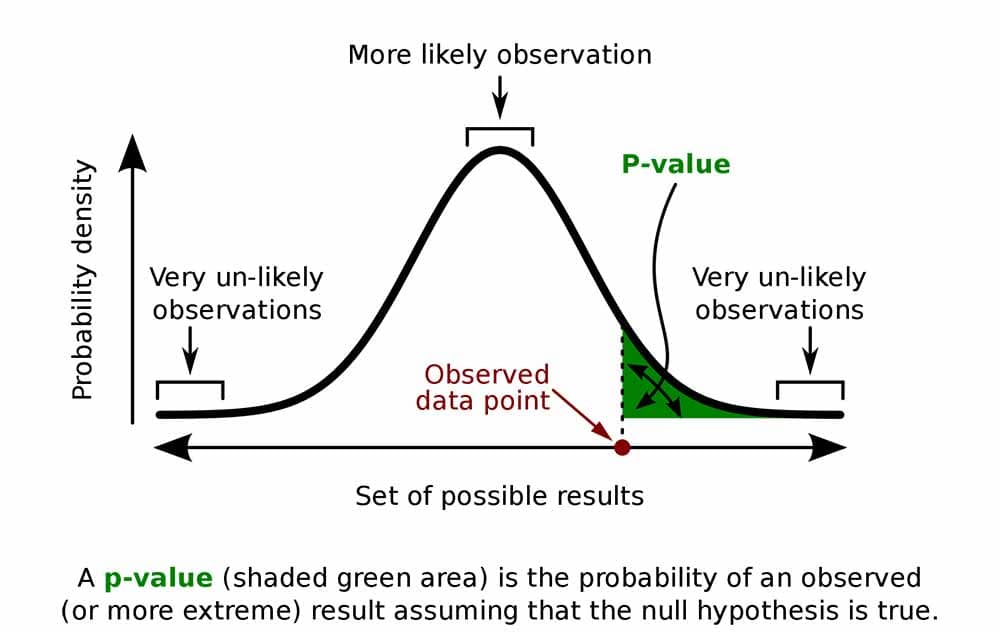
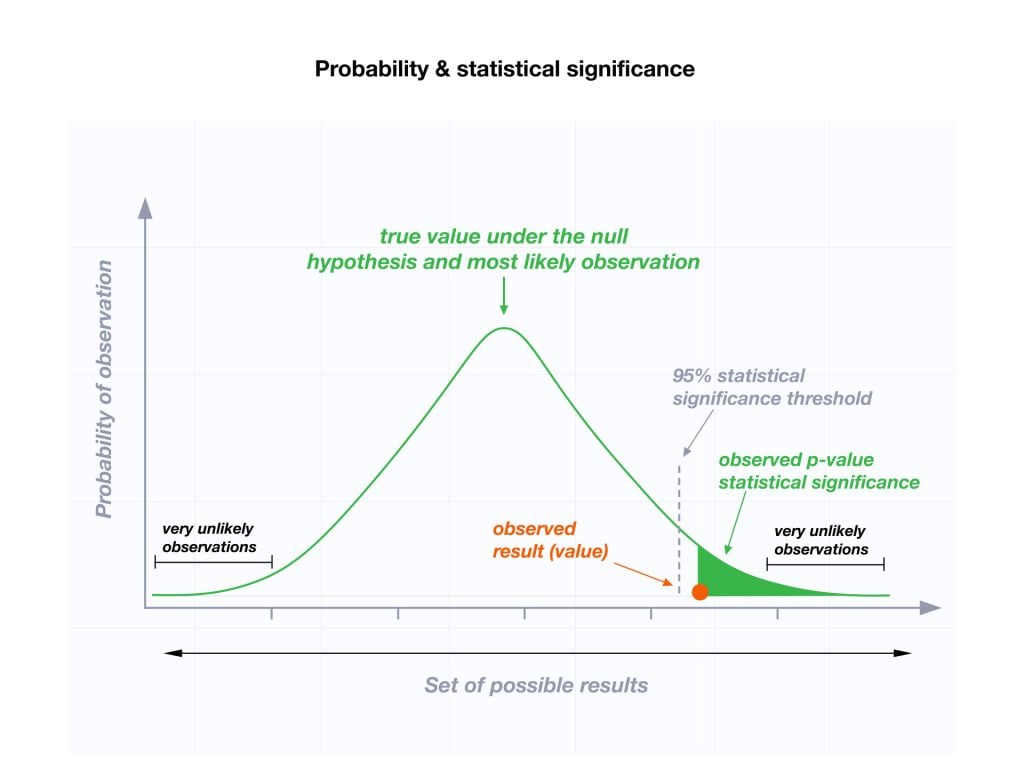
The p-value is a likelihood worth that quantifies the power of proof in opposition to a null speculation. The null speculation (H₀) is an announcement of no impact or no distinction. For instance, in a scientific trial evaluating a brand new drug to a placebo, the null speculation could be that there isn’t any distinction in efficacy between the 2.
The p-value represents the likelihood of observing the obtained outcomes (or extra excessive outcomes) if the null speculation had been true. A small p-value means that the noticed information are unlikely to have occurred by probability alone if the null speculation had been true. Conversely, a big p-value signifies that the noticed information are according to the null speculation.
Deciphering P-values:
The interpretation of a p-value is context-dependent, however a typical threshold is 0.05 (or 5%). This implies:
-
p ≤ 0.05 (important): The outcomes are statistically important, suggesting sturdy proof in opposition to the null speculation. We reject the null speculation in favor of the choice speculation (H₁), which proposes an impact or distinction. Nevertheless, it is essential to do not forget that this does not essentially imply the impact is giant or virtually important.
-
p > 0.05 (non-significant): The outcomes aren’t statistically important. This implies there’s inadequate proof to reject the null speculation. We fail to reject the null speculation, however this does not show the null speculation is true. It merely means we lack adequate proof to conclude in any other case.
Misconceptions about P-values:
A number of frequent misconceptions encompass p-values:
-
P-value isn’t the likelihood that the null speculation is true: The p-value solely displays the likelihood of the information given the null speculation, not the likelihood of the null speculation given the information. Bayesian statistics affords a framework for instantly addressing the likelihood of the null speculation.
-
A p-value alone doesn’t decide sensible significance: A statistically important end result (p ≤ 0.05) may need a small impact measurement, making it irrelevant in a sensible context. Impact measurement measures quantify the magnitude of the noticed impact, offering a extra full image.
-
P-hacking and p-value fishing: Researchers may manipulate information or selectively report outcomes to acquire a desired p-value, resulting in biased conclusions. This unethical apply undermines the integrity of scientific analysis.
2. Levels of Freedom (df): Accounting for Estimation Constraints
Levels of freedom (df) signify the variety of unbiased items of knowledge out there to estimate a parameter. It is basically the variety of values within the ultimate calculation of a statistic which can be free to differ. The idea of levels of freedom arises as a result of statistical estimates usually contain constraints.
For instance, take into account calculating the pattern variance:
- Now we have ‘n’ information factors.
- To calculate the pattern variance, we first calculate the pattern imply.
- This imply imposes a constraint: the sum of deviations from the imply have to be zero.
- Due to this fact, solely ‘n-1’ deviations are free to differ, leading to ‘n-1’ levels of freedom.
Levels of freedom are essential for figuring out the suitable likelihood distribution to make use of when performing statistical checks. Completely different statistical checks have completely different formulation for calculating levels of freedom, relying on the character of the information and the check being carried out.
Examples of Levels of Freedom:
- One-sample t-test: df = n – 1 (n is the pattern measurement)
- Unbiased samples t-test: df = n₁ + n₂ – 2 (n₁ and n₂ are the pattern sizes of the 2 teams)
- Chi-square check: df relies on the variety of rows and columns within the contingency desk.
- ANOVA: df varies relying on the variety of teams and the variety of observations inside every group.
3. The Relationship Between P-values and Levels of Freedom
P-values and levels of freedom are intimately linked. The p-value is calculated utilizing a likelihood distribution (e.g., t-distribution, F-distribution, chi-square distribution), and the form of this distribution is decided, partially, by the levels of freedom.
Particularly, the levels of freedom affect the crucial worth of the check statistic. The crucial worth is the brink that determines whether or not to reject the null speculation. For a given significance degree (e.g., α = 0.05), a better levels of freedom typically results in a smaller crucial worth, making it simpler to reject the null speculation. It is because, with extra levels of freedom, the sampling distribution tends to turn out to be extra usually distributed, resulting in extra exact estimates.
4. Visualizing P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Hypothetical Chart
Whereas there is not a single, universally used chart instantly plotting p-values in opposition to levels of freedom, we are able to illustrate their relationship by way of a hypothetical instance utilizing a t-distribution. Think about a chart with levels of freedom on the x-axis and p-values on the y-axis. For a selected t-statistic (calculated out of your information), you’ll discover the corresponding p-value for various levels of freedom.
This chart would present that for a hard and fast t-statistic, the p-value decreases because the levels of freedom improve. It is because the t-distribution approaches the usual regular distribution because the levels of freedom improve, making it much less more likely to observe excessive values by probability alone.
(Hypothetical Chart Illustration – This can’t be precisely represented with out particular information and software program, however the idea is essential):
Think about a graph the place:
- X-axis: Levels of Freedom (0, 1, 2, 3,…, 100)
- Y-axis: P-value (0 to 1)
For a given t-statistic (e.g., t = 2), you’d plot a line displaying the p-value for every diploma of freedom. The road would typically slope downwards, indicating that the p-value decreases because the levels of freedom improve. This visually represents how the likelihood of observing a given t-statistic adjustments with the quantity of knowledge (levels of freedom) out there.
5. Conclusion:
P-values and levels of freedom are elementary ideas in statistical inference. Understanding their particular person meanings and their interconnectedness is essential for decoding statistical outcomes accurately. Whereas p-values present a measure of proof in opposition to the null speculation, they need to be interpreted cautiously, contemplating elements resembling impact measurement, pattern measurement, and the potential for bias. Levels of freedom account for the constraints in estimating parameters, influencing the form of the likelihood distributions utilized in speculation testing. By understanding these ideas, researchers can draw extra correct and significant conclusions from their information. Keep in mind that statistical evaluation is a device to help in decision-making, and needs to be used responsibly and ethically, avoiding practices like p-hacking that may result in deceptive outcomes. All the time take into account the broader context of your analysis and use statistical strategies appropriately to make sure the integrity and reliability of your findings.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_p-value-fb1299e998e4477694f6623551d4cfc7.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Understanding P-values and Levels of Freedom: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!