Variable Width Column Charts: A Complete Information to Visualizing Proportional Information
Associated Articles: Variable Width Column Charts: A Complete Information to Visualizing Proportional Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Variable Width Column Charts: A Complete Information to Visualizing Proportional Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Variable Width Column Charts: A Complete Information to Visualizing Proportional Information

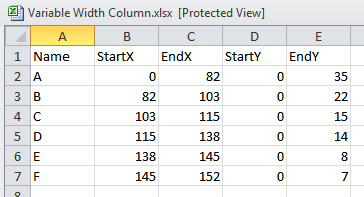
Variable width column charts, also referred to as proportional column charts or weighted column charts, provide a strong and visually intuitive solution to signify knowledge the place each the magnitude and proportion of various classes are essential. Not like conventional column charts the place column width stays fixed, variable width column charts use column width to signify a second dimension of information, usually a proportion or a frequency. This twin illustration permits for a richer and extra nuanced understanding of the info in comparison with utilizing two separate charts. This text will delve into the intricacies of variable width column charts, exploring their functions, design issues, strengths, limitations, and greatest practices for efficient visualization.
Understanding the Core Idea:
In an ordinary column chart, every column represents a class, and its peak corresponds to a numerical worth. In a variable width column chart, the peak nonetheless represents a price, however the width of every column can be significant. This width usually displays a second variable, akin to a share, proportion, or frequency associated to the class. As an example, if depicting gross sales figures for various merchandise throughout areas, the peak may signify complete gross sales, whereas the width may signify the market share of every product inside its area. This permits the viewer to concurrently grasp each absolutely the worth (peak) and the relative contribution (width) of every class.
Purposes of Variable Width Column Charts:
The flexibility of variable width column charts makes them appropriate for a big selection of functions:
- Market Share Evaluation: Illustrating the market share of various firms or merchandise inside a particular business. The peak may signify income, whereas the width represents the share of the whole market captured.
- Demographic Comparisons: Displaying inhabitants distributions throughout totally different age teams or geographic areas, the place the peak represents the inhabitants dimension and the width represents the share of the whole inhabitants.
- Gross sales Efficiency: Visualizing gross sales figures by product class and area, with peak representing complete gross sales and width representing the proportion of gross sales inside a area.
- Useful resource Allocation: Depicting the allocation of sources throughout totally different tasks or departments, the place peak represents the quantity of sources and width represents the share of the whole funds allotted.
- Monetary Reporting: Representing funding portfolios, exhibiting the worth of various belongings (peak) and their proportion throughout the portfolio (width).
- Environmental Information: Visualizing the contribution of various sources to air pollution ranges, with peak representing the quantity of pollutant and width representing the share contribution.
Designing Efficient Variable Width Column Charts:
Creating a transparent and efficient variable width column chart requires cautious consideration of a number of design parts:
- Selecting the Proper Variables: The choice of variables for peak and width is essential. The width variable ought to ideally be a proportion or a share associated to the peak variable. Inconsistent relationships can result in misinterpretations.
- Scaling and Axis Labels: Clearly label each the x and y axes, indicating the models and scales used for peak and width. Constant scaling is important for correct interpretation. Think about using a logarithmic scale if the info spans a number of orders of magnitude.
- Shade and Legend: Use a constant colour scheme and a transparent legend to distinguish classes. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, as this could make the chart cluttered and obscure.
- Information Ordering: The order of columns can affect the interpretation. Take into account ordering by peak, width, or a mix of each to focus on particular patterns or tendencies.
- Annotations and Callouts: Use annotations and callouts to focus on key knowledge factors or tendencies which may in any other case be missed.
- **Chart



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Variable Width Column Charts: A Complete Information to Visualizing Proportional Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!